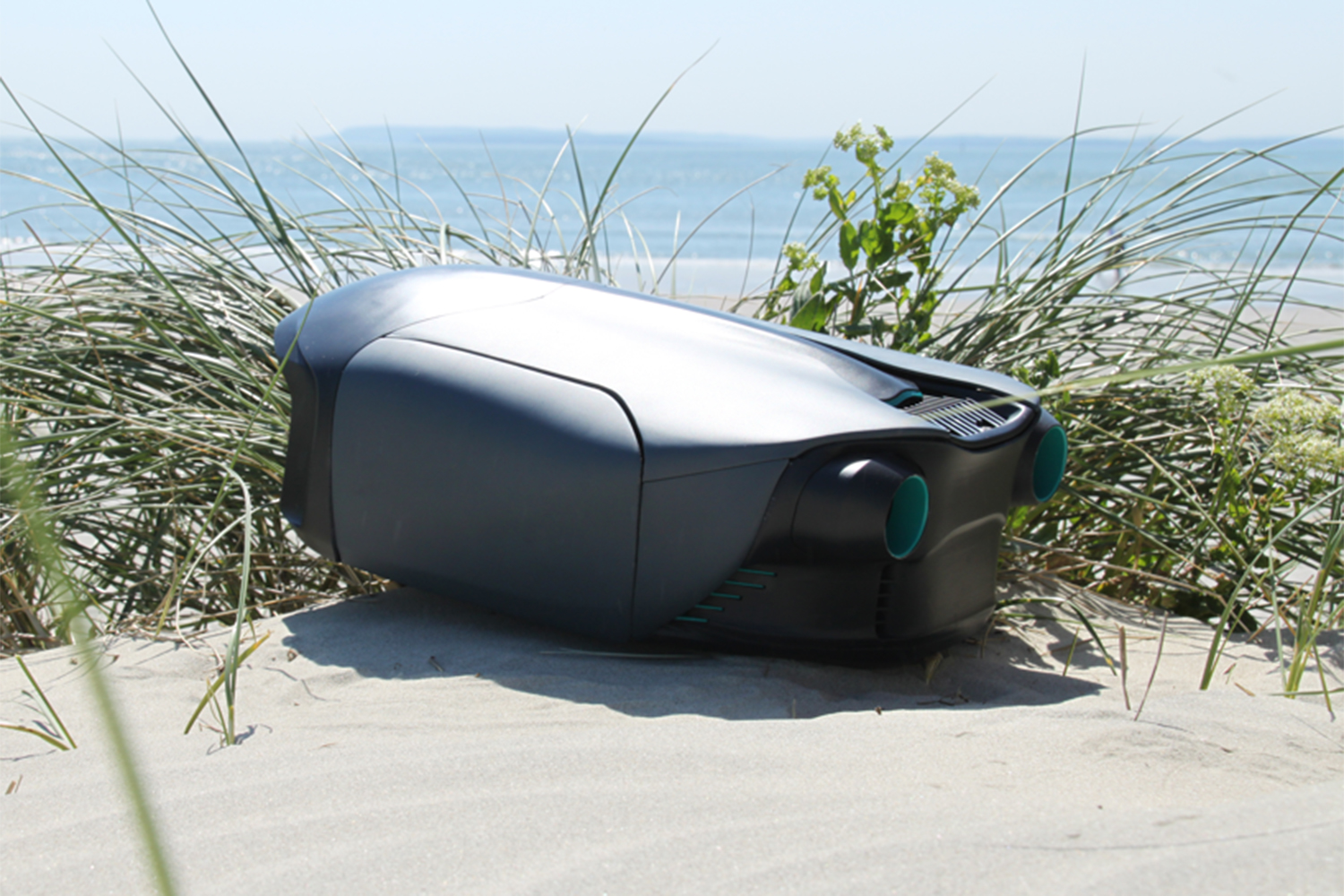
Exterior. An expensive hotel in somewhere like the Amalfi coast that costs more per night than you or I make in a couple of months. Bored, bronzed beautiful people are doing laps in an Olympic-sized swimming pool.
