As previously reported, Zen cores will have 40 percent more instructions per clock than the previous “Excavator” generation. Each core will have two threads (lanes), and access to 8MB of shared L3 cache, a large amount of “private” L2 cache, and a micro-op cache. Other highlights include two AES encryption units for security, and transistors based on energy-efficient FinFET process technology.
AMD considers its Zen core a “clean sheet” design, meaning the company nearly started over from scratch and uses very little from its previous CPU architecture. With Zen, AMD is pushing to increase the performance per clock while decreasing the amount of energy needed per cycle. And while AMD created a wide performance/energy usage gap with its Excavator core technology, Zen seemingly balloons that gap to an even higher amount in a rather short distance on AMD’s core technology timeline.
In a slide displayed during the convention, AMD listed a number of performance and power improvements offered by Zen, including faster L2 and L3 cache, up to five times more L3 bandwidth, a large Op Cache, larger instruction schedulers, and so on. AMD said Zen even includes “low power design methodologies” to achieve higher performance while keeping the power consumption low.
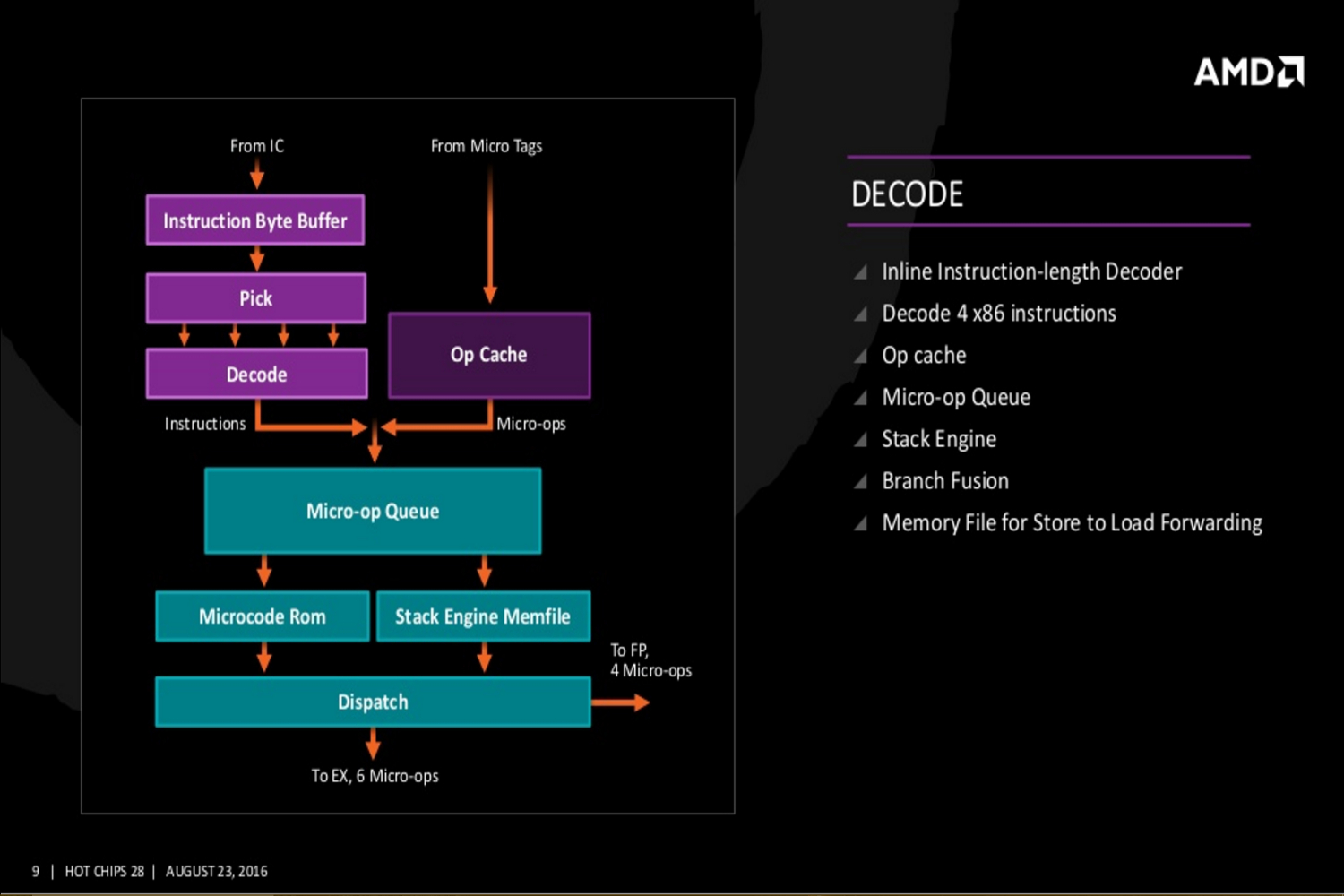
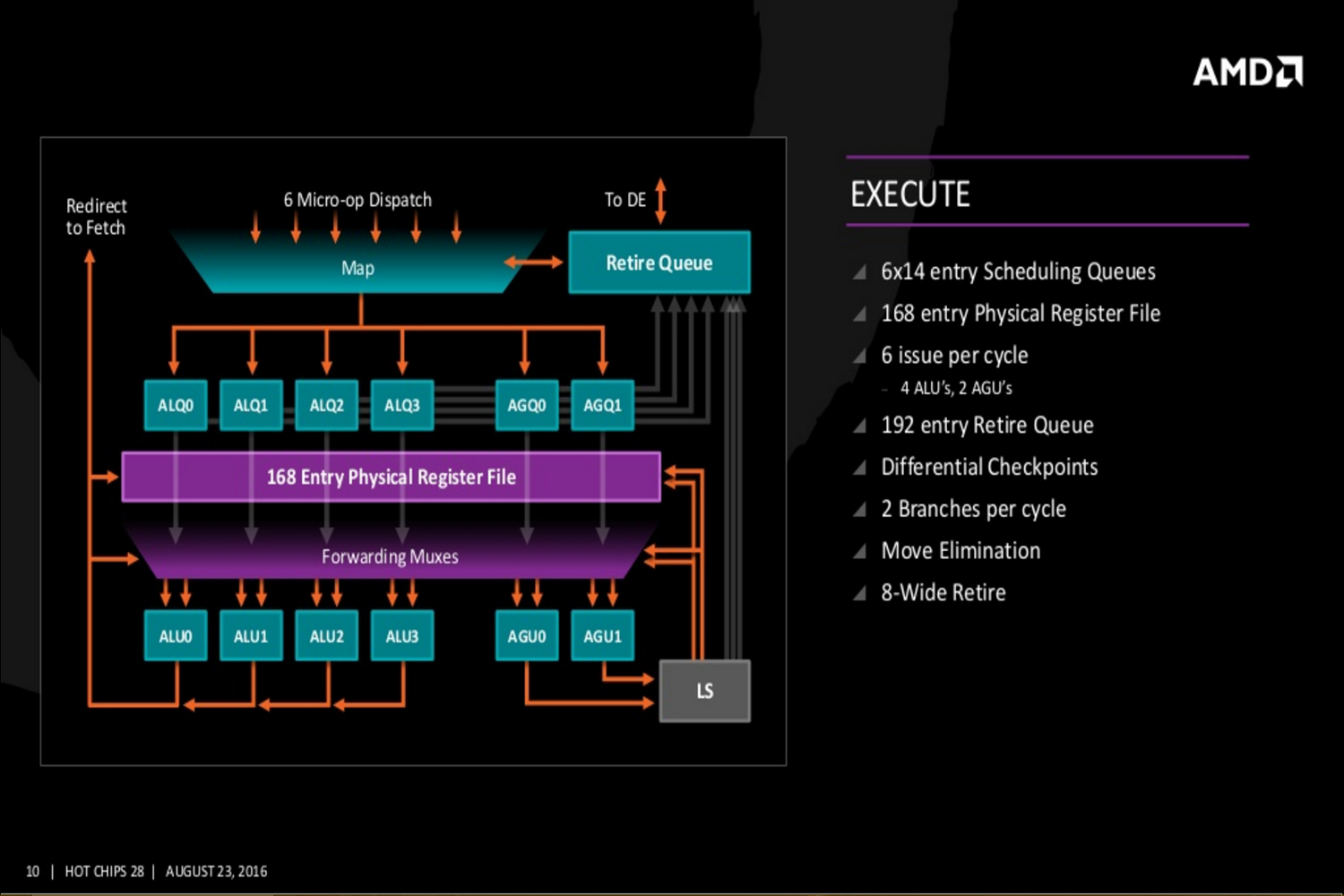
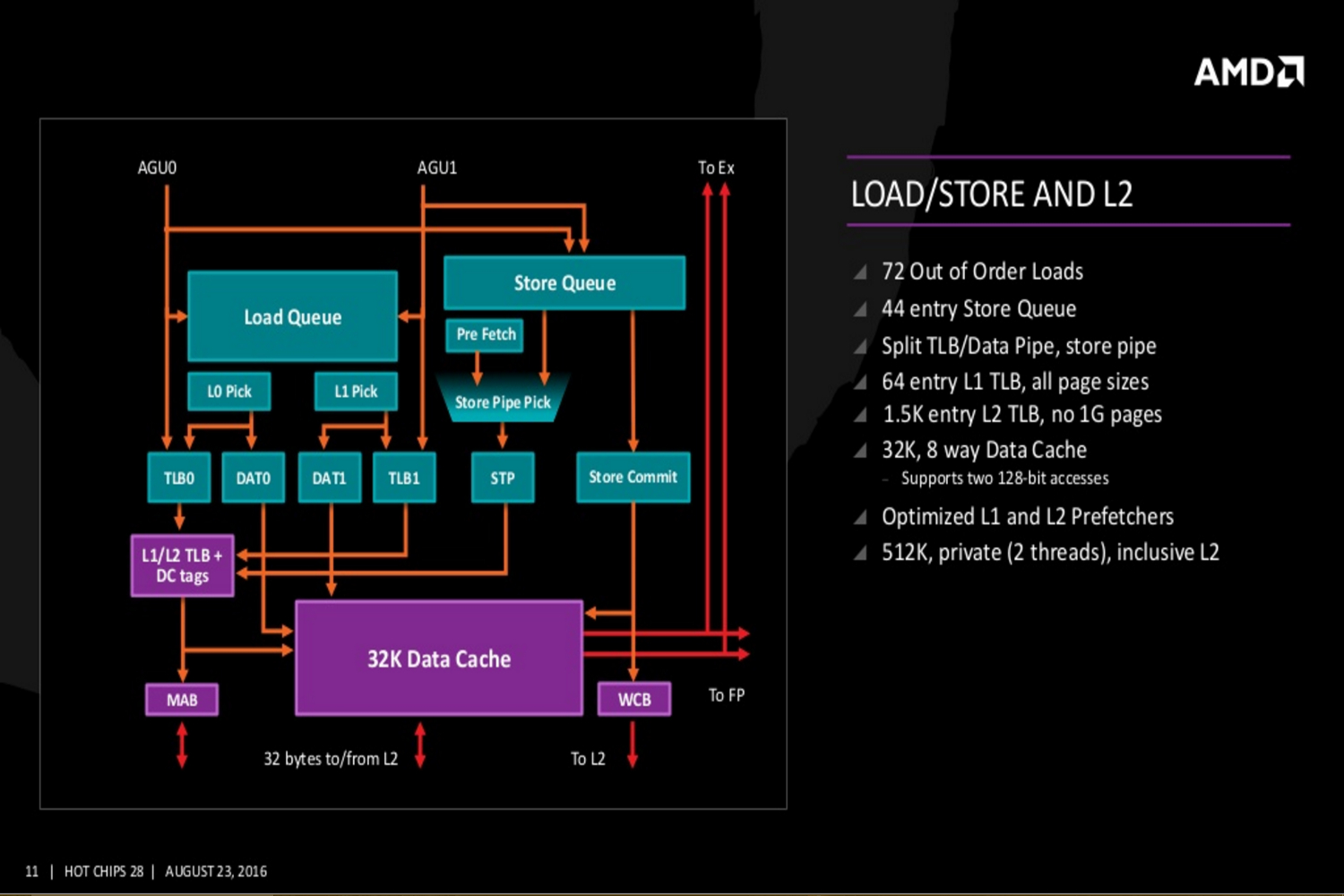
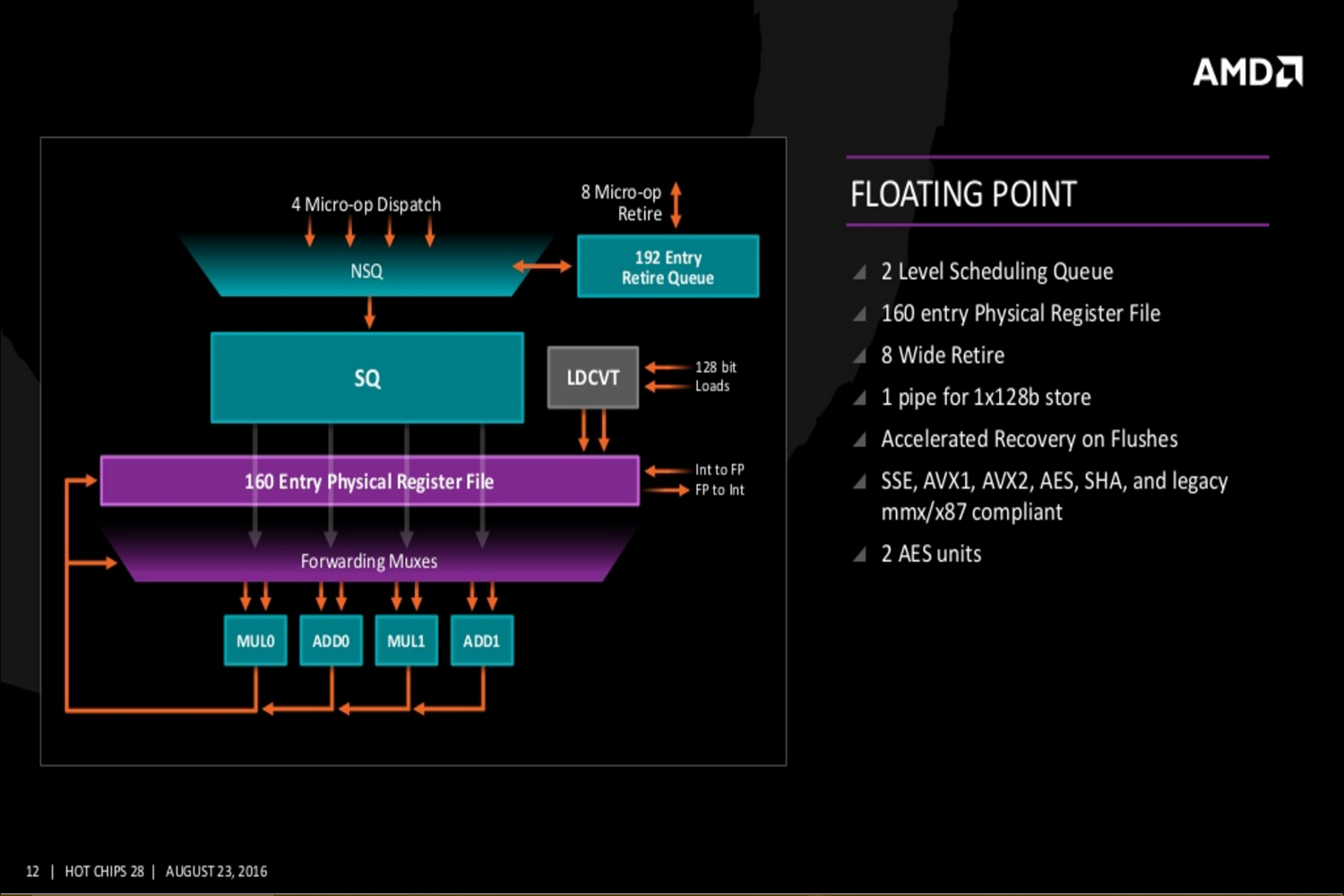
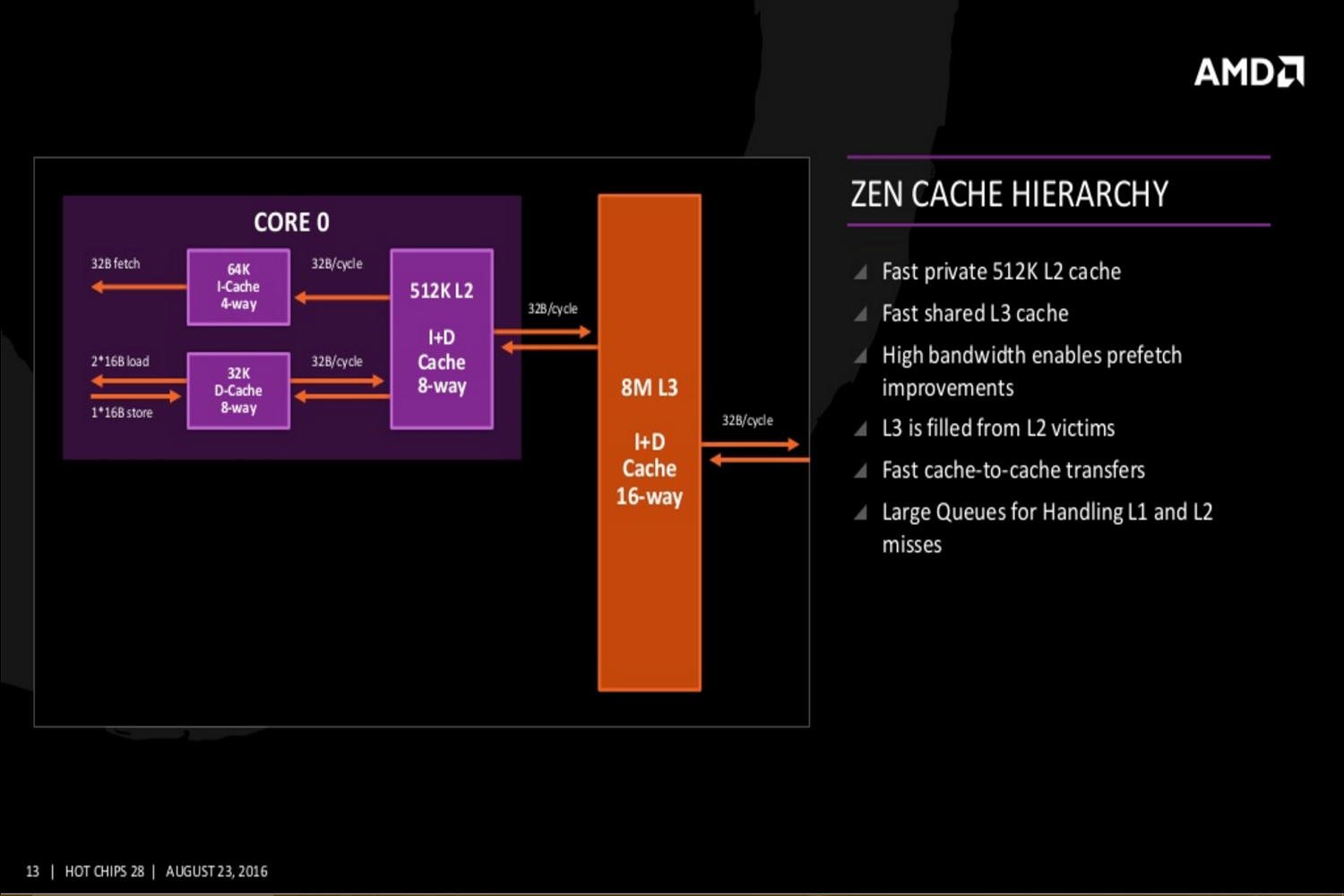
On a more technical level, the Zen core architecture is comprised of a number of parts. AMD’s “Fetch Four” x86 instruction units, micro-operations cache instruction units, four integer units, two load/store units, and two floating point units. There’s also a four-way I-Cache amount of 64K, an eight-way D-Cache of 32K, and an eight-way L2 Cache of 512K.
