Solid-state drives (SSDs) are a core component of any modern PC, whether it’s a traditional SATA SSD or a more modern NVMe drive. Knowing the difference between these two types of SSD is important, too, as they can have a dramatic effect on your system’s cost, size, and performance.
All SSDs are faster than traditional hard drives, but there are some big differences between NVMe SSDs and SATA SSDs that are well worth considering.
NVMe versus SSD

SSD is the broad category of data storage medium that uses integrated circuits and flash memory to store data. SSDs are connected to your system or the motherboard using a physical interface, which is usually SATA or PCIe bus. SATA drives are the larger, 2.5-inch drives that most resemble classic laptop hard drives.
NVMe or Non-Volatile Memory Host Express, on the other hand, is the logical interface specification that is used to access a computer’s non-volatile storage media at high speeds. NVMe is primarily seen on PCIe-based SSDs that are built in the M.2 size. Those are the stick drives that are a few inches long and around an inch wide.
Connector and size
The first iteration of SSDs launched with the SATA interface. This included a small L-shaped connector to transfer data and a similar larger connector for power delivery.
Modern SSDs, however, have now moved to the PCIe interface that has a simple connector allowing it to easily slot into the motherboard without the need for any cables. While the early versions of PCIe SSDs launched as add-on cards, almost like a tiny graphics card, the arrival of the M.2 form factor completely changed the game. M.2 today is utilized by both SATA and PCIe SSDs with at least one or two dedicated slots available on most motherboards.
M.2 drives are also much smaller than 2.5-inch SATA SSDs, almost like a strip of gum, having a flat profile that simply sits on top of the motherboard. Since the NVMe interface is highly efficient with PCIe, you are primarily going to find NVMe on SSDs that have the M.2 form factor in modern PCs, especially in laptops.
Performance
There is a huge difference in terms of raw performance when comparing a standard SSD with SATA protocol and an SSD that uses NVMe. Modern SATA SSDs can reach a maximum possible data transfer speed of up to 550MBps. In the real world, not all SSDs can reach these speeds, but there are a few drives on the market that manage to offer speeds that are at least closer to the claims.
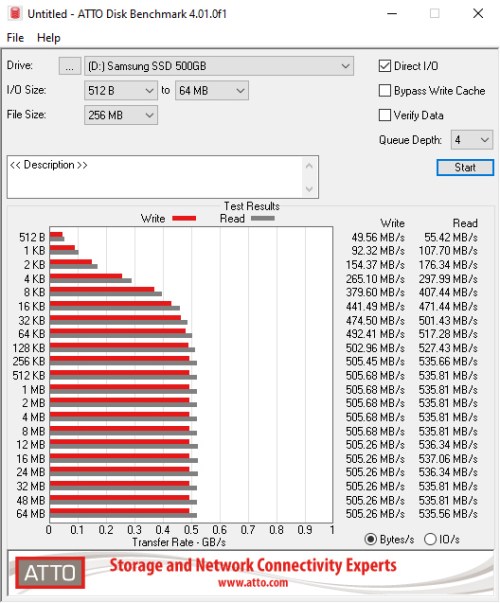
For instance, the Samsung 860 EVO SATA 2.5-inch SSD is rated at 550MBps sequential read speeds and 520MBps sequential write speeds. As you can see from the results below, it manages to reach up to 537MBps read speeds and 505MBps write speeds on ATTO Disk Benchmark, which are pretty solid numbers.
NVMe based M.2 SSDs, however, can go far faster. Different generations of drives, typically twinned with a generation of PCIExpress, have differing speeds, with the latest PCIE 4 drives reaching up to 7,300MBps in sustained read and 5,200MBps in sustained write.
In the real world, you won’t see those kinds of numbers reached unless you are doing very sustained read and write tasks, with more general usage seeing lower numbers. Even then, though, they are far faster than SATA SSDs, and when they can be taken advantage of, that can result in a much snappier experience. Unfortunately, many applications, including games, can’t really make the most of these drives just yet, so you’d only see some games load a few seconds quicker, and Windows doesn’t boot much faster on an NVMe drive than it does on a traditional SATA SSD.

Sabrent’s Rocket 4 Plus series comes with a fairly big heatsink for efficient performance. The potential is there, though, and in the future, as game and application developers begin to better utilize the technology, we should see NVMe SSDs dramatically improve performance in certain settings.
One downside of all that speed, though, is that NVMe SSDs tend to draw a lot of power and can hit high temperatures under heavy loads. In rare cases, these drives can overheat, leading to a drop in performance. To deal with the heat, certain manufacturers have now started shipping NVMe drives with their own dedicated heatsinks — that’s considered mandatory for adding a secondary SSD in the PlayStation 5.
Cost
Considering the fact that they are smaller and faster, NVMe based SSDs launched at a more expensive price tag compared to 2.5-inch SSDs with SATA interface. However, things have changed today as the price is almost the same, and in some cases, NVMe drives are marginally cheaper. For instance, Samsung’s 980 M.2 NVMe SSD starts at $50 for the 250GB size variant, while the 870 EVO 2.5-inch SATA SSD and even the 860 EVO M.2 SATA SSD are both selling for about $60.
To sum it up, NVMe is the future of speedy storage. If you are planning to upgrade your storage, it is highly recommended that you go for an NVMe SSD, with only the largest of capacities of SATA SSD being really worth it on a cost per gigabyte basis.



