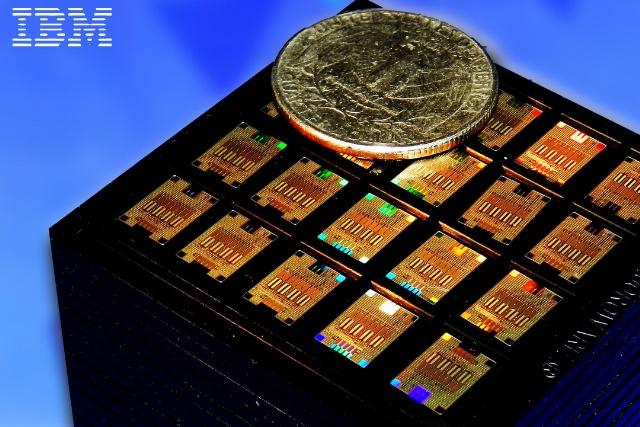
Photonics, or the science of transferring information via light rather than electricity, is just one of several potential future technologies that could take over from silicon. It is however considered one of the most viable and could offer potentially enormous gains in performance over traditional computing, as well as massive reductions in energy consumption, in turn providing a huge knock-on effect around the world.
Related: IBM’s silicon photonics technology could propel data centers into the future
However, in order to achieve these goals, much investment is needed, targeting not only production of the related components, but means of manufacturing them in a cost-effective manner. Hence the investment, which will see many American universities, companies, and government organizations work together to further the development of the technology.
This is the sort of investment that has already played out positively elsewhere in the world. As pointed out by Lionel Kimerling, the Thomas Lord Professor in Materials Science and Engineering at MIT, Europe is ahead in its development of photonics right now, due to more than 10 years of government investment. However, he believes that with this push, the U.S. may be able to catch up and potentially even overtake international competition before long.
Although one day the goal is to create entirely optical computers, in the near future a focus on hybrid optical/digital technology will be pursued. And with a near 30-percent drop in energy is seen as possible in the photon/electron conversion, the improvement over fully digital systems should still be noticeable.
Editors' Recommendations
- Email typo misdirects millions of U.S. military messages to Mali
- Hyundai, Kia recall half a million U.S. cars over fire risk
- The OnePlus Watch Harry Potter Edition is here but you can’t get it in the U.S.
- GM to recall 6 million vehicles in U.S. over Takata airbag issue
- DARPA awards $14 million to develop nuclear rocket engine for U.S. military



