NASA’s Juno spacecraft is famous for the beautiful images of Jupiter it regularly captures using its JunoCam instrument, and its research into Jupiter’s strange atmosphere. But recently the spacecraft has also been investigating Jupiter’s moon, like the icy Europa or the largest moon in our solar system, Ganymede.
Now, Juno will begin an investigation of the intriguing volcanic moon Io. The spacecraft is set to perform a series of nine flybys of Io beginning on December 15, coming within 930 miles of the moon’s surface.
This series of flybys is part of Juno’s extended mission to study Jupiter’s moons. “The team is really excited to have Juno’s extended mission include the study of Jupiter’s moons. With each close flyby, we have been able to obtain a wealth of new information,” said Juno Principal Investigator Scott Bolton of the Southwest Research Institute, in a statement. “Juno sensors are designed to study Jupiter, but we’ve been thrilled at how well they can perform double duty by observing Jupiter’s moons.”
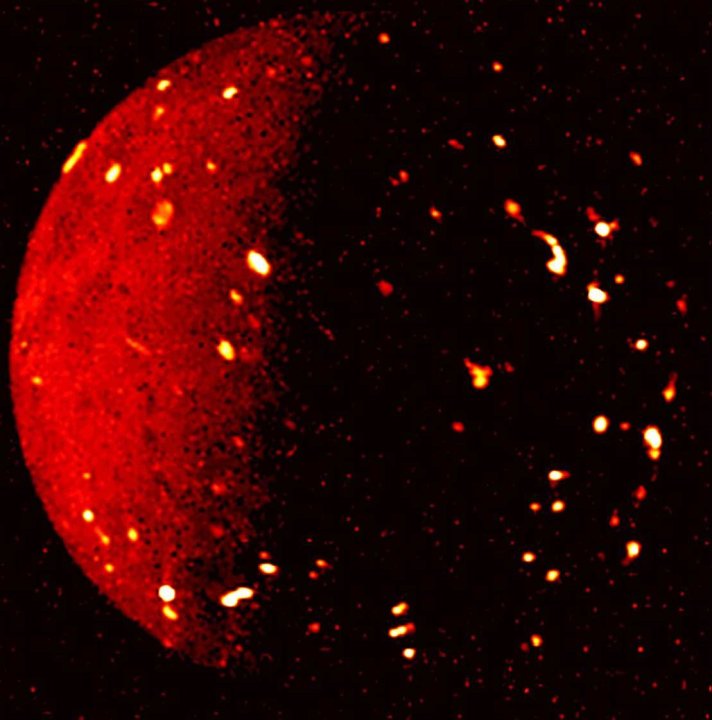
Io is of particular interest because it is the most volcanic place in the solar system, and it also has the highest density and strongest surface gravity of any moon. Previous research has shown it has over 400 active volcanoes, which are powered by tidal forces from Jupiter and its other moons creating friction that heats its interior. Previous observations from Juno captured the infrared image above, showing hot spots across the moon’s surface.
Juno will study the way that Io’s volcanic activity interacts with Jupiter’s magnetosphere, as the planet has a powerful magnetic field surrounding it that interacts with its moons. Juno’s observations of the moons are also paving the way for future missions to study these objects in more depth, like the European Space Agency’s JUpiter ICy moon Explorer or JUICE, and NASA’s Europa Clipper mission to Europa.