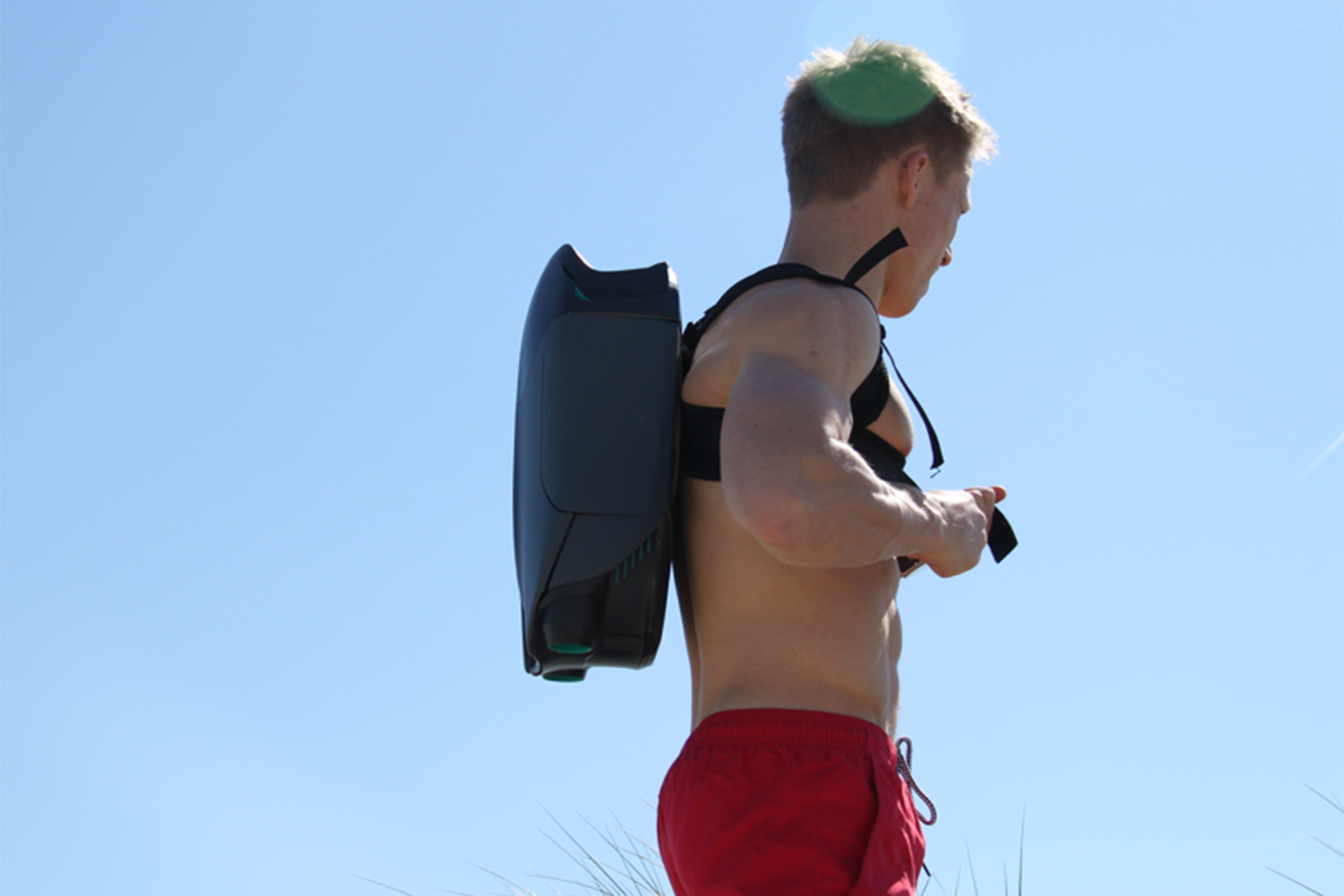
Suddenly, here comes our man: ruggedly handsome with a mischievous streak and a pair of pricey La Perla swimming trunks that leave little to the imagination. On his back there’s what appears to be a jetpack, designed by the world’s greatest carmakers.
He dives into the pool and, suddenly, the jetpack propels him through the water like a missile. At the other end he climbs out and walks into the poolside bar; dripping wet and still naked apart from said jetpack and expensive swim trunks. His appearance causes a scandal amongst a group of stuffy middle-aged accountant types. There’s shock, but also begrudging admiration, and definitely some envy. Especially about that jetpack.
“What’ll you have?” says the bartender, pleased that his mundane day has been disrupted in this manner. “A beer for me,” says our man, as he takes his jetpack off and places it on the barstool next to him. “And something dry for my friend.”
The name’s jetpack, underwater jetpack
Actually, it’ll probably be a line that’s cooler than that. But you get the idea. Anyway, it doesn’t matter yet because the ad’s not been made. Heck, the product this imaginary advert is there to advertise is only in its embryonic stages. But that’s exactly the kind of ad you inevitably start imagining when Archie O’Brien tells you about the thing he’s building.
“I want this to be something so cool that you’re wearing it when you’re not even using it,” O’Brien told Digital Trends. “You feel like James Bond.”

