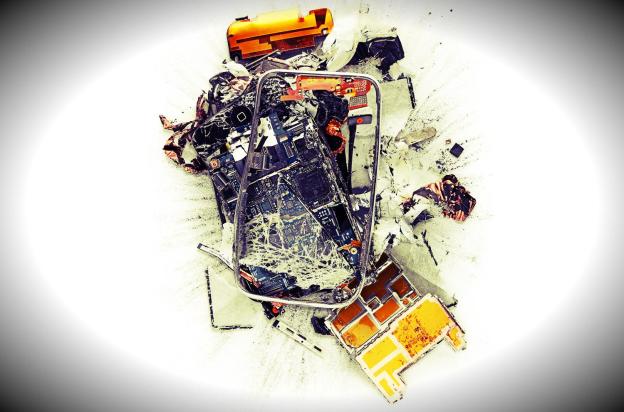
Today’s news that Apple is investigating the death of a 23-year-old woman whose family claims she was electrocuted while talking on a charging iPhone is just the latest story about smartphones putting people in grave danger. Last week, there was the woman who suffered third-degree burns from her Galaxy S3; at the end of May, a Redditor claimed his phone exploded while charging. Concerns about phone-produced microwave radiation or having a fragile sheet of glass inches from your face have circulated since mobile phones were in their infancy, but in the past few years these devices have grown into full-fledged computers – albeit ones that can set your pants on fire.
We are trying to stay on top of advancements and changes in design with electronics…
But there’s a real reason why your smartphone is one of the safest devices you’ll ever use: it’s tested like crazy.
The danger in your pocket
Though there is a lot of talk about carcinogens and harmful components in phones, unless your phone is in a fire or extreme scenario, these components are generally inert and safe. Beyond cutting yourself on the glass display if it cracks, there’s little danger to be had.
The problems we’ve heard of usually stem from the circuitry and the battery, which together pose two real dangers: risk of shock and risk of fire (or explosion).
- Fire hazard: Lithium-ion batteries are basically a slurry of electrodes and contacts that store energy. If improperly discharged, punctured, or overheated, a battery could very well catch fire or explode.
- Shock hazard: When it comes to the circuitry, a short in the system can cause the device to shock you, or lead to overcharging or overheating – which can also cause the battery to catch fire, or explode (see above).
Now, as scary as this sounds, there is danger in all electronics. What phone manufacturers and the government are doing to ensure the safety of these devices is more important. When it comes to regulation and safety protocols for electronics, mobile phones are some of the most closely monitored devices out there.
Keeping your phone safe
There are a number of agencies and companies charged with keeping your phone safe, but one of the largest is the Consumer Product Safety Commission (CPSC), a federal regulatory commission established in the 1970s to keep an eye on the products we buy, and issue recalls when necessary.
We spoke with the CPSC’s Communications Director, Scott Wolfson, who told us that the CPSC has been keeping a close eye on the batteries inside our flip phones and smartphones long before they became the widely popular products they are today.
“We do have reports of these [cellphone] batteries overheating, but it’s an extremely rare occurrence,” explained Wolfson.
In fact, if you never swap out your phone’s OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) battery, meaning the sold directly by the phone’s manufacturer, then the instance of battery overheating is a rarer occurrence still.

“Third-party components are not consistent with the components that come with the phone,” said Wolfson. “We recommend that replacement parts continue to be purchased from the source company of the phone.” He gave us a number of other tips for people to keep in mind. It’s important to keep your phone and it’s battery away from heat sources like a car dashboard, and not to store spare batteries near metal objects that could cause the circuitry to short.
Now the CPSC has gone overboard on product safety in the past, but what they’re recommending is sound advice.
- Don’t use third-party batteries: OEM batteries not only ensure consistency in components, but also the oversight of the phone’s manufacturer during their production, which likely also means better battery life.
- Avoid hot places and storing batteries near metal: Avoiding excess heat and the risk for electrical shortage is yet another logical step to ensure the best safety for your smartphone.
- Check saferproducts.gov: Another great tool the CPSC offers to ensure safety for consumers is a website called saferproducts.gov, where you can personally report product safety concerns. But you can do more than just report incidents; you can search or track any report ever made on a product, and see the action taken by the CPSC as a result of the report.
“We are trying to stay on top of advancements and changes in design with electronics” Wolfson told us. He also noted, “We need consumers to help us by reporting their incidents. This is the biggest open government initiative we’ve ever undertaken.”
