Lazarus, a state-sponsored hacker group based in North Korea, is now using open-source software and creating fake jobs in order to spread malware, says Microsoft.
The well-known group of hackers is targeting many key industry sectors, such as technology, media entertainment, and defense, and it’s using many different kinds of software to carry out these attacks.
The next time you get a message on LinkedIn, you should be careful. Microsoft warns that the North Korea-based threat group has been actively using open-source software infected with trojans to attack industry professionals. Microsoft has determined that these social engineering attacks started in late April and continued until at least mid-September.
Lazarus, also referred to as ZINC, Labyrinth Chollima, and Black Artemis, is a state-sponsored military hacking group from North Korea. It’s said that it has been active since at least 2009, and since then it’s been responsible for a variety of large attacks, including phishing, ransomware campaigns, and more.
The group has been creating fake LinkedIn recruiter profiles and approaching suitable candidates with job offers at legitimate, existing companies. “Targets received outreach tailored to their profession or background and were encouraged to apply for an open position at one of several legitimate companies,” said Microsoft.
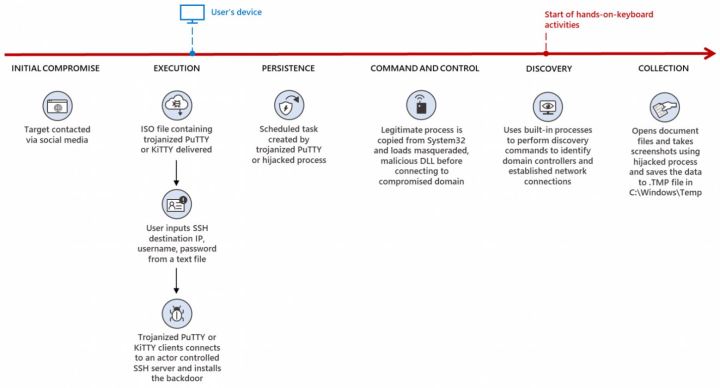
Once the victims were convinced to move the conversation over from LinkedIn to WhatsApp, which offers encrypted communication, the hackers moved on to the next step. During the WhatsApp conversation, the targets received infected software that allowed Lazarus to deploy malware on their systems.
The end goal for the hackers was to be able to steal sensitive information or obtain access to valuable networks. Aside from the malware — which was found in programs such as PuTTY, KiTTY, TightVNC, muPDF/Subliminal Recording, and Sumatra PDF Reader — the attacks were well-engineered on the social side of things, too, with LinkedIn profiles and companies picked to match the victim’s profession.

As noted by Bleeping Computer, ZINC has also carried out similar attacks by using fake social media personas to distribute malware. Earlier, it was chiefly targeting security researchers; this time around, the attacks have a broader range.
These attacks seem like a follow-up to Operation Dream Job. The campaign, active since 2020, focused on targets from the defense and aerospace sectors in the U.S. and lured them in with interesting job offers, all with the goal of conducting cyber-espionage. Lazarus has also been spotted targeting cryptocurrency workers and crypto exchanges in the past.
How to protect yourself from these attacks? Try to keep your LinkedIn conversations on the platform, if at all possible. Don’t accept files from people you don’t know and make sure to use good antivirus software. Lastly, don’t be afraid to reach out to the company and verify that the person trying to send you files actually works there.
Editors' Recommendations
- Microsoft accidentally released 38TB of private data in a major leak
- Hackers are using AI to create vicious malware, says FBI
- This Bing flaw let hackers change search results and steal your files
- Hacker ranks explode — here’s how you can protect yourself
- Microsoft data breach exposed sensitive data of 65,000 companies