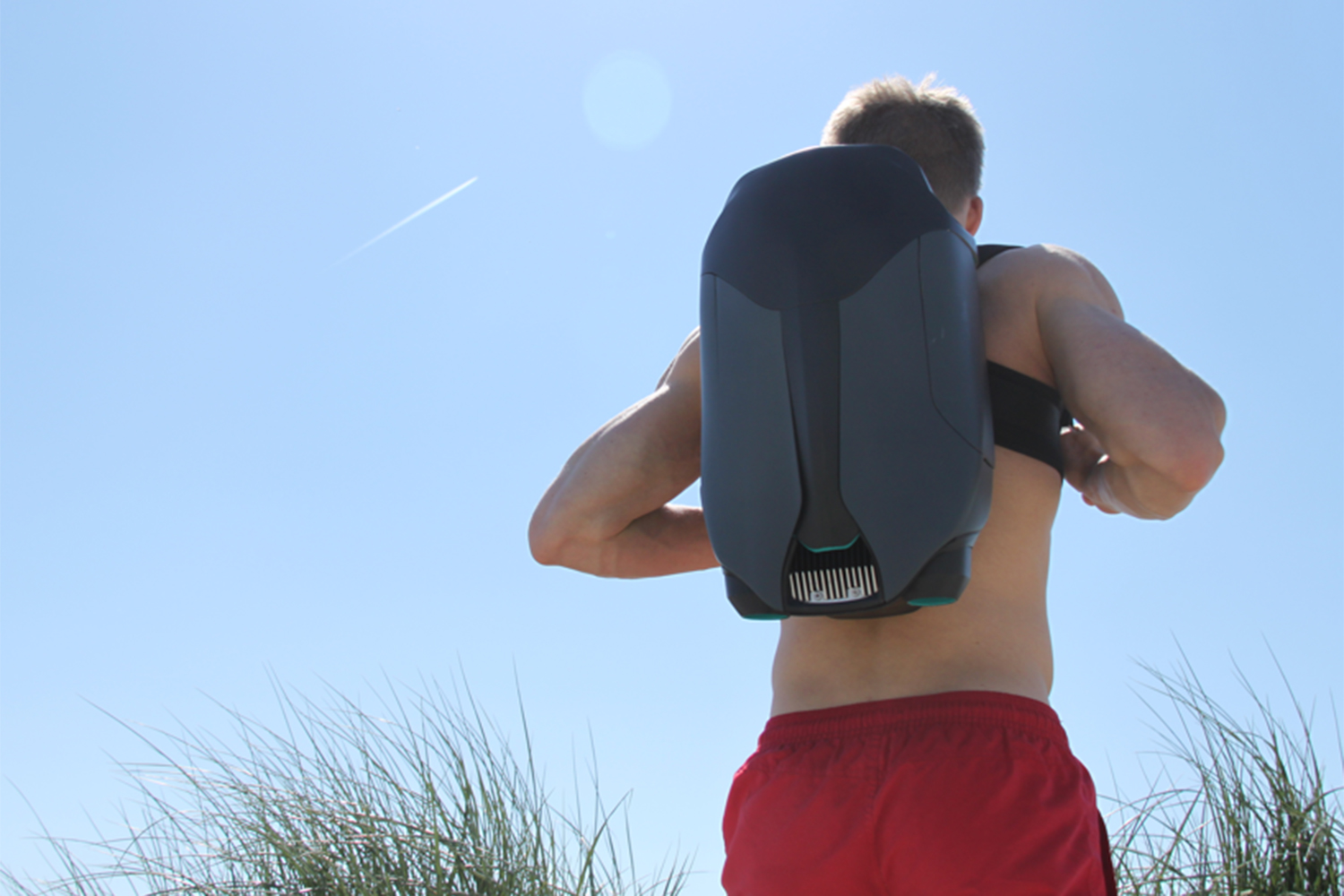
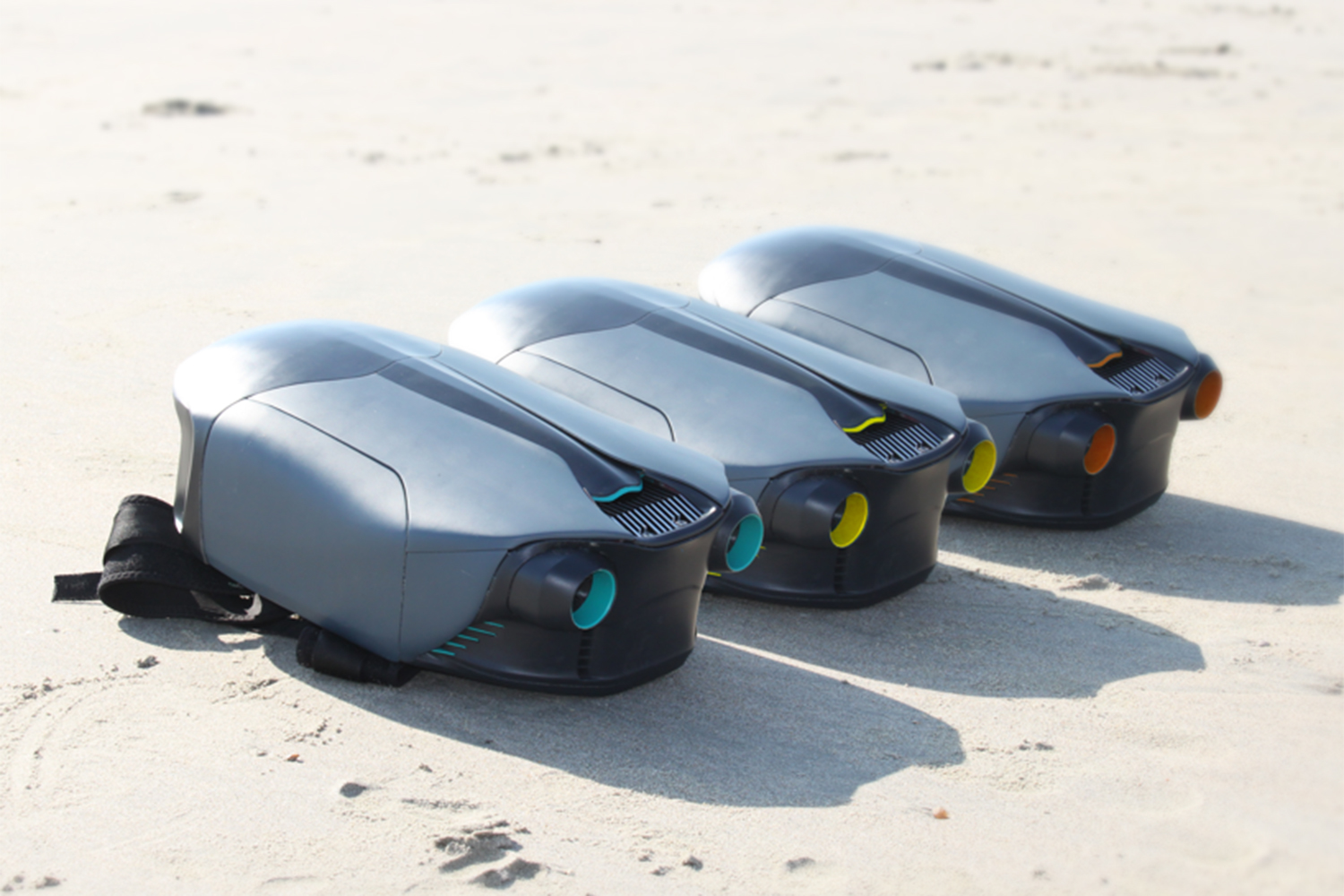
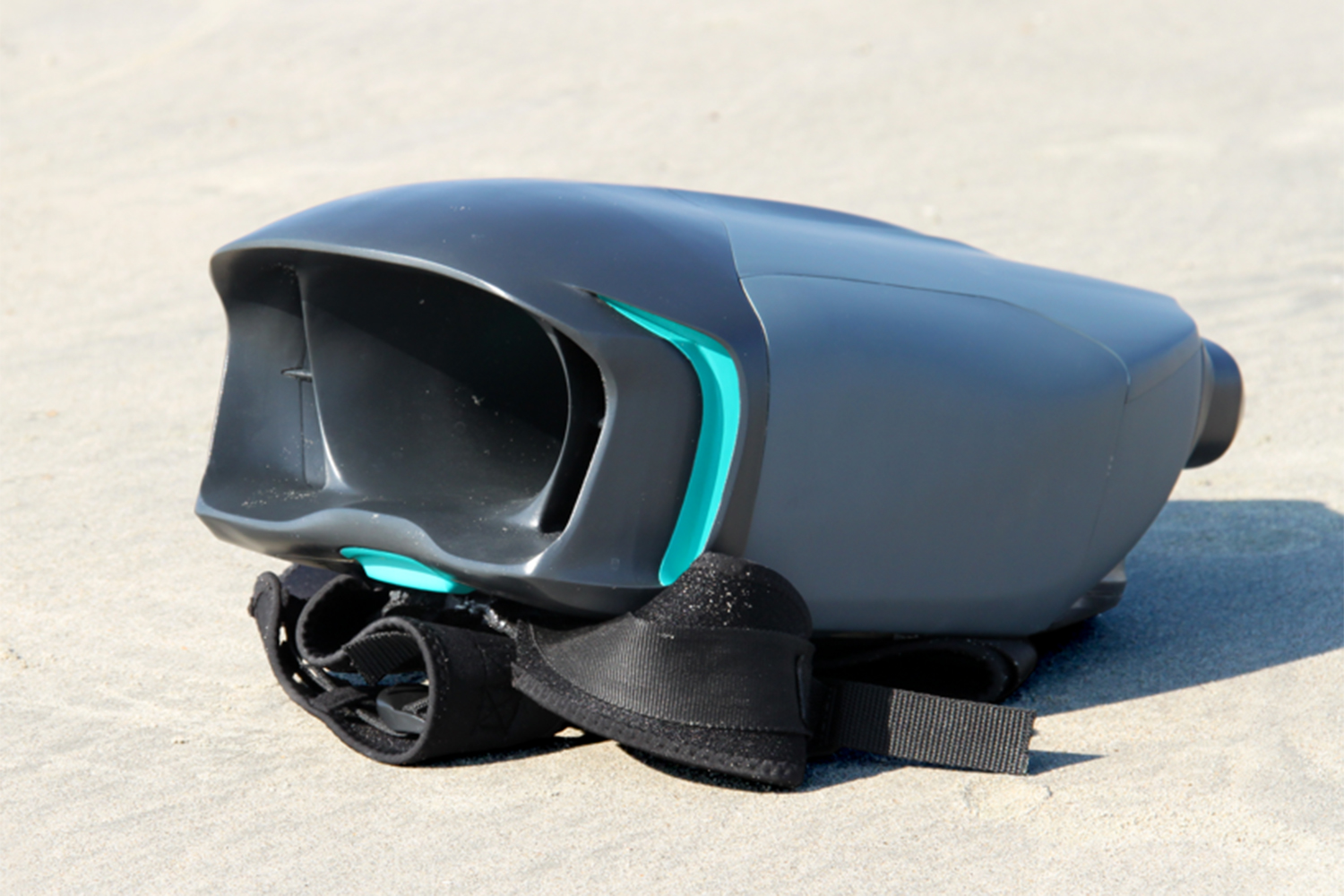
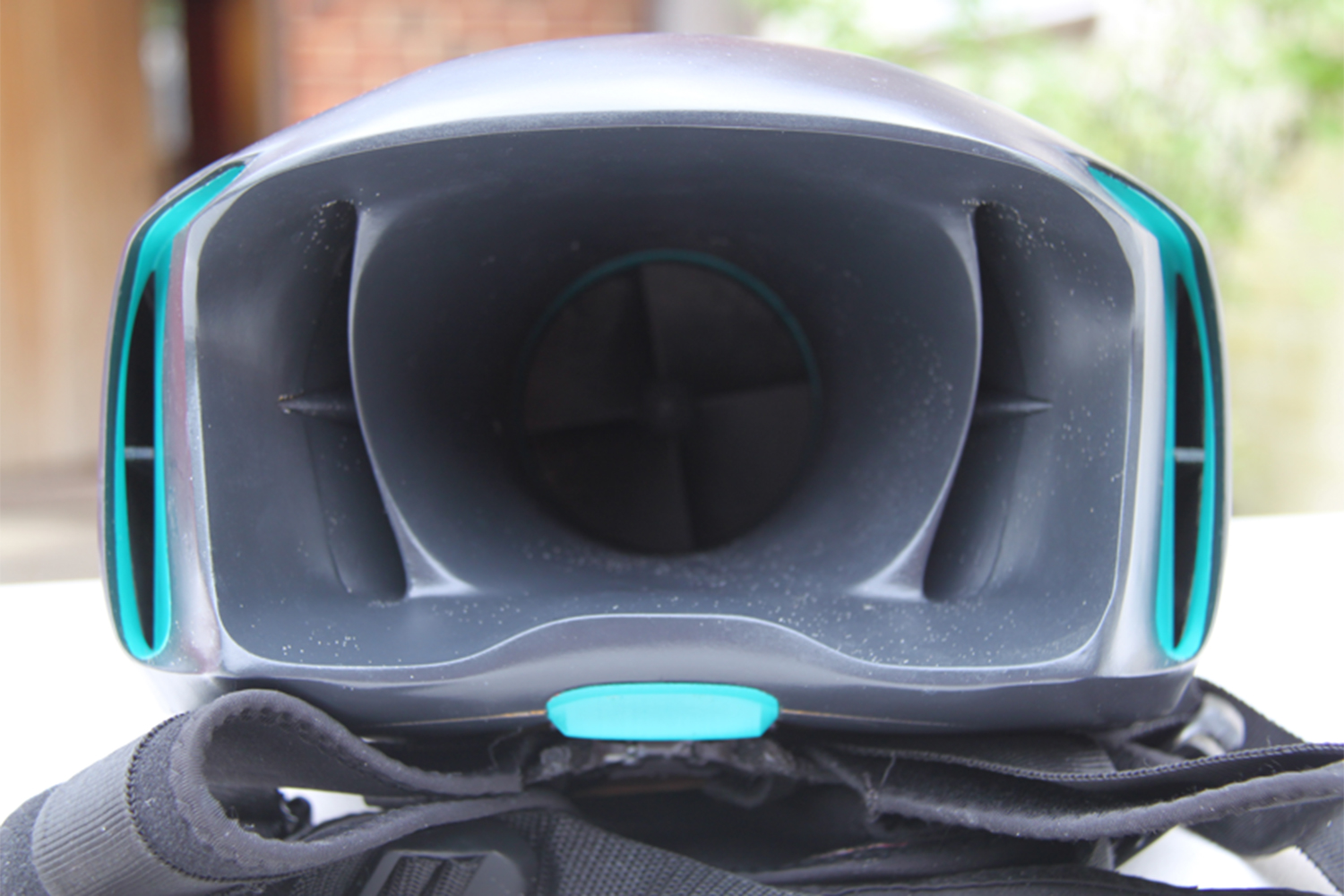
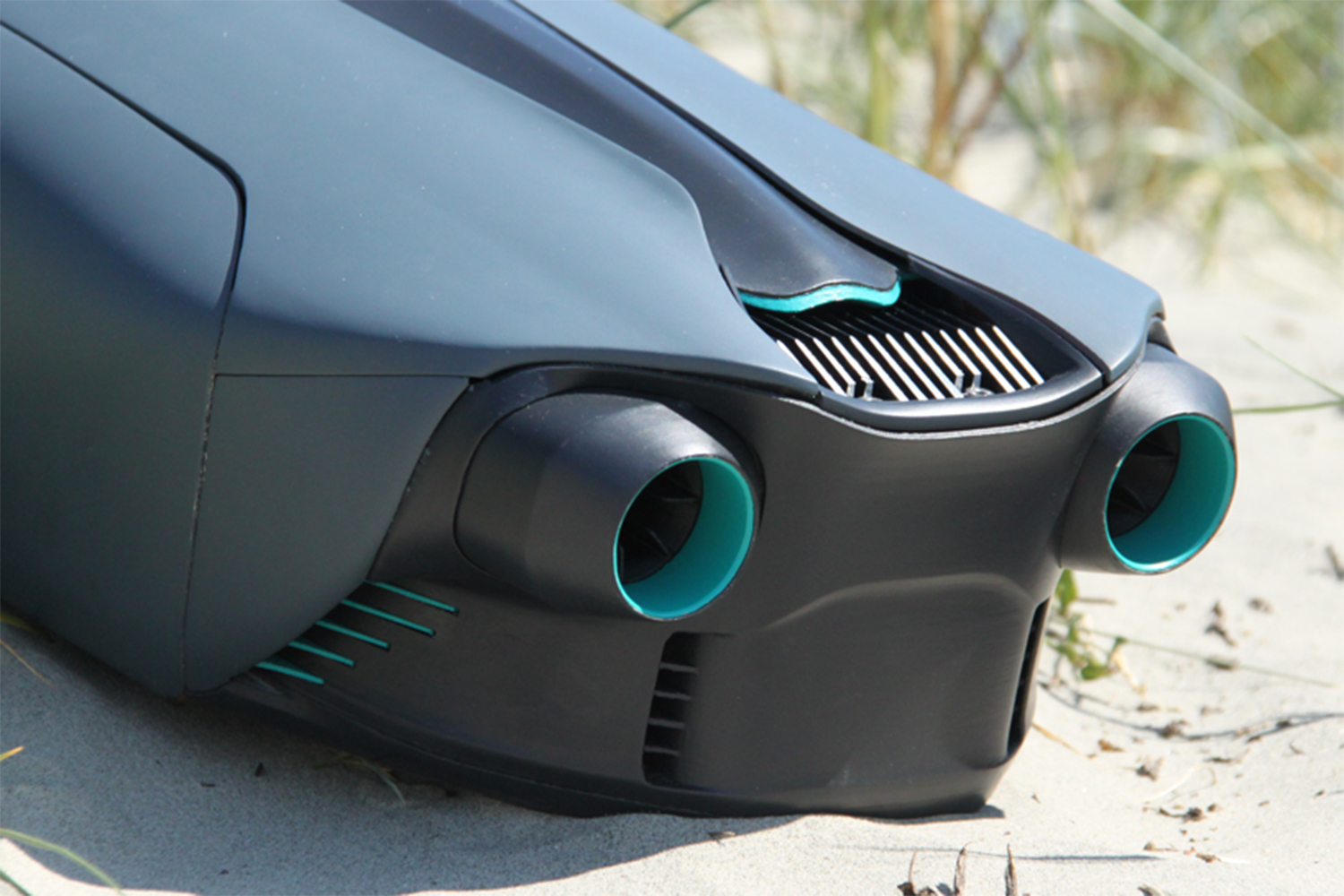
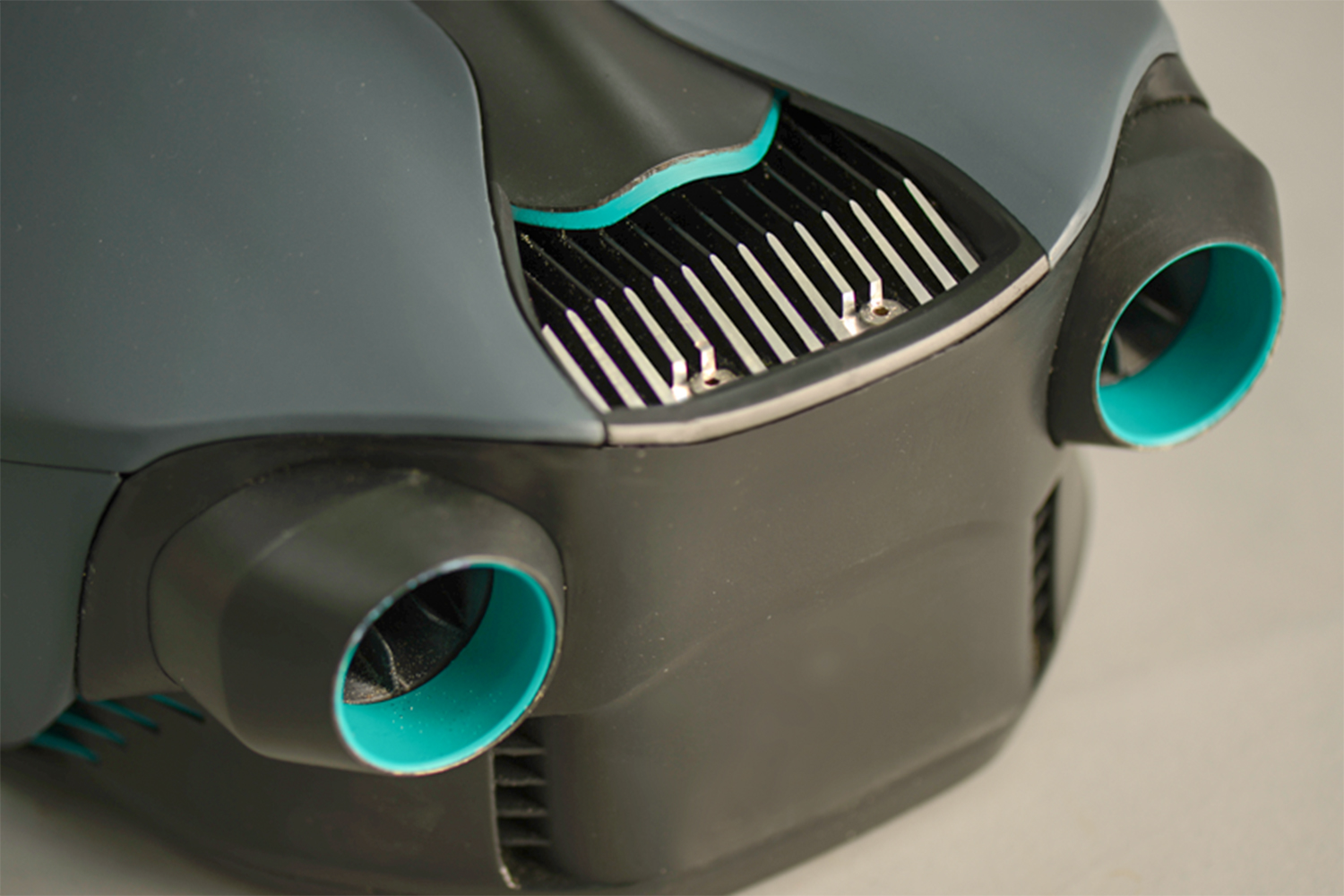
As you’ve probably picked up, O’Brien has created an underwater jetpack: a pair of words about as exciting as any two that you could put together in the English language. The CUDA jetpack was lovingly 3D-printed over the course of several months for a final year project in his Product Design class at the U.K.’s Loughborough