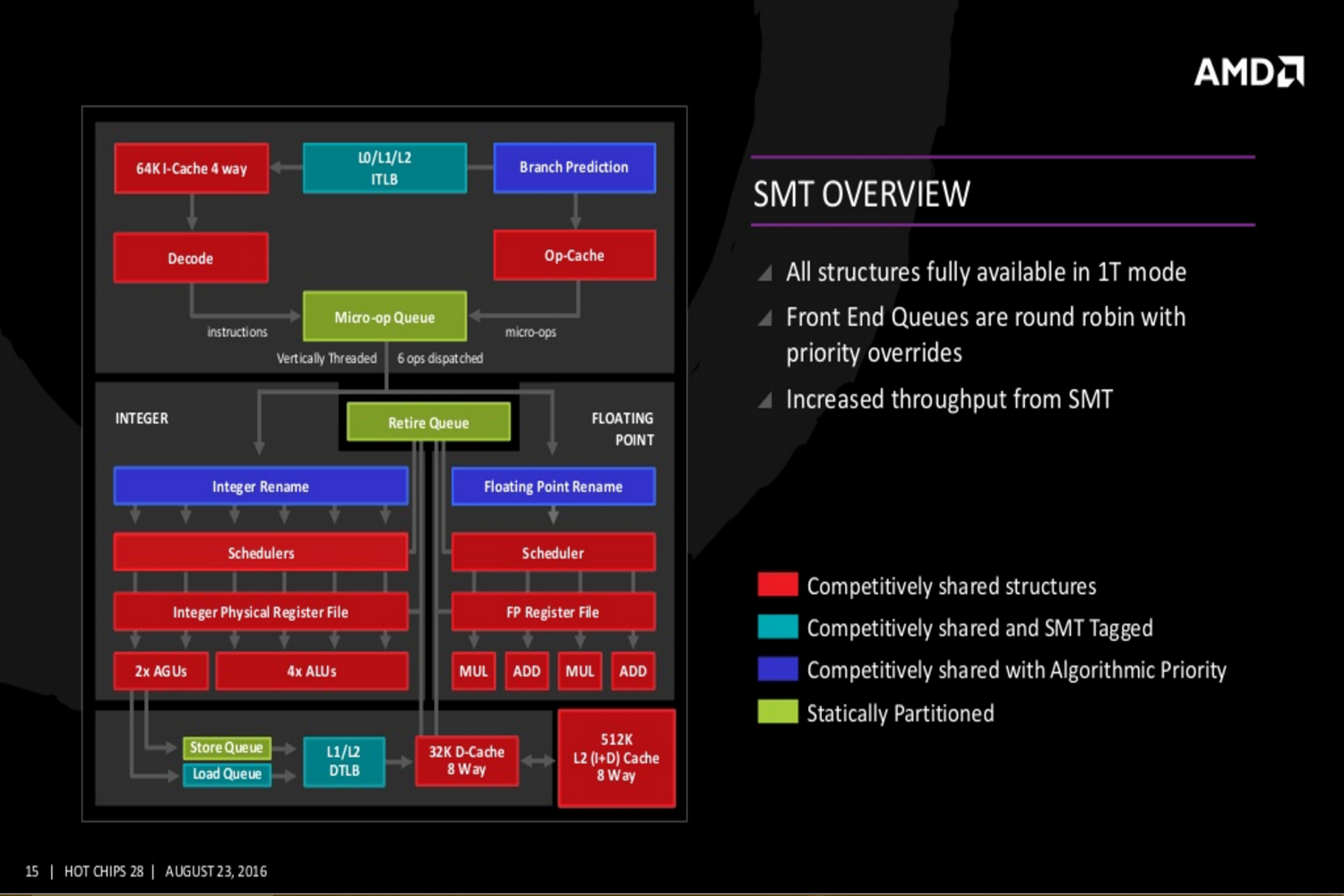
Again, each core supports two threads, and access to a larger shared L3 cache. In practice, this is similar to Intel’s Hyper-Threading, though the architecture that enables AMD’s take on it differs dramatically.
