Nvidia’s Deep Learning Super Sampling (DLSS) has been a staple of PC gaming for several years now, but DLSS 3 turns the tech on its head. It promises impossibly high frame rates in demanding games like Portal RTX by using AI to generate frames all on its own.
It’s a simple concept, but DLSS 3 is complex. We’re here to catch you up on what DLSS 3 is, how it works, and what games you’ll find it in.
What is DLSS 3?
DLSS 3 isn’t a brand-new form of Nvidia’s tech. It’s a bundle of three different features: DLSS Super Resolution, DLSS Frame Generation, and Nvidia Reflex. DLSS Super Resolution works as it did in the past, upscaling your games from a lower resolution to improve performance. Reflex, as we’ll dig into later, continues to reduce latency. It’s Frame Generation that’s new.
This feature uses AI to generate every other frame you see in games, and you can combine it with DLSS Super Resolution for even higher performance. The important note here is that Frame Generation and Super Resolution are separate settings in DLSS 3 games, so you can opt for one or the other, both, or neither. If you have a high-end RTX 40-series GPU, you can even combine Frame Generation with Nvidia’s Deep Learning Anti-Aliasing (DLAA) in supported titles.
Reflex isn’t optional, though. If you turn on Frame Generation, you need to also use Reflex. We’ll dig into why it’s so important in the next section.
How does DLSS 3 work?
The first component of DLSS 3 is the existing supersampling or upscaling methods seen on DLSS 2. Since it is available in a large library of games, it only makes sense to build over the technology. As per Nvidia, DLSS 2 can boost frame rates by 200% to 300%. With DLSS 3, the company introduced “Optical Multiframe Generation” which is the core functionality that separates the latest version from its predecessors.
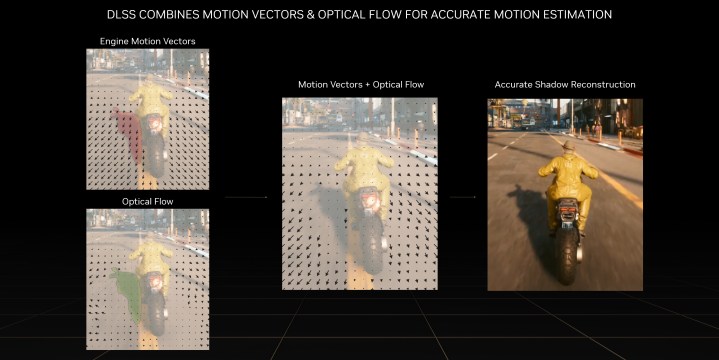
The Optical Flow Accelerator analyzes two back-to-back in-game frames and, after precise calculations, an AI-generated frame is added inbetween. The accelerator has the ability to capture the direction and speed at which pixels are moving from one frame to the other, and can even capture pixel-level information like particles, reflections, shadows, and lighting. Using engine motion vectors and optical flow to track motion, the AI can accurately reconstruct both geometry and effects. Essentially, the AI adds extra frames to your games, thereby enhancing frame rates and overall quality.
While frame generation helps in producing higher frame rates, especially when compared to DLSS 2, it also has the potential to improve the overall response and smoothness in games that are bottlenecked by your CPU. But there is a downside to frame generation. The AI-generated frames end up increasing latency, as they are neither created by the game, nor the user, thus in certain games, one can face reduced responsiveness. DLSS 3 generates every other frame you see, so you only get the responsiveness of half of the final frame rate. For example, a game running at 60 frames per second (fps) will feel like it’s running at 30 fps.
This is where Nvidia Reflex comes in, as it works in tandem with the GPU and CPU to reduce this latency. Having a lower system latency means that your game controls are more responsive, which in turn makes on-screen actions occur almost instantaneously once you click your mouse button or any other control input.
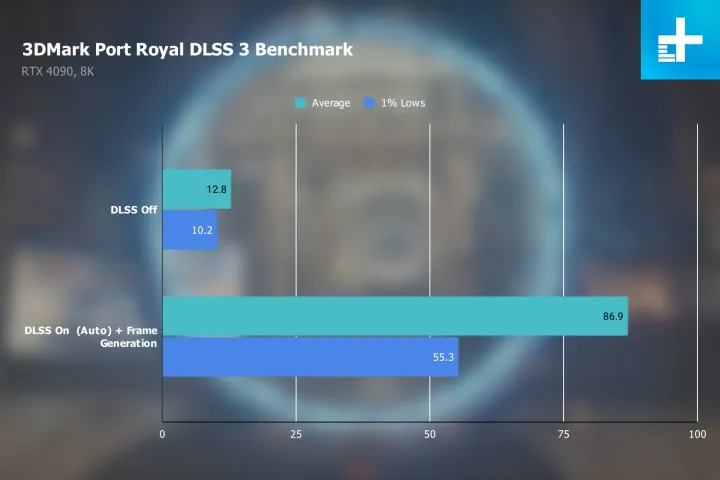
As per our testing, DLSS 3 actually works really well. Using an RTX 4090 graphics card and DLSS 3 enabled, we found Cyberpunk 2077 at 4K with ray tracing set to the max produced nearly 50% more frames than when just using DLSS 2. Compared to not using DLSS at all, DLSS 3 had over three times the frame rate.
It makes some otherwise impossible situations possible, too. For instance, on the RTX 4090, DLSS 3 enables you to play some games at 8K that are otherwise unplayable without the tech.
DLSS 3-supported graphics cards
As of now, DLSS 3 is only available with Nvidia’s latest GeForce RTX 40-series graphics cards. This means if you want to try it, you need to get your hands on any of the following GPUs:
- GeForce RTX 4090
- GeForce RTX 4080
- GeForce RTX 4070 Ti
- GeForce RTX 4070
- GeForce RTX 4060 Ti
- GeForce RTX 4060
- GeForce RTX 4050
DLSS 3 works across laptop and desktop graphics cards, so if you have any of the cards listed above, you’re good to go. It doesn’t work on any competitor cards, though, so you’re locked out if you have AMD or Intel GPU.
It’s worth noting that DLSS Frame Generation is the only feature limited to RTX 40-series GPUs. DLSS 3 also includes DLSS Super Resolution and Reflex, which can be used with all RTX graphics cards.
DLSS 3.5 update

