Last month, researchers at Washington University in St. Louis published a paper detailing their development of a graphene oxide-based nanomaterial to effectively filter filthy water into drinking water.
Graphene oxide — an inexpensive, paper-like form of graphene — is well-known for its ability to absorb light and convert it to heat, making it ideal for tasks that involve harvesting sunlight, according to Srikanth Singamaneni, associate professor of mechanical engineering and materials science and the corresponding author of the paper.
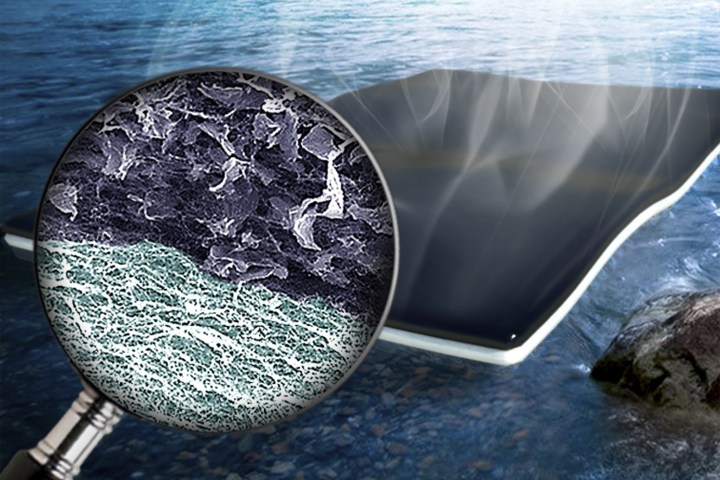
Singamaneni and his team created a two-layered biofoam by combining bacteria-produced cellulose and graphene oxide. The bottom layer consists of a pure nanocellulose network. The top layer is composed of a nanocellulose fiber network that’s embedded with graphene oxide flakes.
“When this bilayered foam-like material is suspended on dirty water, water is [sucked up] by the pure cellulose layer at the bottom — just like a sponge — and brought to the top surface,” Singamaneni told Digital Trends.
“Light shining on the top surface is converted to heat by the graphene oxide, which causes water to evaporate. The process is highly efficient as the heat is not dissipated into the bulk water and confined to the surface where evaporation occurs. The resulting fresh water can be easily collected from the top of the foam.”
The researchers envisage their novel material being used to filter tons of water in developing countries that receive sufficient sunlight for the light-absorption-to-heat-conversion mechanism to occur. But, before that happens, they’ll have to scale the material up and run a few additional tests.
“The next step in this research is to integrate this novel material into a device that can condense and collect fresh water and demonstrate the whole process at a pilot scale,” Singamaneni said. “We are also optimizing the graphene oxide content and investigating other designs of hybrid material,” including their use to boost solar energy harvesting devices.
Editors' Recommendations
- An ultra-thin graphene layer could help protect next-gen solar panels
- What is graphene?
- Pani’s smart home water monitor is the Fitbit of water usage
- New images reveal more about the history of water on Mars
- Graphene’s latest neat trick? Stopping mosquitoes from biting you