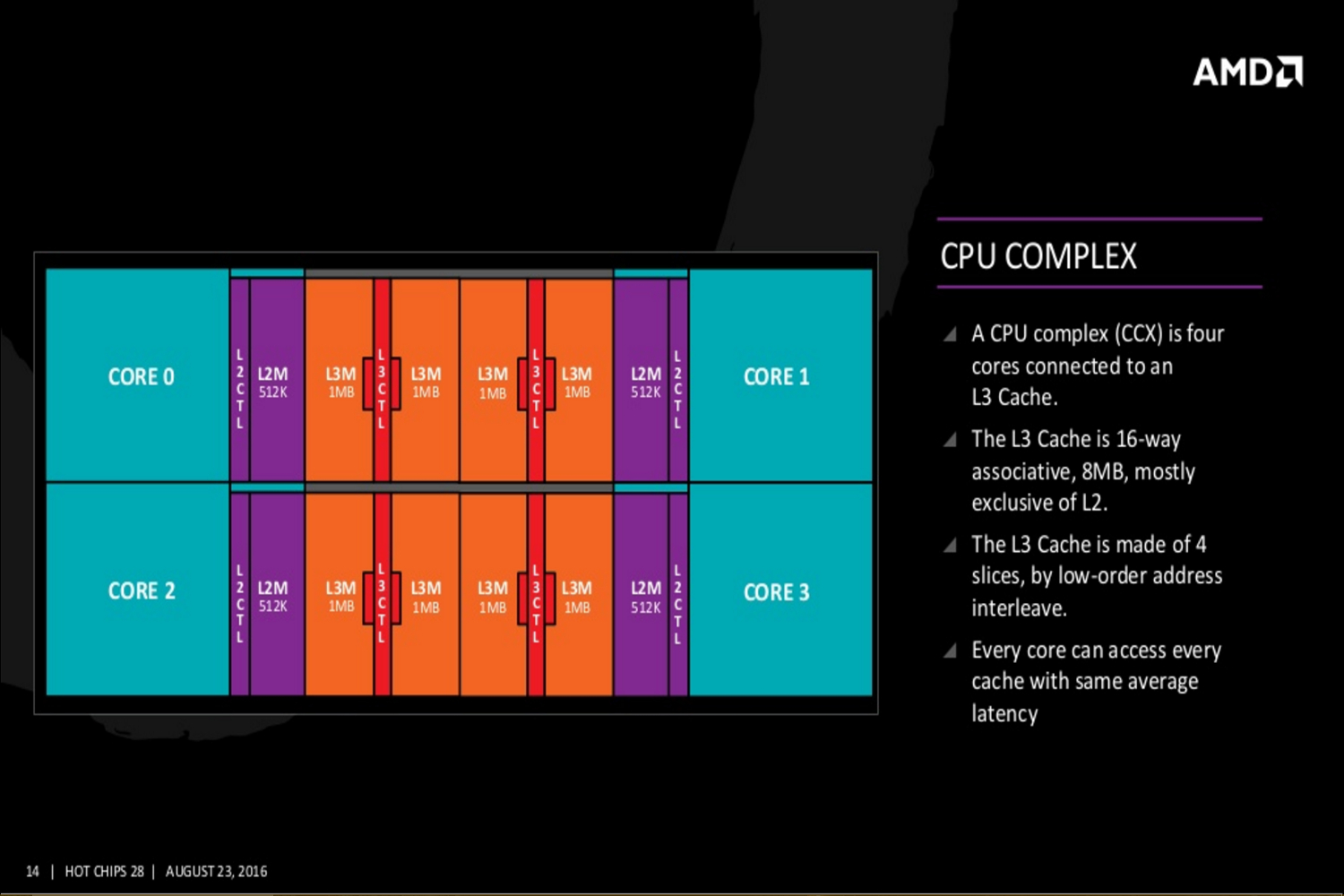
Additional slides provided by AMD reveal even deeper Zen details covering the Zen core’s fetch, decode, execute, load/store and L2, and floating point capabilities. The new slides even reveal Zen’s cache hierarchy, an SMT overview, and a “CPU Complex” diagram showing four Zen cores connected to an L3 cache. This diagram displays each core with 512K of “private” L2 cache and “public” access to eight units of L3 cache at 1MB each.
