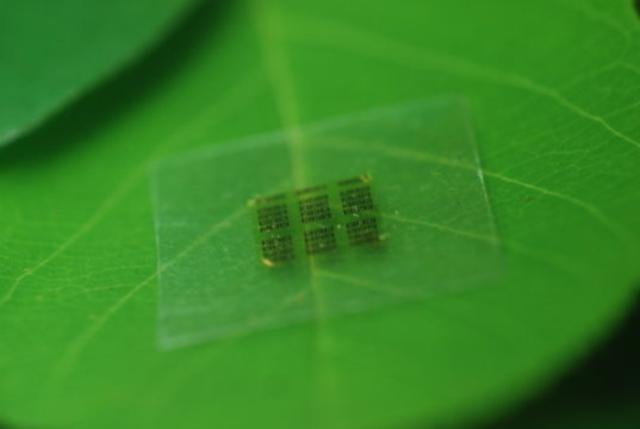
In a paper published in the journal Nature Communications, researchers at the partnered institutions describe their creation: a semiconductor chip composed almost entirely of cellulose nanofibril (CNF), a flexible, biodegradable material made from wood. You read that right: a computer part produced from trees. The key, apparently, was narrowing down the right component for substitution — the team eventually settled on the support layer (substrate) of the computer chip because “a majority of material in a chip is support,” UW-Madison electrical and computer engineering professor Zhenjiang “Jack” Ma told Science Daily. “We only use less than a couple of micrometers for everything else.”
Cellulose made for the most safely disposable chip — “you can put them in the forest and fungus will degrade it,” Ma said — but has a problematic characteristic: a tendency to lose form depending on its dampness.”Wood is a natural hydroscopic material and could attract moisture from the air,” Shaoqin Gong, a UW-Madison professor of biomedical engineering, told Science Daily. The researchers managed to resolve that by coating the cellulose with an epoxy. “With a […] coating on the surface of the [cellulose], we solved the surface smoothness and the moisture barrier,” she said.
Environmental friendliness isn’t the only benefits conferred by cellulose-based chips. Yei Hwan Jung, a graduate student in electrical and computer engineering and a co-author of the paper, told Science Daily that in addition to being “sustainable, bio-compatible and biodegradable,” wireless chips from wood-derived materials also require significantly fewer toxins to fabricate. “I’ve made 1,500 gallium arsenide transistors in a 5-by-6 millimeter chip. Typically for a microwave chip of that size, there are only eight to 40 transistors. The rest of the area is just wasted,” he said. “We take our design and put it on [cellulose] using deterministic assembly technique, then we can put it wherever we want to make a completely functional circuit with performance comparable to existing chips.”
Cellulose-based chips may one day make the jump from laboratory experiment to commodity, and Ma thinks the ease of outfitting modern manufacturing facilities with the necessary materials could accelerate adoption. For health and the environment’s sake, hopefully that day isn’t far away.
Editors' Recommendations
- Researchers find new vulnerability with Apple Silicon chips
- Next-generation batteries could use material derived from trees
- Researchers create tiny particle accelerator that fits on a silicon chip
- Facebook’s ‘brain-computer interface’ could let you type with your mind


