For those of you who might not be familiar, Moore’s Law is a fifty-year-old idea conceived by Gordon Moore, co-founder of Intel. It says the number of transistors on a computer chip will double every 18 months — and has held true over the past half century. For the semiconductor industry, more transistors translates into faster processors, a scenario that has driven the computing industry and paved the way for our current crop of smartphones and smart watches.
Today, companies build their chips using silicon, which is reaching its material limits. As a result, Moore’s Law has slowed down, causing tech pundits the world over to predict the end of the “smaller, faster, cheaper” era of processing tehcnology. Even Intel CEO Brian Krzanich said during a recent earnings conference call that company would not be able to keep up with the pace set by Moore’s Law.
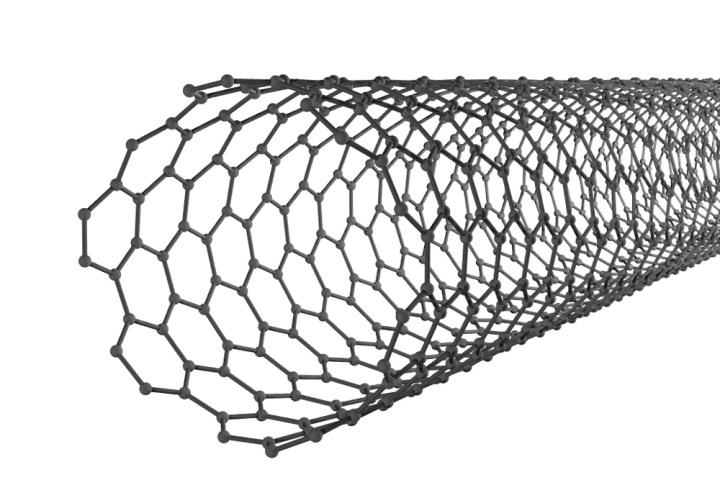
IBM’s breakthrough, which was published this week in Science, describes a way of building transistors with carbon nanotubes instead of silicon. Carbon-based nanotubes are a 10,000 times smaller than a human hair and conduct electricity, making them ideal for their role in semiconductor manufacturing. These new carbon nanotubes theoretically allow engineers to build chips with transistors that are 3-5 nanometers apart, as compared to the 11-14 nanometers present in the current crop of advanced chips.
This potentially is a game-changing discovery, providing reassurance that there will be semiconductors that can advance beyond the limitations set by silicon. In other words, Moore’s Law can continue on. For awhile, anyway.
Editors' Recommendations
- Intel says Moore’s Law is alive and well. Nvidia says it’s dead. Which is right?
- Aluminum-carbon nanotubes could replace copper wiring in cars, report says



