Intel’s attempt to one-up AMD may have backfired. Intel suggested in a recent presentation that it could be very concerned about the performance of AMD CPUs on certain laptops. Intel’s slides highlight what it claims are notable performance differences when both AMD and Intel laptops are powered by battery, rather than plugged in at the wall. While Intel claims victory, the results and the methodology are dubious.
Despite holding ground with recent advancements like Iris Xe graphics, the presentation suggests that AMD’s CPUs could offer better battery life in laptops when compared to Intel’s but at the cost of CPU performance. More specifically, Intel claims that AMD’s CPUs drop their performance by about 40% to 50% versus its own, which it claims drop just 8% when only powered via battery.
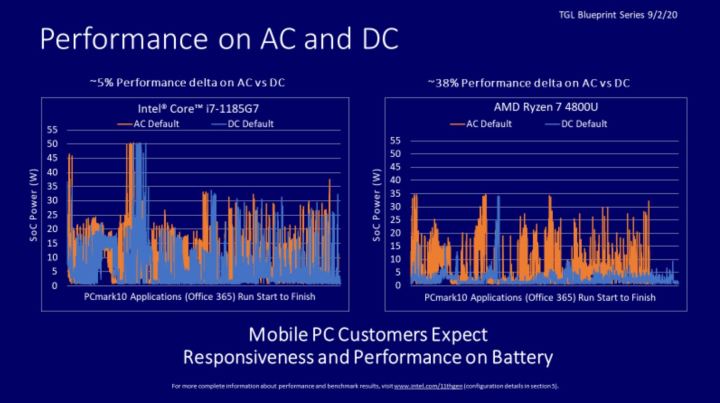
The core conclusion is that in benchmarking without AC power, Intel’s chipsets perform better. Intel also claims that AMD’s CPUs take 7 to 10 seconds to engage in a turbo mode, which allows for performance loss on the battery. Intel’s own systems, meanwhile, are able to do this much faster, in line with how most people use their laptops, it suggests.
As ExtremeTech argues, however, Intel’s methodology in all these tests is flawed, and its conclusions heavily biased. By averaging results, it disregards instances where the AMD CPU pulls ahead in benchmark results and draws a very broad suggestion that battery results are the be-all and end-all of laptop performance metrics. It also fails to mention that manufacturers set many of the parameters of laptop power draw and performance, and specifically chose to test on Lenovo AMD-powered laptops, while looking at a much greater array of Intel systems.
Again, Intel could be purposely skewing these results to make AMD look bad and reignite the AMD versus Intel debate. Its own portfolio is also much larger than AMD’s, with its chips being found in more laptops. Though Intel holds its own in onboard GPU gaming, AMD is pulling ahead in many key areas in the mobile space. Considering it just dominated Intel on desktop with its Ryzen 5000 CPUs, it appears Intel is rather worried it could do the same on



