We’re used to thinking of Jupiter as an orangey-brown sort of color, with its distinctive colored features like the Great Red Spot. But a recent image of Jupiter shared by NASA shows the planet in quite a different color palette, showing the planet’s clouds in two different formats. Firstly, there’s the planet as the human eye would see it, in Earthy, browny beige shades tinged with green. And secondly, there’s a saturated version that shows off the details of the cloud formations in vivid teals and greens.
The images were made from data taken by NASA’s Juno spacecraft, and they were processed by citizen scientist Björn Jónsson, an amateur image processor who shares his work with the public.
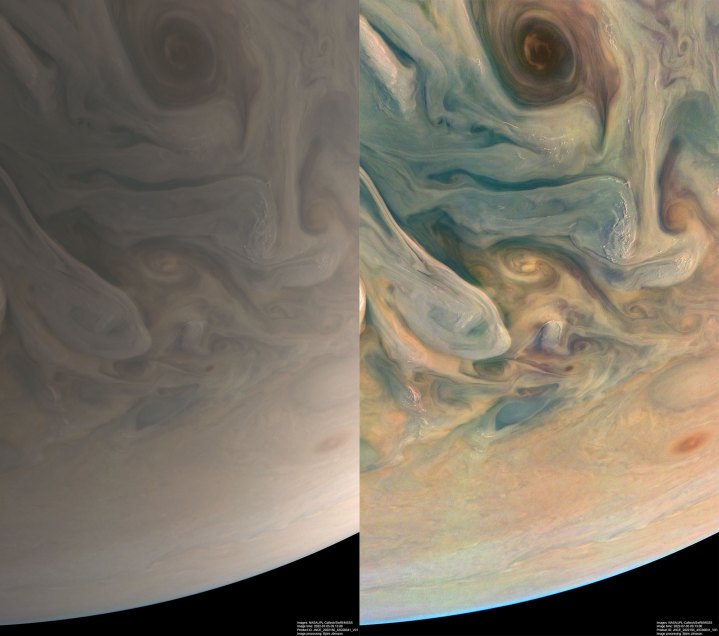
Turning observations from spacecraft or telescopes into an image is a detailed process requiring many particular decisions about color, contrast, and balance, which affect how the final image turns out and which features it emphasizes. It is possible to process an image to make it as close to what we would observe personally if we were to travel to the object, like the image of Jupiter on the left. But it’s also useful to make adjustments like turning up the saturation and contrast to help see features like cloud shapes in sharper detail, as you can see in the image of Jupiter on the right.
In the more saturated image, you can see features of Jupiter’s atmosphere like its deep swirling vortices, and the different colors can help to pick out different chemicals making up the atmosphere.
The reason Jónsson was able to process these images is that all Juno data is made publicly available in its raw form on the mission’s website, and members of the public are encouraged to try their hands at processing the data for themselves. While you’re there, you can also see more of Jónsson’s stunning images, plus many other images processed by other citizen scientists.



