If you’ve ever wanted to take a trip to Mars and go on a hike with the Perseverance rover, now is your chance. Researchers have created an interactive map of Mars’s Jezero Crater, letting you virtually wander around the planet’s surface and follow the rover’s path.
The interactive map shows data like topography, contour lines, and the rover’s path and current position within the crater. There are also panoramic views marked so you can zoom in and appreciate 360-degree views of the vistas of Mars.
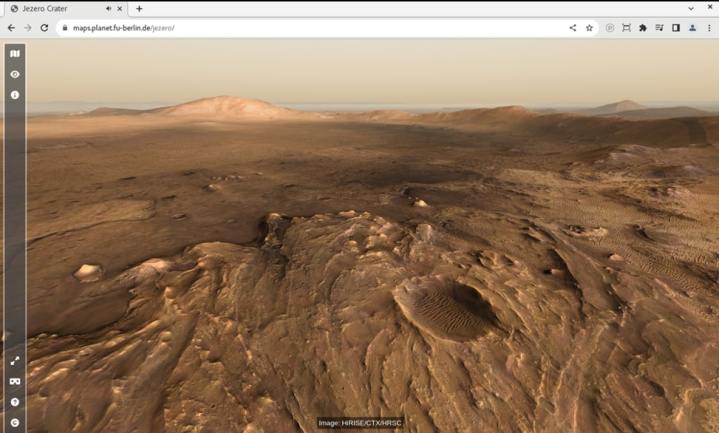
The map was presented at the Europlanet Science Congress 2022 by Sebastian Walter of the Freie Universität Berlin.
“The map is the perfect tool for planning a future visit to Mars, with an interactive interface where you can choose from different available base datasets,” Walter said in a statement. “Some of the slopes are pretty steep, so watch out for those if you want to avoid too much oxygen consumption! To get a real feeling of what to expect on your future Mars trip, you can click on one of the waypoint marker symbols to enter either a fullscreen 3D view or, if you have a Virtual Reality setup, to enter a fully immersive environment. You can even listen to the sounds of the rover if you stand close by.”
The data for the map is a combination of data recorded by Perseverance, like the images from its Mastcam-Z camera and the sounds from its SuperCam instrument, and data taken from orbiters which forms the base layer of the map. This orbital data came from the European Space Agency’s Mars Express and NASA’s Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter, both of which are used to capture high-resolution images of the surface.
The map was originally designed for professional scientists, according to Walter, but as they added more data the research team realized it would be fun for the public to access as well.
“Initially we created the Jezero map as an outreach application to complement the HRSC Mapserver tool, which supports professional scientists to explore the Martian surface,” said Walter. “But as the rover returns more and more high-resolution image data and even audio recordings, it turns out to be the perfect tool for immersive visualization of that data in a scientific context by itself.”



