Researchers have created a tiny prototype particle accelerator, small enough to fit onto a silicon chip. Although it accelerates particles to a far lower velocity than a full-size particle accelerator like the one found at CERN, it can still produce energized particles that could be used for applications in chemistry, materials science, and biology.
“The largest accelerators are like powerful telescopes,” electrical engineer Jelena Vuckovic of Stanford University explained in a statement. “There are only a few in the world and scientists must come to places like SLAC [Stanford Linear Accelerator Center, an accelerator laboratory] to use them. We want to miniaturize accelerator technology in a way that makes it a more accessible research tool.”
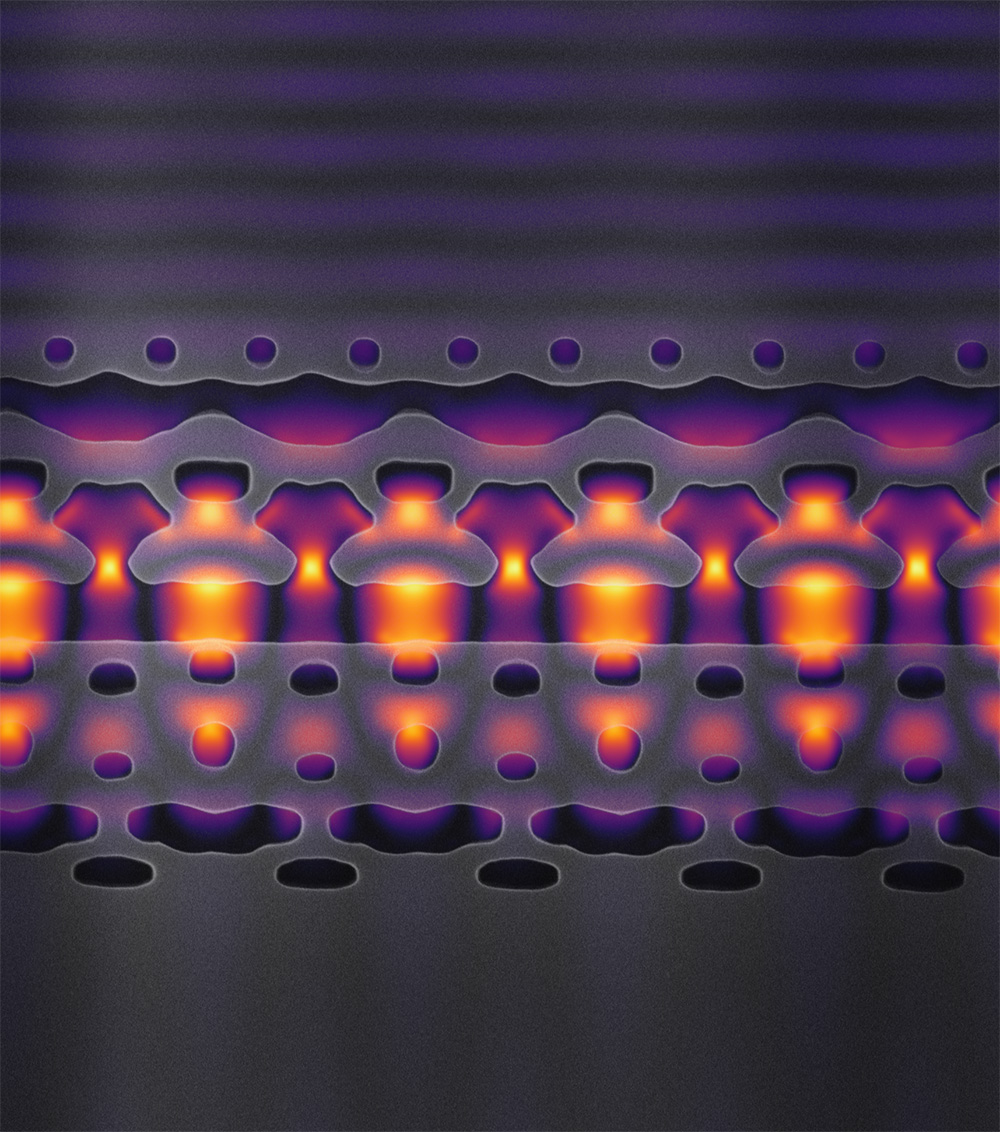
To create the accelerator-on-a-chip, the researchers “carved a nanoscale channel out of silicon, sealed it in a vacuum and sent electrons through this cavity while pulses of infrared light — to which silicon is as transparent as glass is to visible light — were transmitted by the channel walls to speed the electrons along,” according to Stanford.
Eventually, the researchers want to create a miniature system that could accelerate a particle up to 94% of the speed of light. For now, particles would have to be passed through the mini accelerator 1000 times to achieve this speed — but Vuckovic believes it is possible to achieve this goal as the prototype is a fully integrated circuit, which should make increasing its capabilities relatively easy.
This technology is not only useful for research applications: It could also be used for medical purposes. One of the paper’s co-authors, Olav Solgaard, is already developing an application using the technology for fighting cancer. Cancer treatments like radiation therapy can’t currently use highly energized electrons because they would burn the skin — but by using a chip-sized accelerator, electrons could be channeled through a tube inserted below the skin, allowing targeted treatment of tumors without skin damage.
The research is published in the journal Science.




