I’m a tagger. When I hear a song that’s catchy, or just familiar, I need to know who’s singing it and what it’s called. For this reason, I install music tagging apps on almost every smartphone I use. I’m the guy who will hold his phone up in the air in the grocery aisle, hoping it can hear the faint melody coming from a ceiling speaker. I have no shame.
I hadn’t used Shazam in a while (I’ve been on a Soundhound kick), but a few weeks ago, I whipped it out to tag a song that definitely sounded like The Goo Goo Dolls (it was). To my surprise, Shazam identified the song almost instantly – in less than a second. Not long ago, you had to spend half a minute trying to tag songs. Shazam is getting fast. Damn fast. So good that it can predict hit songs with remarkable accuracy.
Yesterday, a Mexican billionaire, and the world’s richest man, Carlos Slim invested $40 million in Shazam. He must have tried tagging The Goo Goo Dolls, too. But his real interest is with Shazam’s future. Though more than a third of a billion people use it to identify music today, in the next few years, Shazam is plotting to become one of the largest names in tech.
Shazam is fast becoming a hub for connecting the entire world of audio to the Internet.
Like Google did with search in the last decade, by focusing on speeding up and doing one thing, tagging, really well, Shazam has opened up a lot opportunity. Though it’s become the most popular tool for figuring out who sang what song, it’s fast becoming a hub for connecting the entire world of audio to the Internet.
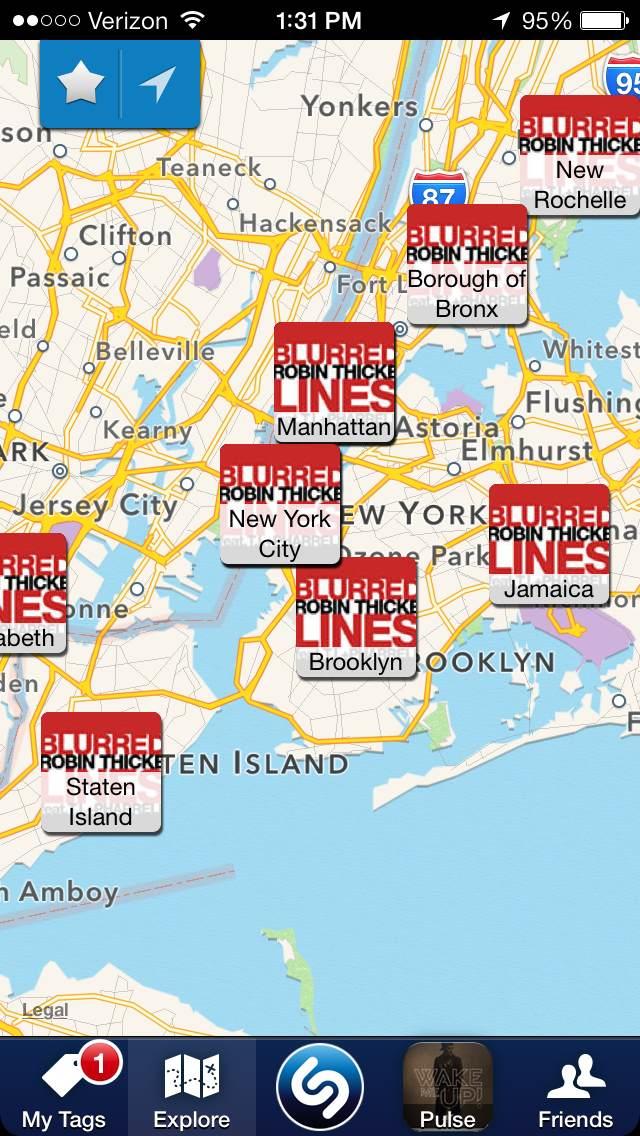
Today, if you tag a song – say “Seven Nation Army” by Zella Day – you have a ton of options. You can comment on how much more you like the Jack White version, share it on Facebook (or any other way), watch its YouTube video, read its lyrics, find out if the Zella Day is playing near you, read her bio, buy the track on iTunes, or play it on streaming services like Pandora, Rdio, and Spotify. By playing around with the locations and times where users tag songs, Shazam now shows you your own tags on a map, and what other people are listening to in every country, region, city, and even block around the world. It’s beginning to create lists of the most popular songs in different areas.
