NASA’s Juno spacecraft recently made a close flyby of the solar system’s most volcanic body, the Jovian moon of Io. During the flyby, the spacecraft came within 1,000 miles of Io, which is the closest any craft has come to the moon within the last 20 years.
During its flyby, the spacecraft snapped images using its JunoCam instrument, and some of those images are now publicly available.
The JunoCam instrument aboard our #JunoMission acquired six images of Jupiter's moon Io during its close encounter today. This black-and-white view was taken at an altitude of about 1,500 miles (2,500 kilometers). More images will be available soon at https://t.co/mGfITRe57Y pic.twitter.com/9GcamrhxPt
— NASA Solar System (@NASASolarSystem) December 31, 2023
Data from JunoCam is all shared on the Juno website, as part of a program encouraging the public to try their hand at image processing. One of the most prolific image processors is Kevin M. Gill, who works for NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory and processed the image of Io below. This was taken on December 30 as Juno made its close approach:
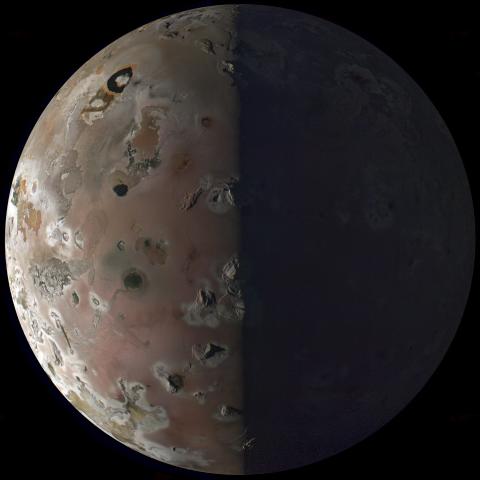

This is a follow-up of sorts to previous images of Io that Juno has taken during aerlier approaches to the moon. These previous images were taken from distances of down to 7,000 miles, such as this image from a flyby in October of last year:
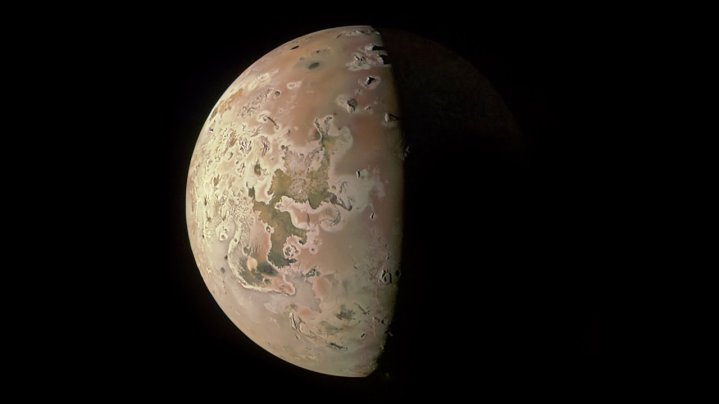
Juno will be making another flyby to Io in February of this year, allowing researchers to get another close look at the moon. That’s exciting because scientists know that there are over 400 volcanoes on Io, and looking at it twice within a relatively short time period allows them to see whether surface changes are visible because of all this volcanic activity.
The Juno spacecraft was originally designed to primarily study Jupiter, but it is now on its extended mission and is making seven additional flybys of Io to gather more data about this relatively little-studied body. Once the spacecraft has made its Io flybys, it will be in a different orbit relative to Jupiter and will have to deal with short periods when the planet is blocking the sun, meaning it will not receive power from its solar panels. But NASA says that the five minute periods of darkness will be short enough that they won’t affect the spacecraft’s overall operation.



