 College students have long complained that text books cost too much. But woe is the poor sap who has to pick up a copy of genetics textbook, The Making of a Fly, by Peter Lawrence, which was recently listed at the ridiculous price of $23,698,655.93 on Amazon.com.
College students have long complained that text books cost too much. But woe is the poor sap who has to pick up a copy of genetics textbook, The Making of a Fly, by Peter Lawrence, which was recently listed at the ridiculous price of $23,698,655.93 on Amazon.com.
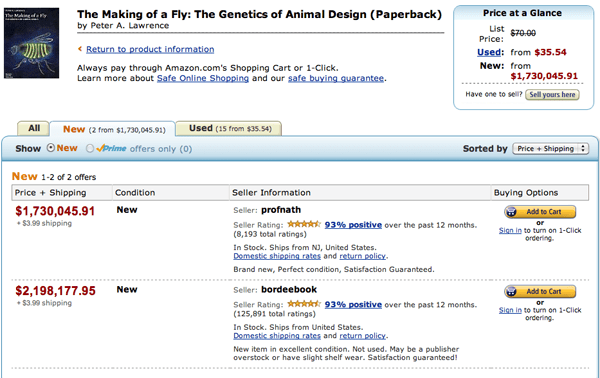
The absurd price of this out-of-print book, first published in 1992, was discovered by UC Berkley evolutionary biologist Michael Eisen, who went to Amazon to purchase the book. There, he found “17 copies for sale: 15 used from $35.54, and 2 new from $1,730,045.91 (+$3.99 shipping).”
“At first I thought it was a joke –- a graduate student with too much time on their hands,” writes Eisen on his blog. “But there were TWO new copies for sale, each be offered for well over a million dollars. And the two sellers seemed not only legit, but fairly big time (over 8,000 and 125,000 ratings in the last year respectively). The prices looked random –- suggesting they were set by a computer. But how did they get so out of whack?”
To Eisen’s surprise, the price of the new copies actually rose the next day to nearly $28 million apiece. Adding to the peculiarity of the situation was that the difference between the price of the two new copies closed from $400,000 to about $5,000. “Now I was intrigued, and I started to follow the page incessantly,” writes Eisen. “By the end of the day the higher priced copy had gone up again. This time to $3,536,675.57. And now a pattern was emerging.”
What Eisen discovered is that Amazon sellers are using algorithms to set the price of the products they sell. Each day, one seller, profnath, would adjust its price of The Making of the Fly to be 0.9983 times the price of the other seller, bordeebooks. In response, bordeebooks would inflate its price by 1.270589 times profnath’s price. Eventually, the two sellers’ pricing algorithms elevated the cost of the textbook to hilarious levels.
“Both profnath and bordeebook were clearly using automatic pricing – employing algorithms that didn’t have a built-in sanity check on the prices they produced,” writes Eisen. “But the two retailers were clearly employing different strategies.”
Indeed. While profnath’s strategy seemed perfectly reasonable — set the price of its book just slightly lower than that of a competitor — bordeebook automatically made sure its listing was more expensive than any other seller. Not exactly the best strategy for drawing in customers. So why would bordeebook, a seller with highly positive reviews, employ such a strange tactic?
“My preferred explanation for bordeebook’s pricing is that they do not actually possess the book,” writes Eisen. “Rather, they noticed that someone else listed a copy for sale, and so they put it up as well –- relying on their better feedback record to attract buyers. But, of course, if someone actually orders the book, they have to get it – so they have to set their price significantly higher – say 1.27059 times higher – than the price they’d have to pay to get the book elsewhere.”
Ultimately, Eisen brought attention to the staggering pricing mishap, and profnath dropped its price to the far more reasonable $106.23. (Bordeebook’s price was still 1.27059 times higher than profnath’s, at $134.97.) But this curious tale serves as a perfect example of why computers can’t be trusted.


