 Apple’s answer to music streaming is finally upon us, and now iCloud will assume the responsibility as iTunes for the Web, as well as MobileMe replacement. It’s a feature a long time in the making and one every Internet company is trying to offer, and iCloud’s familiar UI and price tag (or lack thereof) will likely give it a nice comfortable cushion to launch on.
Apple’s answer to music streaming is finally upon us, and now iCloud will assume the responsibility as iTunes for the Web, as well as MobileMe replacement. It’s a feature a long time in the making and one every Internet company is trying to offer, and iCloud’s familiar UI and price tag (or lack thereof) will likely give it a nice comfortable cushion to launch on.
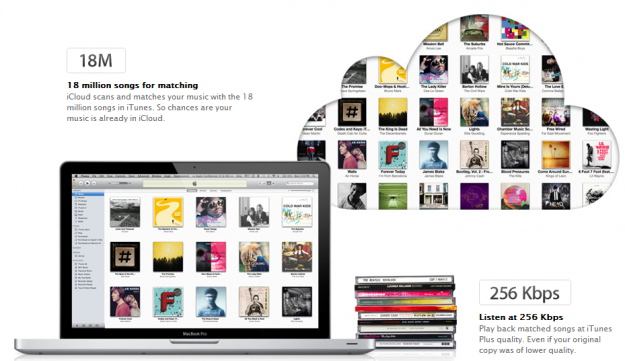
What will cost you is iTunes Match. For a $25 annual fee, iTunes Match will grab all your non-iTunes-purchased (or otherwise obtained…) music, find its information in the iTunes Store. It will pull this data, and sync it with your cloud-based music library while also converting those files to a 2456 Kpbs DRM-free AAC format, making it available on all your iOS devices. This also means you don’t have to go through the painful process of manually uploading your non-iTunes-purchased music file by file.
The entire cloud-based music storage and player has gotten a lot of attention lately for its impact on record companies. Google Music and Amazon Cloud Player both struggled to find compromise here: Google has yet to get song permissions and Amazon got sued for failing to do so and using music anyway. There were reports that the music industry wanted Google to use its music player as a sort of watchdog for P2P file sharing. So at first glance, it may seem like music industry execs would be horrified that iTunes Match will convert many an illegally downloaded song and wrap it up with everything its paid-for version gets. Instead, record companies are seeing how this could benefit them. It’s speculated that Apple is cutting labels a deal in order to offer iTunes Match, in lieu of the royalties they would have made off of the (alleged) illegally downloaded songs.
If this is true, it may be the biggest step toward compromise in 21st century music yet: Users aren’t being forced to quit P2P file sharing, Apple isn’t policing anyone or punishing them for failing to buy songs on iTunes, and record companies will get to see a profit from content that they see as routinely being stolen from them. Of course, record labels will still lose far more than they get – but it’s better than nothing.
What there’s still disagreement about is the long-term habits iCloud and iTunes Match could have on consumers. Some believe – maybe naively – that this will cause users to pirate music less, and find value in subscription services. People will again start paying for music – not how they used to, but instead via services like iCloud and iTunes Match. Others seem a bit more realistic: People are smart enough to realize this means they can continue to download music and pay a fraction of the price for the bonus features iTunes Match offers. Think about it: If you download all your music – say 1,000 songs a year – and pay the $25 iTunes Match yearly fee, it’s as if you’re buying a little more than one album.
Regardless of its effects on how we consume music, this type of solution could be a nice middle ground between the labels, provider services, and users.


