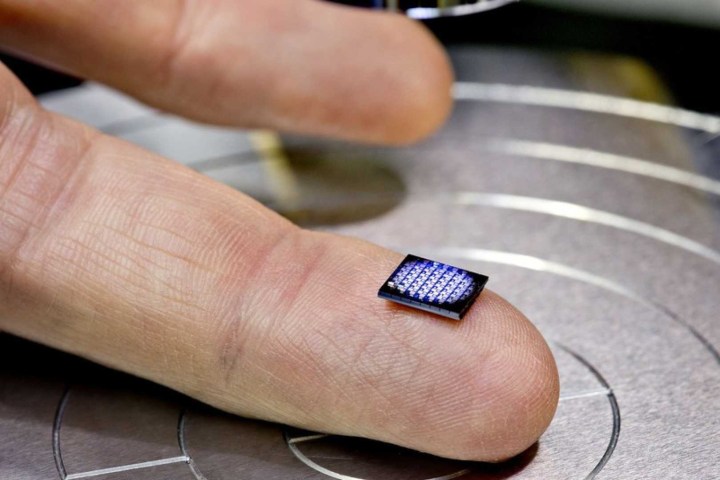
IBM kicked off its Think 2018 conference today with a bombshell announcement: It has made the world’s smallest computer, and it’s designed from the ground up to work with the blockchain. The computer itself is smaller than a single grain of salt, coming in at 1 millimeter by 1 millimeter and reportedly has about the same computing power as a 1990s era CPU.
Disposable Computing
From the beginning, IBM’s tiny computer was designed with blockchain technology in mind. The company wants to extend digital authentication to objects in the physical world – think the next generation of barcodes used in retail. While a miniature computer isn’t strictly needed to do that, it expands what’s possible.
The device’s capabilities go well beyond simple authentication. It has the potential to perform data summarization and local data analysis tasks that often fall to IoT devices. It’s all a matter of how developers choose to use the architecture.
“It’s a general purpose machine, so it can do these things,” said Dan Friedman, an IBM researcher who contributed to the project, speaking to Digital Trends earlier today. “What kind of limits it, to some extent, is that in order to keep it physically small, the amount of memory that it has is small.” Suffice it to say that the smallest computer around isn’t exactly a powerhouse. It’s been compared to a desktop processor circa 1990.
The computer’s limited horsepower keeps its manufacturing costs low – just 10 cents per unit. That’s inexpensive enough to allow the component to be embedded in packaging, or anything else that’s meant to be thrown away. “I think it would always be the case that you would consider this to be a disposable computer, but you might not be able to afford it on a really low-value item initially,” said Friedman, noting that costs will continue to drop over the coming years. He compared the technology to RFID, which was niche a decade ago, but has become commonplace thanks to lower costs.
The concept of disposable computing might prompt concerns about the environment – should we really be creating electronics that are intended to be thrown away? – but Friedman anticipates that will be no great worry. The computer itself is so small that it is expected to have a very minor impact.
Power Struggle
IBM has worked on numerous innovations to power its new, tiny chip. The first prototype was built to be as small as physically possible, so the team used a method where a photo diode region was illuminated with laser light, which generated power. This configuration is compact, but it requires the laser and the reader to arranged in a specific way. This could work well on an assembly line, but it won’t work elsewhere.
The company is also pursuing RFID-like approaches, where an antenna would be used to pick up microwaves, resulting in wireless power. The antenna would likely need to be larger than the computer to offer satisfactory range, however. Compact batteries are also being investigated, but today’s technology doesn’t supply the power density needed.
“Right now, we’re looking at the battery more as an assist, or something that could run a subset of the computer as an always-on engine,” said Friedman. Today, we don’t see a path for a battery that is really, really compact. If the battery was significantly larger than the computer, you could imagine a battery-powered system and that would open up even more communication opportunities – but then it becomes the world’s smallest computer sitting on a big battery, and that’s a different thing. If I make a very, very small headlight for the car, that doesn’t really change the size of my car.”
At present, IBM is hard at work creating initial prototypes of the optical configuration described above, with an early RF-compatible prototype expected to be finished before the end of 2018. The team hopes to have complete prototypes that can be put to the test with applications in two years, which would be followed by a push for commercialization.
You may think that computers have already invaded every aspect of modern life, but this is just the start. This project is creating systems that are small enough and cheap enough to monitor everything from the rightful owner of a pill bottle to the best before date on your frozen pizza. At this point, the only question is how quickly we’ll see this tech out in the wild.



