A new image of the moon’s far side shows the region selected for the landing of NASA’s Artemis III mission, which aims to return humans to the lunar surface for the first time in over 50 years. The mission will be to the moon’s south pole, a region of particular scientific interest because it is thought to host water ice in permanently shadowed craters.
NASA has partnered with National Geographic to release a mosaic image of the Shackleton Crater, located at the moon’s south pole. The image of the crater was captured using NASA’s ShadowCam instrument on the Korea Pathfinder Lunar Orbiter spacecraft, with additional images of the surrounding area coming from the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter. It’s one of the permanently shadowed craters in the region, meaning it could potentially hold water ice. The crater is also close to several of the potential landing sites.
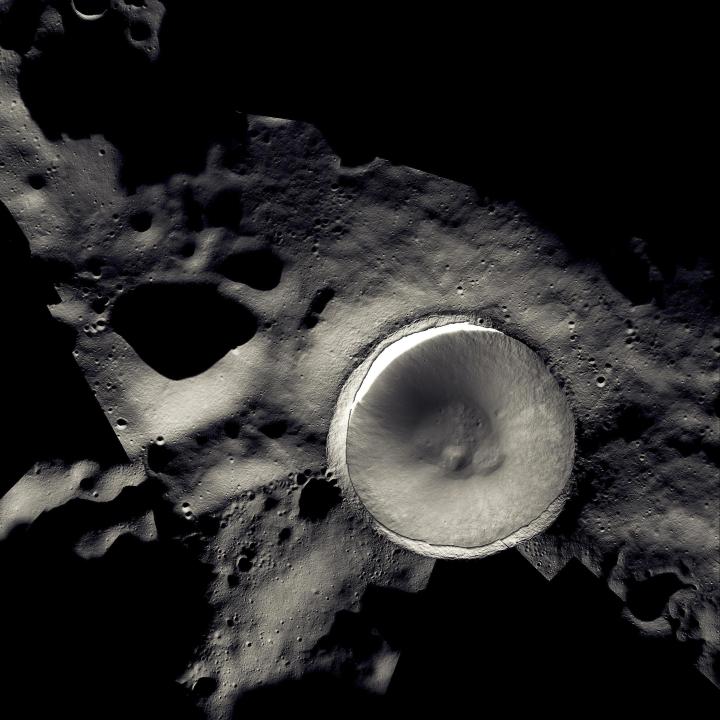
Water ice is rare on the moon as it most often evaporates when the surface it is on faces the sun. However, there are some impact craters around the south pole that the sun’s rays never reach, making them permanently shadowed. It is thought that water ice could persist in these craters, which gives the opportunity for both scientific research and practical resource gathering for crewed missions.
“If there is water ice there, then that water ice can be recovered and it can be used for astronaut consumables, it can be used to shield astronauts from harmful space radiation, and the water can be used for rocket propellant,” David Kring, a planetary scientist at the Lunar and Planetary Institute, told National Geographic.
Last year, NASA shared the 13 candidate locations for the Artemis III landing, all of which are close to the lunar south pole and shown below:

Ahead of Artemis III, which is scheduled for 2025, NASA plans to first send a crewed mission around the moon called Artemis II and a lunar rover called VIPER that will search for ice deposits. Both of those missions are set for launch next year.
Editors' Recommendations
- China confirms target date for landing taikonauts on the moon
- NASA astronauts will try to grow plants on the moon
- Meet NASA’s trio of mini moon rovers set to launch next year
- See images of the tilted Odysseus lander on the moon
- NASA astronauts need good weather for Crew-8 launch. Here’s how it’s looking





