Why touch screens?
Before we take a look at why command wheels have come so far, it’s worth understanding why companies are moving towards touch screen controls. For starters, thanks to smartphones, everyone from toddlers to people on social security are familiar with the technology. The public familiarity matters for automakers that have limited budgets and attention spans for infotainment development.

Beyond simple familiarity with the concept of touch screen, technologies like Apple CarPlay — which use the in-car screen to mirror the driver’s smartphone — may revolutionize touch screens. Not only do such systems limit the direct cost to automakers, they’re also appealing to customers. For instance, the average luxury buyer, often well into their fifties, may not like the idea of learning a new user interface when they already understand their phone.
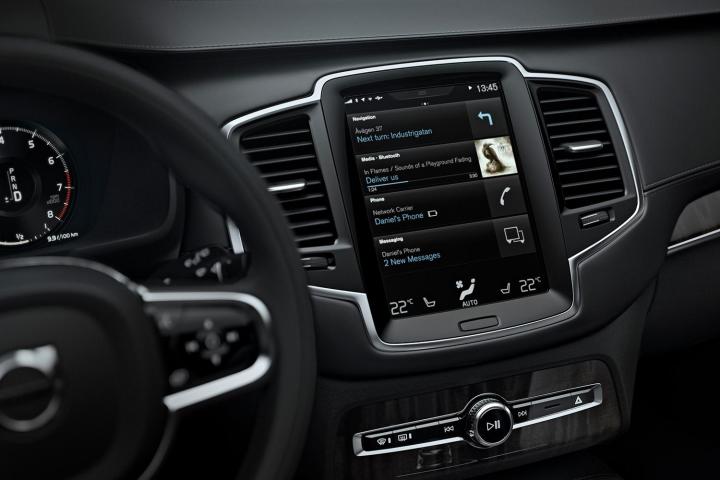
There’s also the Tesla factor. When Tesla introduced the Model S with its glacier-sized touch screen, it set the industry standard for how “high tech” should look. Other automakers haven’t been that far behind. Volvo’s new XC90 will feature a massive touch screen that is clearly reminiscent of both an iPad and Tesla’s system. Audi plans to introduce a similarly large and impressive touch screen in its new system.
- 2. Chrysler Uconnect
Throw in the fact that one of Digital Trends very favorite infotainment systems, Chrysler’s Uconnect, is a touch screen and the case for this technology seems obvious. But actually it isn’t.
Commanding reasons for the wheel
So with all of those compelling reasons for touchscreens, why should any company continue to pursue the command wheels? The simple answer is flexibility.
Designing an infotainment system is about more than simply making a good interface or even using good hardware. Placing the system within the interior of the car is crucial to making it a useful feature. Factors such as how easy the controls are to reach, where the screen is placed, and how it affects the overall interior design are crucial to success.
One advantage of the command wheel is they are easier to use without the driver taking their eyes off the road.
Perhaps even more important the screen must be mounted low in the dash so that it can be reached. This has a massive but not altogether obvious effect on how usable a system is. A Mazda engineer was explained to me that one of the biggest impacts on how much time a user needs to use a system is literally the time it takes to refocus their eyes from road to screen. This is why Mazda and Audi have chosen to place their screens on top of the dash rather than buried in it: It allows the driver’s eyes to slide effortlessly to and from the road. This is also bolstered by cleverly choosing resolution and font size so that the focal distance changes as little as possible.
This placement is only possible when using a command wheel, because such screens are out of reach too all but NBA players. However, even when the system isn’t raised above the dash, it can still help with comfortable seating. I noticed that in the Kia K900, where I was able to take full advantage of the lounge-like seats and still comfortably reach the command wheel.

One of the other advantages of command wheels is that they are easier to use without the driver taking their eyes off the road at all. If the driver has been using the system for some time it is possible to know the position of various icons and commands simply by feel. A far more difficult task on a touch screen that lacks and buttons at all. This advantage does come courtesy of a steeper learning curve, but it is nonetheless an advantage.
Still all of that is likely for naught.
Touch screens clearly do have advantages, and more than that they have a high-tech appeal that physical controls lack. Audi’s decision to move away from its heretofore successful use of physical controls is instructive, and will likely result in a good system. There are already any number of good touch screen systems, after all.
In the end, the changes will be more for aesthetics and marketing purposes then purely practical ones. And that’s too bad.
Editors' Recommendations
- Apple wants to supercharge CarPlay, but here’s why carmakers won’t bite
- Infiniti’s latest InTouch system finally adds Apple CarPlay and Android Auto