University. And soon he wants to sell it to you for an as-yet-unconfirmed price in the vicinity of $6,000.
“By this time next year, I’m planning on having the production model,” he continued. “I’ll be going around doing promo videos around the world. I plan to get sponsored by GoPro and Red Bull… The idea is to be able to produce this one, get enough funding to reinvest it into the company, and try and make a much cheaper model. That’s almost working it like Tesla did, with something that really grabs people’s attention, and then bringing that price down to something people can afford more.”
The path to get here
O’Brien’s journey to the potential Elon Musk of the watersport propulsion world began when he saw a promotional video for the SEABOB, a handheld aqua scooter that’s half jet-ski and half one of those foam floats they used to give the kids at school who couldn’t swim properly. He liked what he saw — at least, with the exception of its $17,000 price tag.
“I was so surprised to find that there really wasn’t anything like this that you could wear on your back.”
Fortunately, O’Brien had just found out about 3D printing, and the idea occurred to him that, if he couldn’t afford a SEABOB, he might just be able to build his own.
He began poring over research papers like “Numerical Analysis of a Waterjet Propulsion System,” cover to cover. He hooked up with 3D Hubs, a manufacturing platform that provides affordable and fast 3D printing, CNC machining and injection-molding services. He studied the design of high-end cars made by Lamborghini, Mclaren, and Aston Martin, which he wanted his product to resemble aesthetically.

Things were progressing nicely until a friend gave him a copy of Daniel Wilson’s 2007 non-fiction book Where’s My Jetpack: A Guide to the Amazing Science Fiction Future that Never Arrived. Suddenly the project parameters changed. Handheld devices were out. Underwater jetpacks were in.
“I’ve always wanted to fly, and I just thought that if you can make the experience hands-free it’s a lot better for many reasons,” O’Brien said. “I was so surprised to find that there really wasn’t anything like this that you could wear on your back.”
“Think of it like an airplane. If it’s not moving you can’t turn. It kind of feels like you’re a little underwater airplane.”
