We may find the labels on soup cans and cracker boxes confusing, but least they use a common format that makes comparison shopping easier.
Costs for service aren’t the only information the FCC wants clearly stated. It also wants buyers to be able to see information about data allowances and performance. The point is that regular folks like you and I aren’t supposed to be confused or surprised by charges or performance.
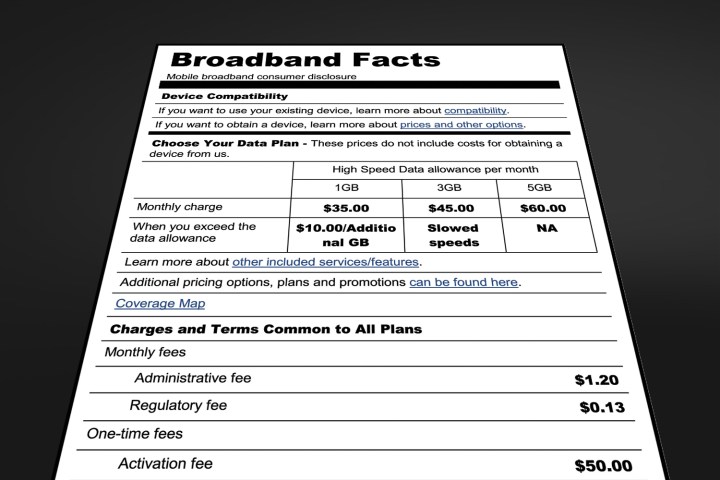
The suggested label formats are just that, suggested. The FCC isn’t requiring the nutrition-style format but makes it clear to broadband service providers that transparency is the game and it’s watching. The labels’ primary purpose is to help consumers make “informed broadband purchasing decisions,” according to a release on the FCC site. The disclosure requirement aren’t in effect yet because the rules still have to jump through additional Washington hoops.
Carriers can use designs other than the nutrition-label style, but the FCC also stated that using its suggested labels could serve as a “safe harbor format” for meeting the transparency rule requirements. To be acceptable to the FCC a format must be presented in “an accurate, understandable, and easy-to-find manner.”
This whole issue of service and fee transparency for broadband providers is part of net neutrality. Title II of the Communications Act classified internet service providers as common carriers, which why there are new disclosure requirements. The FCC’s Consumer Advisory Committee, with members including consumer advocates and carrier representatives, was unanimous in its approval of the suggested label format. That unity hasn’t stopped the CTIA and some of its member carriers from complaining about that format, or any change at all from current disclosure practices. Some groups are trying to reverse the Communications Act and get rid of net neutrality entirely, which would throw everything off course.
In the end, the purpose of full disclosure of fees, data allowances/caps, and speed is intended to help us be less confused about what we’re paying for broadband service and how much we’re really getting for our money. The suggested labels may not be perfect but they look like a step in the right direction that the internet service providers have not taken on their own.