Nvidia is gearing up to release the DLSS 3.5 update that adds Ray Reconstruction into the mix. This feature is available on all RTX GPUs, and its said to make ray tracing more immersive and accurate.
The feature adds an AI-driven denoiser to ray tracing, allowing the lighting effect to be more accurate. In some cases, Nvidia says that Ray Reconstruction can even improve performance. The feature isn’t out yet, but it’s expected to launch in Cyberpunk 2077: Phantom Liberty in September.
Can you use DLSS 3 on the RTX 30-series?

DLSS 3 is only available on Nvidia’s latest Ada Lovelace architecture, thus it can only work on GeForce RTX 40-series GPUs. One cannot use DLSS 3 on RTX 30-series graphics cards as they do not include an Optical Flow Accelerator, which is the core component to achieve frame generation.
It’s worth noting, however, that DLSS 3 seems to be software-locked to RTX 40-series GPUs. You can bypass it with a config file, according to Wccftech, though it will likely cause instability, crashes, and poor performance in most games.
Note, however, that DLSS Super Resolution still works on all RTX GPUs. In DLSS 3 games, you can still use the Super Resolution portion on RTX 20-series and RTX 30-series GPUs. Only Frame Generation is locked to RTX 40-series graphics cards.
DLSS 3 games

There are close to 50 games that currently support DLSS 3, with more titles being added almost every month. Here are all the games that we currently know support Nvidia’s latest supersampling tech.
- A Plague Tale: Requiem
- Atomic Heart
- Bright Memory: Infinite
- Chernobylite Enhanced Edition
- Conqueror’s Blade
- Cyberpunk 2077
- Dakar Desert Rally
- Deliver Us Mars
- Destroy All Humans! 2 – Reprobed
- Diablo IV
- Dying Light 2 Stay Human
- F.I.S.T.: Forged In Shadow Torch
- F1 22
- Forza Horizon 5
- Hitman 3
- Hitman World of Assassination
- Hogwarts Legacy
- Icarus
- Jurassic World Evolution 2
- Justice
- Loopmancer
- Marvel’s Midnight Suns
- Marvel’s Spider-Man: Miles Morales
- Marvel’s Spider-Man Remastered
- Marauders
- Mount & Blade II: Bannerlord
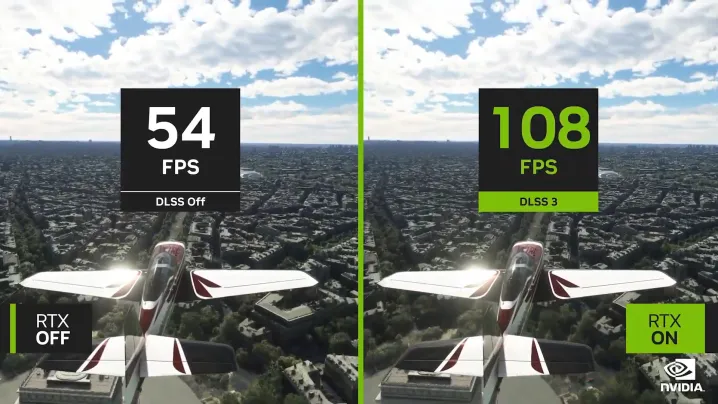
- Microsoft Flight Simulator
- Midnight Ghost Hunt
- Nakara: Bladepoint
- Need For Speed Unbound
- Perish
- Portal with RTX
- Ratchet & Clank: Rift Apart
- Redfall
- Returnal
- Ripouy
- Sackboy: A Big Adventure
- S.T.A.L.K.E.R. 2: Heart of Chornobyl
- Super People 2
- Sword and Fairy 7
- Super People
- Synced
- The Finals
- The Lord of the Rings: Gollum
- The Swordsmen X: Survival
- The Witcher 3: Wild Hunt
- Tower of Fantasy
- Warhammer 40,000: Darktide
- WRC Generations – The FIA WRC Official Game




