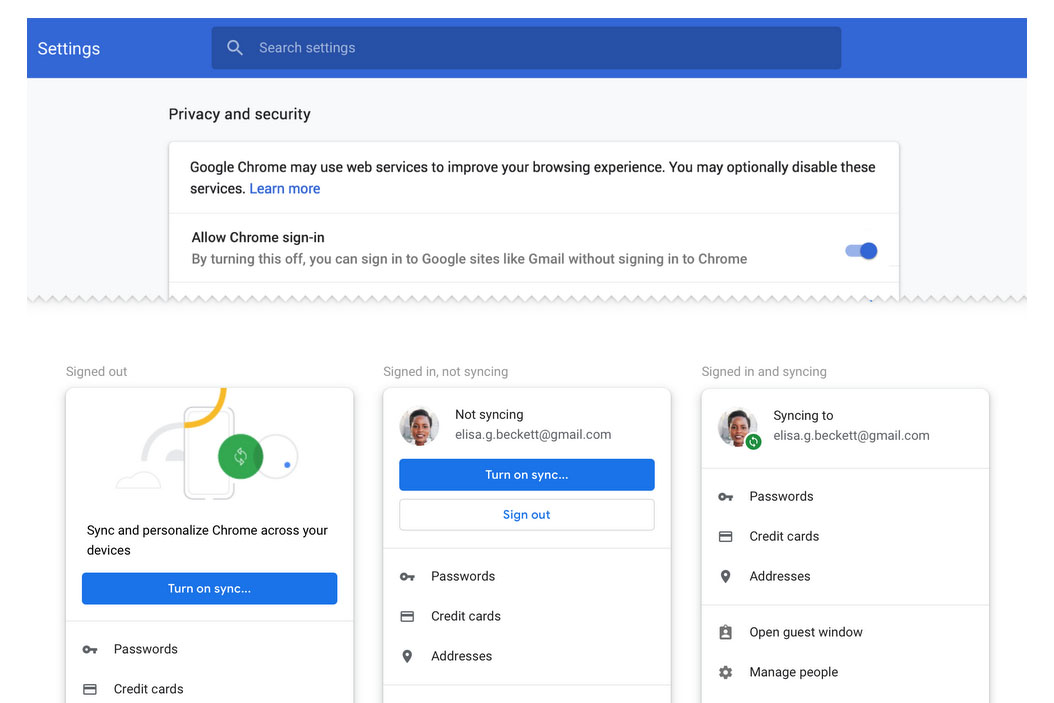
Users who downloaded the latest edition of Google’s Chrome web browser may have found a bit of unexpected activity taking place without their consent. The introduction of Chrome 69 brought with it a feature that would automatically sign users into the web browser if they attempted to sign into any other Google services such as Gmail or YouTube. After much backlash, the company announced that Chrome 70 will allow users to disable the feature in the future.
Cryptographer and John Hopkins University professor Matthew Green sparked concern with the new auto-login feature that Google introduced with Chrome 69, stating that it could be an invasion of personal privacy and security. Green’s complaint noted that the possible move could help to relay browser tracking information back to Google without any need of explicit consent.
Additionally, concerns brought up concerning whether or not Chrome would automatically start uploading personal preferences, bookmarks, and passwords to the cloud. Google stepped forward with a statement, noting that while the new feature auto-logs users into the Chrome platform, an additional step is needed for the synchronize feature to begin uploading.
Again, we appreciate the feedback. Here are some updates we have planned for Chrome 70: https://t.co/xpW8RyFiTn https://t.co/4HLCjeGfPY
— Parisa Tabriz (@laparisa) September 26, 2018
However, in the end, the pressure was too intense for the Mountain View, California-based company and it decided to announce the ability to disable the feature in an upcoming release. Chrome 70 will include a toggle switch under its privacy and security settings that allow users to opt out of allowing the browser to sign you in when using other Google Services automatically.
Concern is still prevalent as users who are unaware of the automatic feature may still find their data being uploaded to Chrome’s servers without any knowledge. Google says that the function has been put in place to enhance the overall browsing experience, but their actions still manage to throw doubt as the company’s primary source of income is its ad platform.
A collection of other features have also been announced for Chrome 70, including an enhanced indicator making it easier for users to discern whether or not their data is being synced to the cloud, and a clear cookie function that removes any authorization cookies from your machine after signing out of the browser.
Editors' Recommendations
- Google may build Gemini AI directly into Chrome
- Chrome is still a RAM killer, but this new feature would be a huge help
- These 2 new Edge features are making Chrome look outdated
- Google Chrome gets one of Microsoft Edge’s best features
- Why Google Chrome Incognito Mode isn’t what it claims to be