Most situations we’ve heard of in the news appears to be related to batteries (possibly non OEM) or circuitry. When Samsung got back to the unlucky Redditor whose phone self destructed, it deduced the battery he was using with the device was not OEM, though he claims it had the Samsung logo on it. We’ve yet to hear the full resolution on this story, and while we’re still waiting for comment from either Samsung or the victim, it may have been caused by a faulty or non-OEM battery. Others have experienced battery issues with their smartphones, including a different Galaxy S3 owner whose phone made a sound “like a firecracker” and proceeded to get so hot it gave her third-degree burns on her thighs. As for the woman in China who may have died while taking a call on her iPhone 5, it could have been because of her battery, or charger, if it was the phone at all.
Even if you do everything wrong…
Even if you ignore all these preventive measures, your phone is still safe, thanks to another third-party firm: Underwriters Laboratories (UL). Though the name is vague, there’s a good chance you’ve seen its mark all over the place. UL is one of the biggest third-party safety testing firms in the world.
“We have been testing thousands of products for more than 100 years,” UL Consumer Affairs Manager John Drengenberg told us. “Cell phones are just one of the many products we evaluate … When we UL test a product, we look at all fire hazards and shock hazards.”
Drengenberg said there isn’t much to fear when it comes to getting shocked by the mobile phone itself: “Once you get beyond the battery, you don’t have much energy in the cell phone … the shock hazard in pretty minimal.”
UL testing helps minimize the risk of explosion due to overheating, electrical shortage, or battery puncture.
Batteries also go through UL testing, so you can easily check for the UL mark on them, as well. UL sets a number of safety standards with various electronics including lithium-ion batteries. Some of the testing they do helps minimize the risk of explosion due to overheating, electrical shortage, or battery puncture.
The UL has a number of standards already set, but continues to make changes as our devices continue to rapidly evolve with faster processors, bigger batteries, and smaller form factors.
“The Standards of UL are a dynamic document” Drengenberg explained, noting that they are constantly reviewing testing methods and developing new means to ensure our devices and their batteries are continually tested against the very worst of scenarios that could occur. These scenarios could range from a number of cases, and all are designed to ensure that the design of the battery is not compromised in the process.
As important as UL’s tests are, what’s equally important is their ability to enforce the standards they set. “Manufacturers want the UL mark,” Drengenberg said, expressing the importance it has on the reputation of manufacturer’s products. He also added how UL tests and monitors manufacturers worldwide, and that inspectors can make unexpected visits to ensure the products being built continue to meet UL standards – all this handled from a private company, not a federal agency.
“We’re engineers here at UL,” Drengenberg added, “We take a very statistical approach to our testing and inspections. If we see something wrong, we make more inspections.” Thankfully, few phone manufacturers have had their UL marks revoked.
There’s always a chance, but use your phone with confidence
In the end, the lithium-ion batteries in our cellphones are really much safer than we make them out to be. While lithium-polymer batteries, which are found in tabets like the iPad, pose a slightly greater risk of fire, the standards lithium-ion batteries meet, along with the phones they come on, should help you rest easier. It’s extremely unlikely that your phone will explode in your pocket.
There are always going to be extremely rare incidents that get blown up on the Internet (on sites like ours), but remember that hundreds of millions of people use flip phones and smartphones every day without incident. The manufacturer, government agencies, and even third-party regulatory companies are all hard at work ensuring your phone – along with most other electronics in your home – remain as safe and reliable as we like to think they are.
The odds of getting struck by lightning are about one in a million. Your phone could be far less than that. Assuming there are 1000 cases of smartphone fires or shocks each year (only 40 have been reported on safterproducts.gov) and Gartner’s projection of 1.875 billion mobile phones sold in 2013 is correct, you have a 0.00000053 percent chance of being shocked or experiencing a problem. In other words, you have a 1 in 1.875 million chance. Granted, you could argue that despite the low odds, we generally try to stay indoors during thunderstorms. That’s true. Following the battery and storage advice above is similarly wise.
There is an extensive behind-the-scenes army that keeps our phones safe. If you want to air on the side of caution, it may be best to heed the advice of the CPSC, but either way, keep on texting, tweeting, emailing, or whatever it is you do with your phone these days.
Top image courtesy of Michael Tompert
Editors' Recommendations
- Samsung Galaxy S24 Ultra vs. S24 Plus: closer than you’d think
- You may want to think twice about buying a Samsung or Pixel phone