“I was googling online about two and a half years ago, looking for creatures that change their color, and found out about this beetle,” project leader, Subramanian Sundaram, an MIT graduate student in electrical engineering and computer science, told Digital Trends. “The golden tortoise beetle is incredibly interesting. One of the things it does is that, when it’s disturbed or scared, it drains out the fluid in its shell which is normally golden in color, but becomes a reddish-brown. I was interested by the idea that this beetle was able to respond to mechanical disturbances by changing the color and transparency of its outer shell. I thought we might be able to replicate that.”
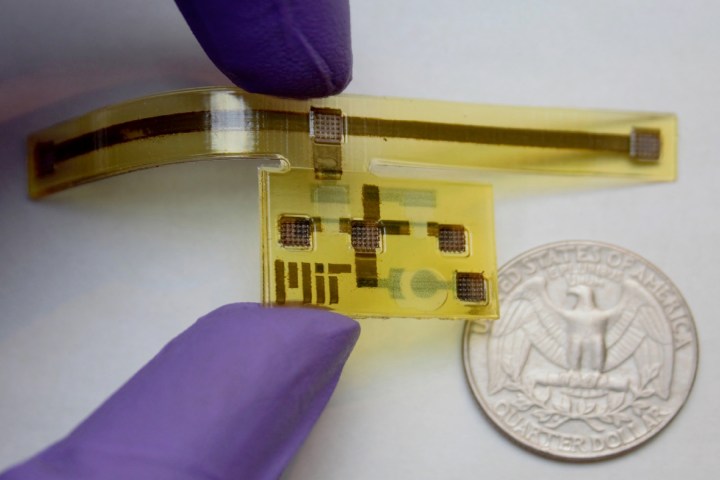
To create a similar effect in their robot “skin,” Sundaram and colleagues used 3D-printed flexible circuitry on a plastic substrate. The substrate was printed using an MIT MultiFad 3D printer, with the color-changing part being prompted by electrodes that are attached to the T-shaped object. The printed circuit board boasts two printed transistors and a so-called “pixel,” referring to a semiconducting polymer.
In all, it serves as a neat proof of concept for scientists’ newfound abilities to print flexible substrates made up of multiple materials that are capable of demonstrating unique behaviors. Right now, there are no obvious useful applications for the robot skin, but it fits into a broader research theme of materials capable of drastically changing when outside stimuli are applied.
“Going forward, I think that adding actuation to this would be very interesting,” Sundaram continued. “I don’t know how long it will take to reach that point, but it would also be interesting to add elements of communication so that you could have it transfer data to a larger computer. All of this will require key breakthroughs to take place, but these are definitely the directions we’re interested in.”
A possible future robot that could change its skin tone to camouflage itself at a moment’s notice? Color us interested — no pun intended.
Editors' Recommendations
- This 3D-printed four-legged robot is ready to take on Spot — at a lower price
- MIT’s tiny walking robot could eventually build other, bigger robots



