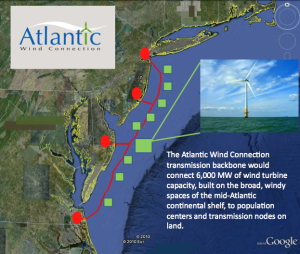
The company has invested in the Atlantic Wind Connection (AWC) which is building offshore wind turbines along 350 miles of the Atlantic, stretching from New Jersey to Virginia. The AWC project will be able to connect 6,000MW of offshore wind turbines, the equivalent of 60% of the wind energy that was installed in the entire country last year.
The project will be able to serve power to roughly 1.9 million households.
“The AWC backbone will be built around offshore power hubs that will collect the power from multiple offshore wind farms and deliver it efficiently via sub-sea cables to the strongest, highest capacity parts of the land-based transmission system. This system will act as a superhighway for clean energy. By putting strong, secure transmission in place, the project removes a major barrier to scaling up offshore wind, an industry that despite its potential, only had its first federal lease signed last week and still has no operating projects in the U.S.,” Google explains on its blog announcing the deal.
The Mid-Atlantic is a prime building ground for offshore wind turbines. Because of the relatively shallow waters that extend for miles out, it’s easier to install turbines. That means both no unsightly wind turbines to look at since they’d be out of eye shot all while being able to take advantage of stronger winds.
“With few other renewable energy options ideally suited for the Atlantic coast, the AWC backbone helps states meet their renewable energy goals and standards by enabling a local offshore wind industry to deploy thousands of megawatts of clean, cost-effective wind energy.”
The AWC project is led by independent transmission company Trans-Elect and is financed by Google, Good Energies and Marubeni Corporation.


