Researchers may have produced the loudest sound possible to make under water. The 270 decibel sound, created by blasting tiny jets of water with an X-ray laser, had a greater intensity than that of a rocket launch. It was carried out by a team from Stanford University and the Department of Energy’s SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory, using SLAC’s Linac Coherent Light Source (LCLS) X-ray laser.
“This type of sound is generated in many scientific experiments that study chemical and biological samples at X-ray lasers, where the samples are often carried by liquid jets,” Claudiu Stan, one of the project researchers, told Digital Trends. “In principle, the sound wave and the shocks may damage a sample before it arrives in front of the X-ray laser. We found that the shock wave is attenuated very rapidly. However, it may still be detrimental for experiments in which the X-ray pulses have high repetition rates. Our study is useful for understanding which experiments are more likely to be affected.”
The project began with the goal of observing shock waves made by X-ray laser pulses inside liquid microjets. X-ray lasers generate incredibly short pulses with extremely high energy, which can be focused into very small areas. The result is a large amount of energy being deposited in a very small volume of the jet, followed by an explosive release of this energy. The amount of energy in this latest demo was equivalent to directing the electrical power of an entire city into a single square meter.
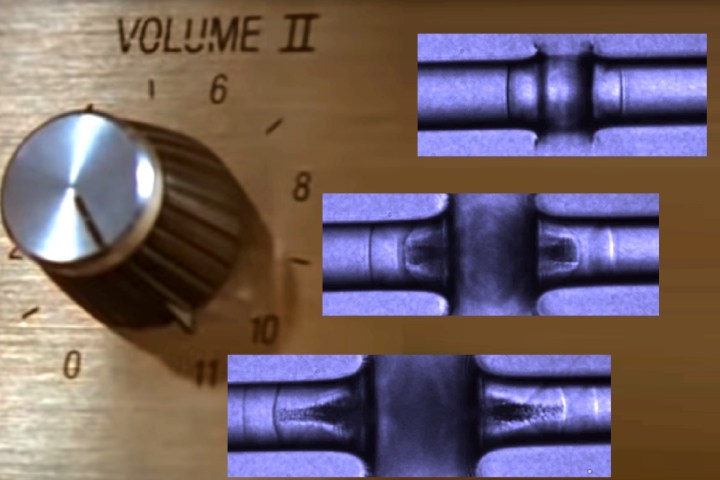
“Part of the released energy takes the form of a shock wave that lasts only a few millionths of a second, but has pressures of many thousands of atmospheres,” Stan said. “These pressure are high enough to make the shock visible. In our experiments, we made movies of this shock at more than a billion frames per second, using a very fast microscope that used femtosecond light flashes.”
The footage showed that, as the shock moved along the jet, it generated bubbles in its wake. Copies of the shock then appeared and traveled along with it. When the shock reached the jet’s surface, it produced a wave reflection which physically stretched the liquid.
“When the first shock copy appeared, we encountered a situation where multiple oscillations from high to low pressure traveled in the jet — in other words, we made a sound wave,” Stan continued. “When the sound wave first appears, we know that it cannot have higher amplitudes and intensities because it would rupture the water, so this is an example of a sound that is as intense at it can possibly be.”
A paper describing the research was published in the journal Physical Review Fluids.


