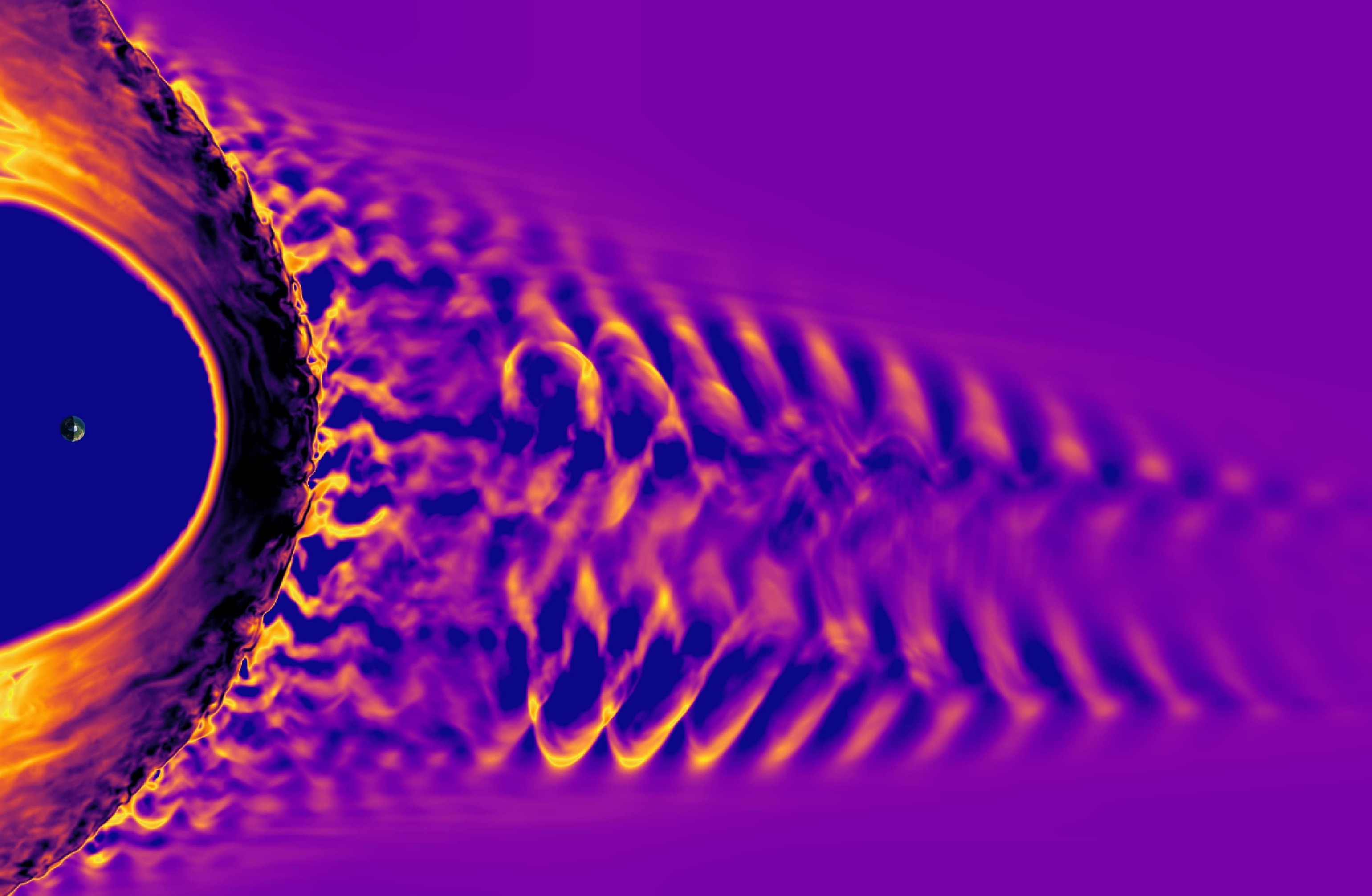
The sun doesn’t only shine light and heat down on our planet — it also bombards the Earth with solar winds consisting of electrically charged particles. These solar winds spread out through the solar system are responsible for space weather and can trigger bursts of energy when they interact with the planet’s magnetosphere. Now, researchers from the European Space Agency have caught these solar winds in action, by recording the sound of a solar storm colliding with the Earth’s magnetic field.
The eerie sounds are a ‘sonification’ of the magnetic waves generated by the incoming solar winds. The first clip, with data from 2003, was taken during a period of relative calm in the space weather. The second clip, using data from 2005, shows the sounds of a full-on solar storm.
To create those sounds, researcher Lucile Turc and colleagues took data of the fluctuations in the planet’s magnetic field and translated those frequencies into sound waves. You can hear how the sounds recorded during the solar storm are higher pitched than those in the calm period. The sounds during the solar storm are also more complex, showing how the magnetic fields resonate in a complicated way.
When solar storms reach our planet, they first interact with a region called the foreshock. When particles bounce off the magnetic field from our planet’s molten core, they interfere with incoming particles, creating magnetic waves. “Our study reveals that solar storms profoundly modify the foreshock region,” Turc said in a statement. “It’s like the storm is changing the tuning of the foreshock.”
The way that these complex patterns in space affect us here on the surface is a question that scientists are still investigating. Behind the foreshock is a region called the bow shock which slows down the charged particles of solar winds. Scientists have conjectured that a magnetosphere like the one our planet has may even be an essential component for life to flourish, as it protects inhabitants from harsh solar radiation.
The research is published in the journal Geophysical Research Letters.
Editors' Recommendations
- Solar Orbiter to perform its riskiest flyby before heading to the sun
- Solar Orbiter will be paying a Christmas visit to Venus
- Europe’s Solar Orbiter makes its first close approach to the sun
- What the solar minimum really means for life on Earth
- Mercury mission BepiColoumbo takes its final glimpse of Earth