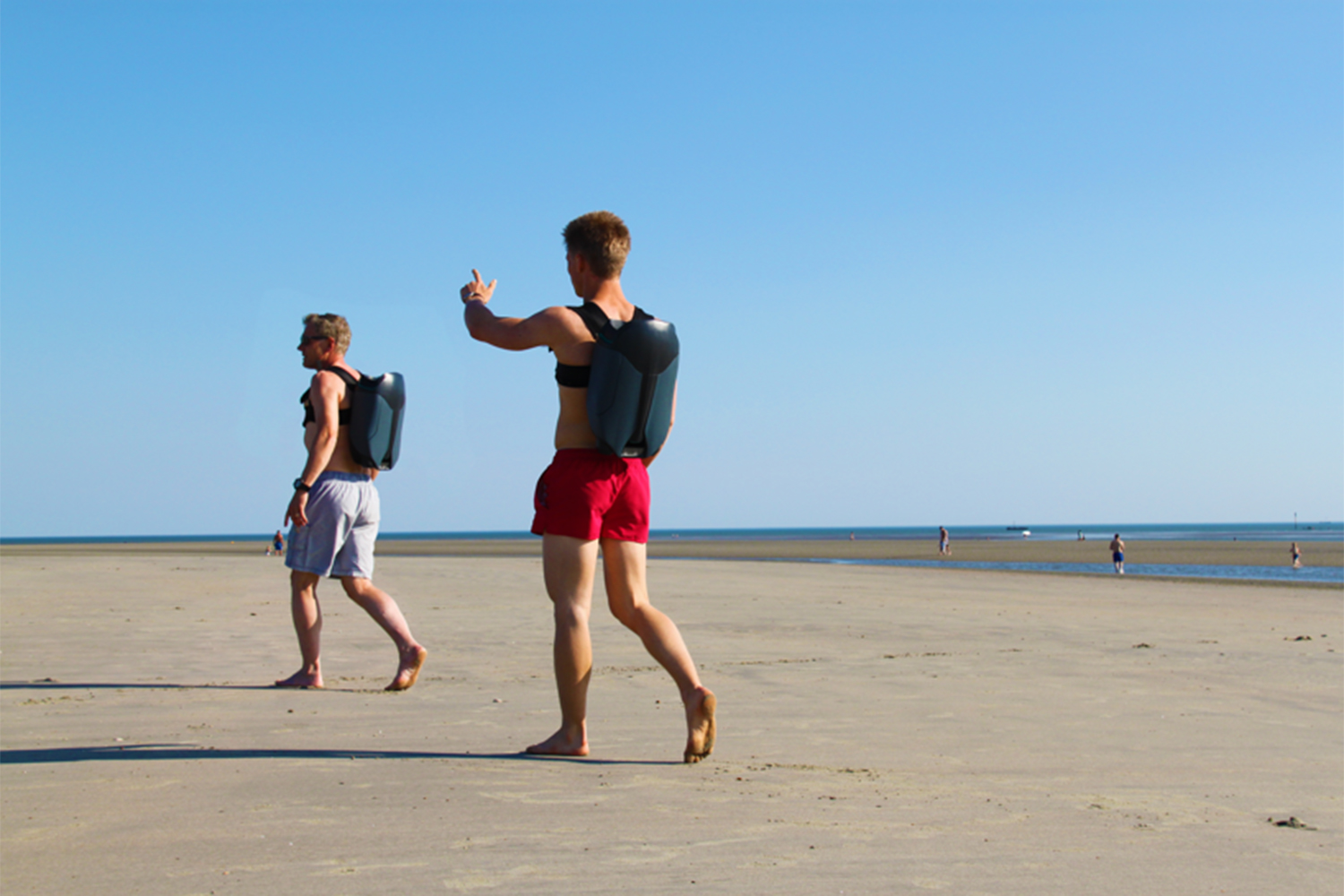
The final CUDA is almost exclusively 3D printed, with the exception of the battery and electronics. Because he wasn’t able to get permission to test it in public spaces, he’s so far put it through its paces in private swimming pools — although he hopes this will change in the future.
He hasn’t yet been able to decisively measure a top speed, either, due to the lack of a speedometer and limited testing space. It’s definitely faster than regular swimming, though. “Oh yeah,” he assured us. “Yeah, yeah, yeah.” It needs to go fast because it won’t steer properly unless you’re going quickly. “I’m still learning how to use it,” he admitted. “It seems that the faster you go the easier it is to turn. Think of it like an airplane. If it’s not moving you can’t turn. It kind of feels like you’re a little underwater airplane.”
The commercial version will be even faster, he explained, since the current prototype doesn’t have the more powerful battery pack he’s hoping to add. “It would have taken me an extra week and I didn’t have a week to do it,” he said.
The leader in watersports propulsion
Archie O’Brien has big plans for his product. As noted, he’s currently targeting Q2 2019 for the first CUDA production models. It won’t stop there, though. This is just product one of a larger water sports brand.
“I’ve got many more ideas I’m not working on at the moment, but I’ve got draft drawings for to expand this brand,” he said. “I’ve got a very clear vision of where this can go. The plan is to be the market leader of watersports propulsion.”
Where do you go after the awesomeness of an underwater jetpack? We’re excited to find out!
Editors' Recommendations
- Fighting football injuries with 3D-printed, hyper-personalized pads
- Inside the quest to 3D print a perfectly palatable steak
- 3D printing lets hospitals make ventilator substitutes with common equipment
- 3D-printing technique produces tiny, highly detailed objects in seconds
- This 3D-printed four-legged robot is ready to take on Spot — at a lower price