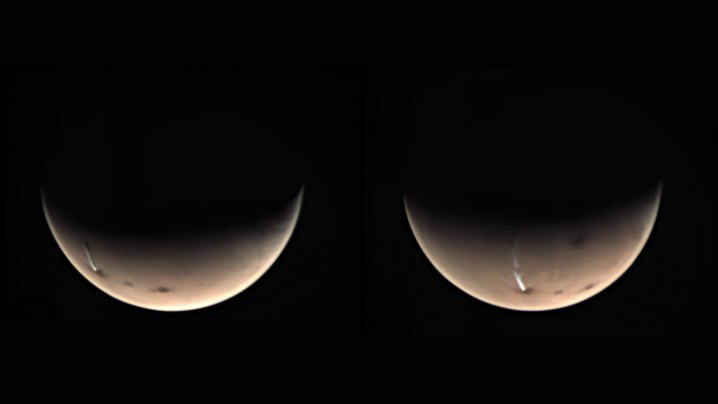
There’s an unusual feature in the skies of Mars: a huge, elongated cloud stretching over 1,100 miles long over the Arsia Mons volcano, appearing and disappearing one per martian year. Now, an unexpected tool aboard the Mars Express spacecraft has revealed more about how this cloud grows and shrinks considerably on a daily cycle that lasts for several months.
The cloud is difficult to observe from orbit as it changes so quickly and stretches so wide. Most orbiters focus on a small area in high resolution, but the Mars Express has a secret weapon on board.
“To clear these hurdles, we used one of Mars Express’s secret tools — the Visual Monitoring Camera, or VMC,” said lead author Jorge Hernández Bernal of the University of the Basque Country in Bilbao, Spain in a statement.
The VMC is nicknamed the “Mars webcam” because when it was installed in 2003, it had roughly the same resolution as a typical webcam. It was originally intended just to confirm whether a lander had made it to the Martian surface, and was later reactivated to take pictures of the surface for public outreach.
“However, recently, the VMC was reclassified as a camera for science,” Jorge said. “Although it has a low spatial resolution, it has a wide field of view — essential to see the big picture at different local times of day — and is wonderful for tracking a feature’s evolution over both a long period of time and in small time steps. As a result, we could study the whole cloud across numerous life cycles.”
Using the VMC along with other science instruments on various Mars orbiters, the team were able to measure the size of the cloud and confirm that it is an “orographic” type, meaning it is formed when winds hit the huge volcano on the surface and are funneled upward, condensing into a cloud when they reach higher altitudes. Before each sunrise, the cloud starts to grow at an incredible rate of 370 mph before being pulled westward and evaporating each morning.
While there are similar processes that happen on Earth, they are not as large or dramatic. “Although orographic clouds are commonly observed on Earth, they don’t reach such enormous lengths or show such vivid dynamics,” said co-author Agustin Sánchez-Lavega. “Understanding this cloud gives us the exciting opportunity to try to replicate the cloud’s formation with models — models that will improve our knowledge of climatic systems on both Mars and Earth.”
Editors' Recommendations
- Final communications sent to the beloved Ingenuity Mars helicopter
- NASA is looking for volunteers for yearlong simulated Mars mission
- NASA says goodbye to Mars helicopter Ingenuity after an incredible 72 flights
- NASA has lost communication with the Ingenuity Mars helicopter
- See the passing of a day on Mars with the Curiosity rover




