Volvo is known for safety fanaticism. And lately it’s been focusing on the most unsafe part of most cars: the driver.
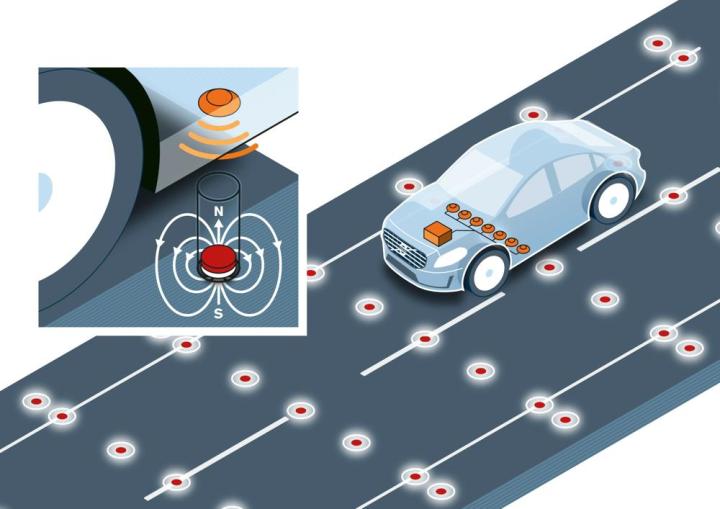
The Swedish carmaker’s latest experiment with self-driving cars involves installing magnets in the road surface to help orient a car’s robot brain.
A car needs to know where it is in order to navigate the environment, and Volvo believes allowing it to talk to the road is the most reliable and cost-effective way to to do that.
Unlike the GPS, cameras, and other sensors used in existing autonomous cars, it says road magnets aren’t affected by physical obstacles or weather.
The ferrous magnets create an “invisible railway,” giving the car a path to follow. Volvo says the system is accurate to within one decimeter, and has already been tested on a track at the company’s facility in Hällered, Sweden.
In addition to the obvious safety benefits of a car that automatically stays in its lane, Volvo believes the system will make road use more efficient by allowing for smaller lanes, as well as more precise snow clearing in winter.
The company also says its magnet setup is relatively cheap. However, it would be interesting to see how well they hold up after years of use, especially on poorly-maintained roads.
This is the latest autonomous driving experiment for Volvo, which has already linked cars together into a robotic “road train”, and demonstrated a self-parking car concept. It also plans to put 100 self-driving cars on the public streets of Gothenburg for a large pilot project.
We have a hard time believing, though, that reworking an entire country’s roadway infrastructure is cheaper than cameras, lasers, and radar sensors. The U.S. alone has four million miles of roads. Rejiggering those to include magnets for cars to read would be a huge and costly undertaking.
America can’t afford to keep the roads it has in decent shape. Adding magnets? Forget about it.

