A stunning new set of images from the Daniel K. Inouye Solar Telescope shows the surface of the sun in incredible detail — including frankly disturbing images of sunspots seen up close. The images have been collected over the telescope’s first year of operations and have been shared as a preview of the data that can be expected from this tool.
Located in Maui, Hawai’i, the Inouye Solar Telescope is specifically designed to be able to look at the surface of the sun to learn about its magnetic fields, which are important for understanding the space weather which is caused by solar eruptions. The newly released images show calmer, quieter areas of the sun’s surface and the deep black of sunspots, which are temporary dark regions that periodically appear on the surface, or photosphere.

Sunspots can be as small as 10 miles across to as large as 100,000 miles, and they typically last for a period between a few days and a few months. Their appearance is related to the solar cycle, which is an 11-year period over which the sun’s activity varies, with more sunspots observed during certain parts of the cycle.
One reason that scientists want to study sunspots is to understand and eventually predict solar activity like flares or coronal mass ejections. These events send bursts of energy and matter out from the sun, which travel through the solar system and affect other planets in a phenomenon called space weather. These events can cause damage to satellites and would be dangerous for any humans who were on missions outside of low-Earth orbit, so being able to predict them would be valuable.
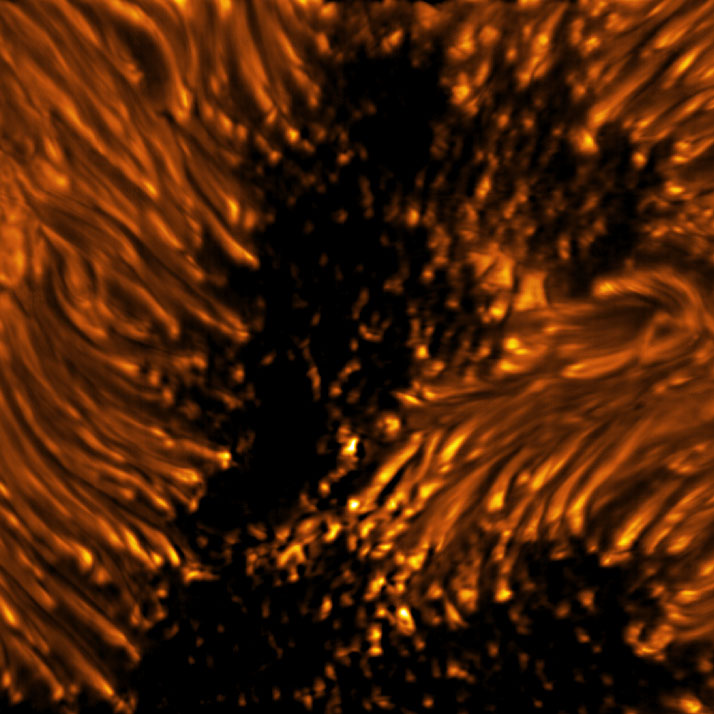
To study the sunspots, the telescope has a 4-meter mirror and instruments like a slit spectrograph and high-resolution cameras that can detect changes to the sun’s surface. The images above were collected using the telescope’s Visible-Broadband Imager (VBI), a set of two cameras that can take images of the sun’s surface and lower atmosphere.
Editors' Recommendations
- James Webb images capture the galactic winds of newborn stars
- See a festive cosmic chicken captured by the VLT Survey Telescope
- James Webb telescope captures a dramatic image of newborn star
- Solar Orbiter and Parker Solar Probe work together on a puzzle about our sun
- Scientists ‘hack’ Solar Orbiter’s camera to get a better look at the sun




