To make the game more immersive, we’d need some way for the pocket monsters to interact with the environment they’re in, and have it react back. How would that be possible? A research team at MIT believes it’s found a way — through the use of micro-vibrations.
“Essentially, we’re looking at different frequencies of vibration, which represent a different way that an object can move. By identifying those shapes and frequencies, we can predict how an object will react in new situations,” Abe Davis, the lead researcher on the project, told Digital Trends. Along with fellow researchers Justin Chen and Fredo Durand, they’ve built upon previous research they conducted on the concept of visual microphones, to draw even more data from standard video.
“This might be something that’s more suitable for Pokémon Go 4 or 5, than Pokémon Go 2.”
“One way to think about it, is if I point my camera at a bush and I watch the wind rustle that bush for a whole minute, I’m watching a bunch of tiny movements of the bush, which are responses to various forces,” Davis explained.
Those movements are categorized as vibrations operating at various frequencies. Then, software can take the video and analyze those vibrations. It can figure out the types of forces at play to create those movements, and then guess at how larger forces, or different combinations of those same forces, may make the object react.
By recording the bush’s reaction to the wind, the software can eventually figure out how it might react to a brick — or Pikachu.
Bringing pocket monsters to life
Extrapolating more than just visual data from video became a focus of Davis’ interest throughout his time at MIT, and it was ultimately the core of his dissertation. However, explaining just how visual data from a video can be used beyond the norm isn’t easy. When Pokémon Go was released, he saw a great way to break it down.
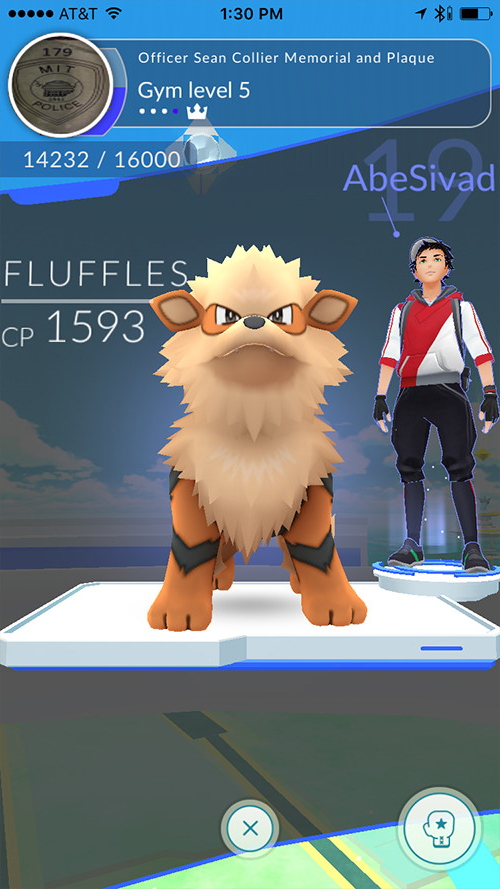
Davis is a Pokémon Go player, having reached level 19 at the time we conducted our interview. We were even introduced to his most powerful Pokémon — Fluffles, a CP 1,592 Arcanine, who’s been tearing up the gyms in his local area. Fluffles was caught at the SIGGRAPH conference where Davis and his fellow researchers first showed off vibration model technology.
To use Pokémon as a showcase, Davis set up his phone on a tripod pointing in a specific direction. He then proceeded to catch a Pokémon, and then captured footage from that exact same position.
“I caught it and recorded about a minute of video, using the tripod for stability. I took that video back and processed it using the code I had written,” and the result was the video you see above.
A bush from the real world, which reacts (somewhat realistically) with a digital creation, is much closer to the sort of augmented reality future we’ve all been promised. Indeed, it even goes further than some of the things we’ve seen with Microsoft’s Hololens and the Magic Leap. Because of that, we shouldn’t expect this sort of technology to appear in the next Pokémon Go patch, or even its sequel.
“This might be something that’s more suitable for Pokémon Go 4 or 5, than Pokémon Go 2,” Davis cautioned.
That said, Davis and his fellow researchers had been working on this well before Pokémon Go was released, and there are many other potential applications for this technology beyond catching pocket monsters.
Shaking seconds off rendering CGI
What if, instead of rendering are entire explosion of an object or building, film makers could simply record video of an object and utilize this sort of algorithm to create a barebones animation? This has the potential to save huge chunks of time.
Of course, the artificially created movement that Davis has shown doesn’t look quite as good as the latest CGI blockbuster, but that’s not due to the weakness of the technique. Davis simply isn’t an artist. He has no idea how to polish his algorithm’s results.
“If you gave this tool to the world’s best artists, I suspect you could make it look really good.”
“The most expensive CGI is the most expensive CGI, because you pay the most expensive artists to do the most expensive art,” Davis said, jokingly. “If you gave this tool to the world’s best artists, I suspect you could make it look really good.”
“It’s about giving artists the best starting point. That’s how a lot of technology and special effects are used. If you want to make something look really good, you don’t want a canned solution. You want your artists to dictate every aspect of the look and feel of the final product.”
Another exciting use for the technology may be found in architecture, as well as insurance, where the tech could be used for structural health monitoring. Vibration modes and frequencies are already used in that profession, but they utilize much more complicated capture techniques to acquire the data.
“Typically that data is captured through lasers and accelerometers that have to placed on the object. The big advantage [with my technique], is that it’s very easy to point a camera at a building, but it’s pretty hard to paint a whole building with accelerometers or laser points,” said Davis. “This offers a convenient way to capture slightly lower quality data, which is great to figure out where you need to focus your attention.”

If a company can test a building’s structural integrity by just recording some video of it and throwing an algorithm at it, it’d be possible for an intern with a camera to do work that’d previously demand a team of engineers.
Frame rates, resolution and magnification
Obviously, a commercial camera is much cheaper, easier to acquire and easier to operate than the technology this technique could help supplant. But there are certain hardware requirements that have a big effect on how well the algorithm works.
As with most video, a tripod is essential. While it wouldn’t be too difficult to separate out vibrations that effect the entire video, versus those that effect subjects within it, that’s a step that can be practically eliminated by using a sturdy vantage point for the camera to rest.
The type of camera, and its quality, can be important, too.
“The frame rate of the camera can actually determine what frequencies you can recover,” Davis said. “If you’re doing special effects, the frequencies you want to simulate are the frequencies that you can see, so frame rate isn’t so important. However, if you wanted to simulate a detailed solid object, then having higher frequencies which are captured at a higher frame rate is going to help.”
In one instance, Davis and his team wanted to track the vibrations from a Ukelele. But because of the way the strings on such an instrument vibrate, it was very important to use a high-frame-rate camera.
Conclusion
With all of the potential uses of the video vibration analysis work that Davis and his peers have been conducting, where does the technology go from here?
Although Davis plans to continue working on it in the future, he doesn’t have any immediate plans to leverage it for financial gain. There will be no micro-vibrations-from-video start up that Google or some other mega-corporation buys out in the near future. Part of that is because MIT owns the patent, having defensively applied for it.
However, you have to imagine that the likes of Microsoft and Magic Leap will be keeping an eye on this sort of technology, as it could be great for augmented reality.
Davis himself has now finished his dissertation, a comprehensive paper on all of his MIT conducted research, and will be graduating this September, before moving on to Stanford University for his post-doctorate.
For more information on any of Davis’ research, you can find all of his papers and studies on his official site. He also covered several aspects discussed here in his Ted Talk.