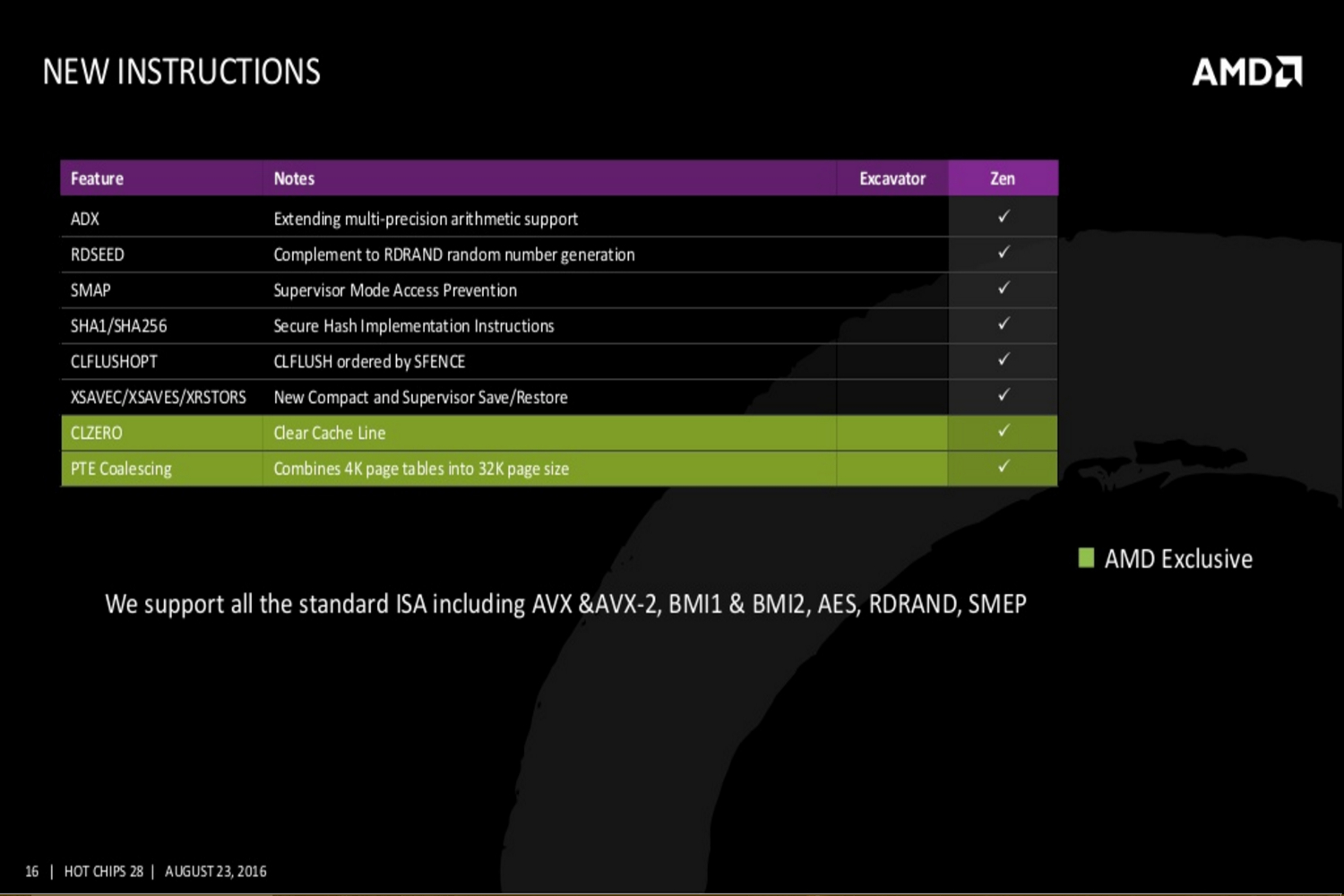
Finally, AMD provided a new list of instructions not offered in the previous Excavator generation. One instruction is called ADX, which extends the multi-precision arithmetic support. Another instruction called RDSEED compliments the RDRAND random number generation. There are six additional new instructions for clearing the cache line, combining 4K page tables into a 32k page size, and more.
Intel may have a challenger once again
Okay, okay, that’s a lot to take in. What does it mean? Accroding to AMD, it means its processors will again be performance-competitive with Intel hardware. Zen is a huge leap in performance — about 40 percent more instructions per clock — compared to Excavator, far more than we’ve seen from new generations of AMD hardware in recent years.
The company is also lower power targets with Zen. It expects the fastest desktop parts to have a thermal design power between 95 and 100 watts. That’s right in line with high-end Intel hardware, which over the past few generations as hovered in the 90 watt range. AMD further believes the design will scale down better than past architectures, which means low power envelopes — such as 15-watt parts intended for laptops — should fair well.
AMD’s new Zen cores will first be used in its “Summit Ridge” processors. The first Zen-based product will appear in the high-end desktop market. A release date is not confirmed, but will be in early 2017. After that, the Zen-based chips will roll out to the enterprise-class server market, followed by mobile PCs, and the embedded application market (tablets, smartphones, and the like).
Editors' Recommendations
- AMD’s upcoming APUs might destroy your GPU
- AMD’s next-gen CPUs are much closer than we thought
- The one AMD 3D V-Cache processor you should avoid at all costs
- AMD’s new CPU slammed as ‘anti-consumer at best’
- We have some good news about AMD’s next massive CPU launch