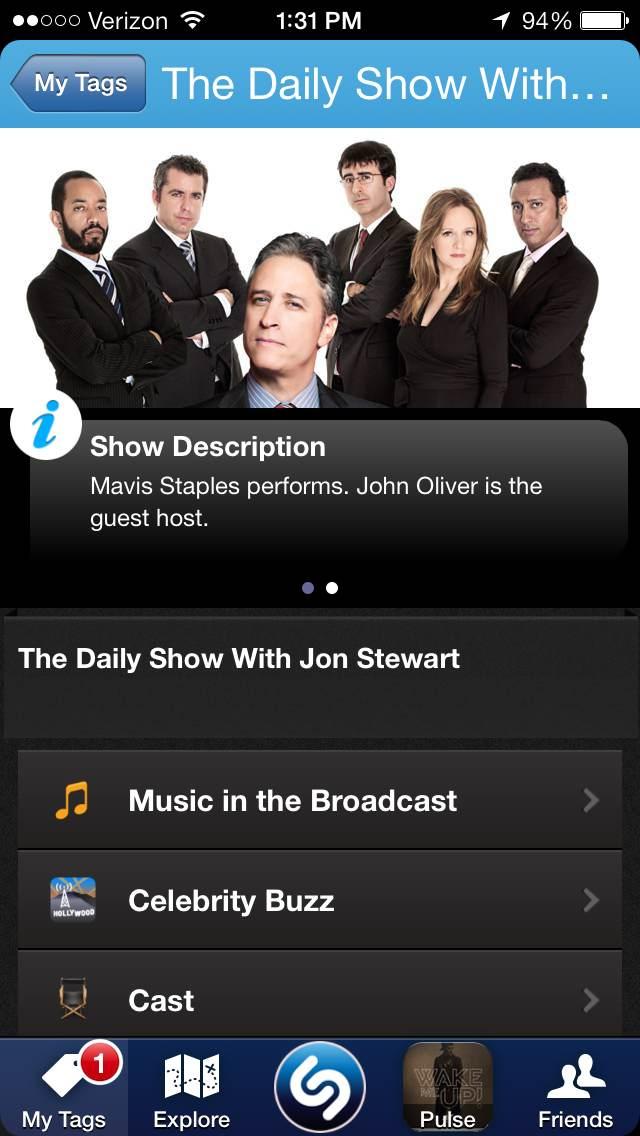
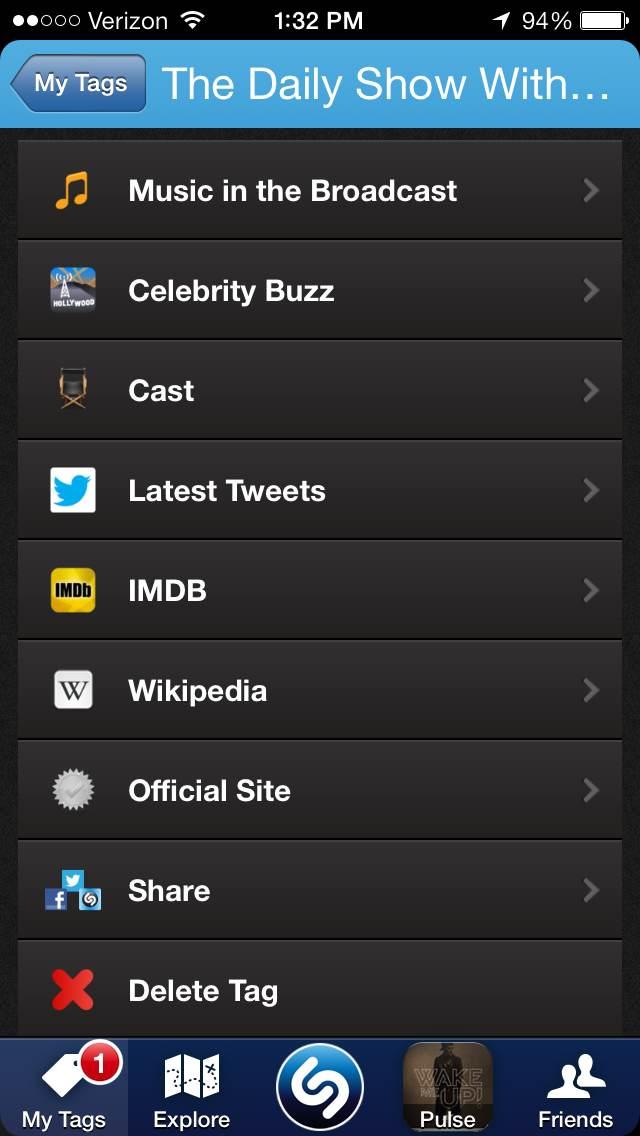
But though music may have gotten Shazam this far, it’s television that is helping it attract a wider audience. Though there have been Shazam-able commercials for a while, last fall, it added TV show tagging to its arsenal. Tagging a TV show – like The Daily Show – will let you see all the music in the broadcast, view the cast, connect to IMDB, read about it on Wikipedia, read the show’s latest tweets, and connect to its official site, among other things. Though it sounds strange to say you’re going to Shazam a show, the TV service is taking off.
We spoke with Jason Titus, Shazam’s Chief Technology Officer, who told us that 54 percent of Shazam users (there are 95+ million in the U.S.) have already tagged at least one TV show. And remember that Mexican multi-billionaire who just invested $40 million in Shazam? He said he’s investing because “Shazam is defining a new category of media engagement that combines the power of mobile with traditional broadcast media and advertising.”
But like a lot of features, TV tagging was only added after user demand.
“We could see huge spikes in usage during primetime on nights when The Voice or other shows [like American Idol] would air,” says Titus. Claiming that “There should never be a time when [Shazam] doesn’t have a result” when something legible is being tagged. More than 160 channel schedules have been added to Shazam since last autumn.
Though it’s striving for greater accuracy, users can now Shazam almost any performance, even during live TV shows like Saturday Night Live. It can even distinguish between different versions of a particular song or recording – that means it can tell if you listened to the SNL performance of a new Vampire Weekend song, or the Late Night with Jimmy Fallon version. The goal of Shazam is to continue adding more audio, help you tag it faster, and deliver everything you want to know about it.
Keeping this mission in mind, Shazam’s next phase is to eliminate the few seconds it takes you to tag things at all. It has already launched a new autotagging feature on its iPad app that will constantly listen (without draining the battery, I’m told) to every TV show or piece of audio that your iPad comes in contact with, even while the app is off. Soon, this feature will roll out to other platforms, allowing Shazam a near 24/7 window into your listening habits, and ensuring that you have a complete record of everything you hear.
There are a lot of scary or annoying things Shazam could do if it listened and tag all the audio we encounter on a daily basis, but the benefits are even more interesting. With such complete access, Shazam could recommend music or TV better than Pandora or Netflix; after that, all it has to do is deliver on those recommendations. Eliminating the need to tag and predicting what you want before you want it could set up Shazam’s next big achievement: to go public in the next two years, becoming one of the first apps to grow into a major tech player. By being everywhere, listening to everything, and helping us identify the audio in our lives, Shazam may end up being the next big thing in tech.