It’s not easy powering a robot on Mars. NASA rovers like Curiosity and Perseverance use a nuclear power system, but other explorers like the InSight lander rely on solar power. The good news is that the sun provides a constant source of energy. The bad news is that Mars is a very dusty place, and dust eventually covers solar panels and stops them from working. That’s what happened to the now-defunct Opportunity rover, which ran out of power when a dust storm rolled in and prevented it from charging via its solar panels.
So the InSight team has come up with a counterintuitive approach to fixing this problem, which they recently tried out: They got the lander to dump more dirt onto itself.
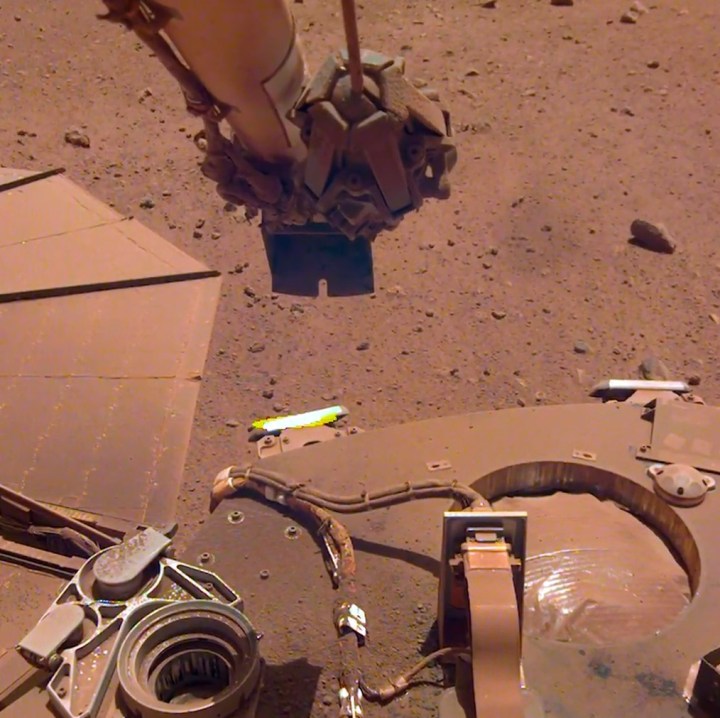
The team has been considering how to approach the power issue for a year and has tried other approaches like using motors to shake the dust loose — but without success. So they decided to try something wild: They used lander’s robotic arm to scoop up some sand and trickle it next to a solar panel. The wind picked up the sand and blew it across the panel, which carried some of the dust away as it went.
This surprising approach resulted in an improvement of 30 watt-hours of energy per martian day.
“We weren’t sure this would work, but we’re delighted that it did,” Matt Golombek, a member of the InSight science team at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, said in a statement.
The power issue is becoming pressing because Mars will soon approach its aphelion, or the point at which it is furthest from the sun. That means there is less solar energy available, and although the lander has turned off many of its science instruments to minimize power usage during the cold season, it still needs enough power to keep its heaters and computer running.
InSight recently had its mission extended by two years, but we’ll have to wait and see whether the dust management approach yielded enough power for the lander to keep running. “While it’s no guarantee that the spacecraft has all the power it needs, the recent cleaning will add some helpful margin to InSight’s power reserves,” NASA wrote.



