Computer security firm Trend Micro says fake digital certificates from compromised Dutch certification authority DigiNotar were part of a broad-scale man-in-the-middle attack targeting Iranian Internet users—and may have left political dissidents, activists, and others trying to bypass Iran’s online censorship regime vulnerable to eavesdropping.
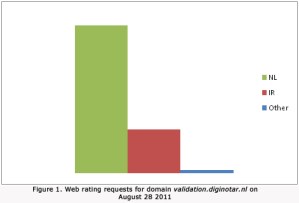
DigiNotar catapulted into the news late last month when it was discovered to have issued a rogue certificate for Google.com, making it possible for third parties to carry out man-in-the-middle attacks on Google services—like Gmail—as if they were trusted and verified systems controlled by Google. Online security professionals tried to react quickly, but Trend Micro noticed something very odd about requests for domain validation through diginotar.nl: it’s a small firm that mostly serves customers in the Netherlands, so one would expect most of its domain validation requests to come from the Netherlands. And that’s true. However, beginning August 28 a significant number of Internet users requesting domain validation through DigiNotar were from Iran. No other countries saw any significant uptick in domain verification requests through DigiNotar.
The unusual spike in requests started on August 28, dropped off substantially by August 30, and was all but gone on September 2.
“These aggregated statistics [..] clearly indicate that Iranian Internet users were exposed to a large scale man-in-the-middle attack, where SSL encrypted traffic can be decrypted by a third party,” Trend Micro senior threat researcher Feike Hacquebord wrote.
Trend Micro also notes that several Web proxy systems in the United States—which are widely used by individuals wishing to access sites anonymously and without revealing their IP address or other details—were also sending Web validation requests for DigiNotar. Trend Micro speculates that these proxy services were being used by Iranian citizens seeking to work around government censorship—but the fake trust certificates would have meant their encrypted communications could have been intercepted anyway.
Trend Micro’s analysis is based on the company’s Smart Protection Network, which collects and analyzes data from Trend Micro customers around the world, including what domain names are accessed by customers at particular times.


