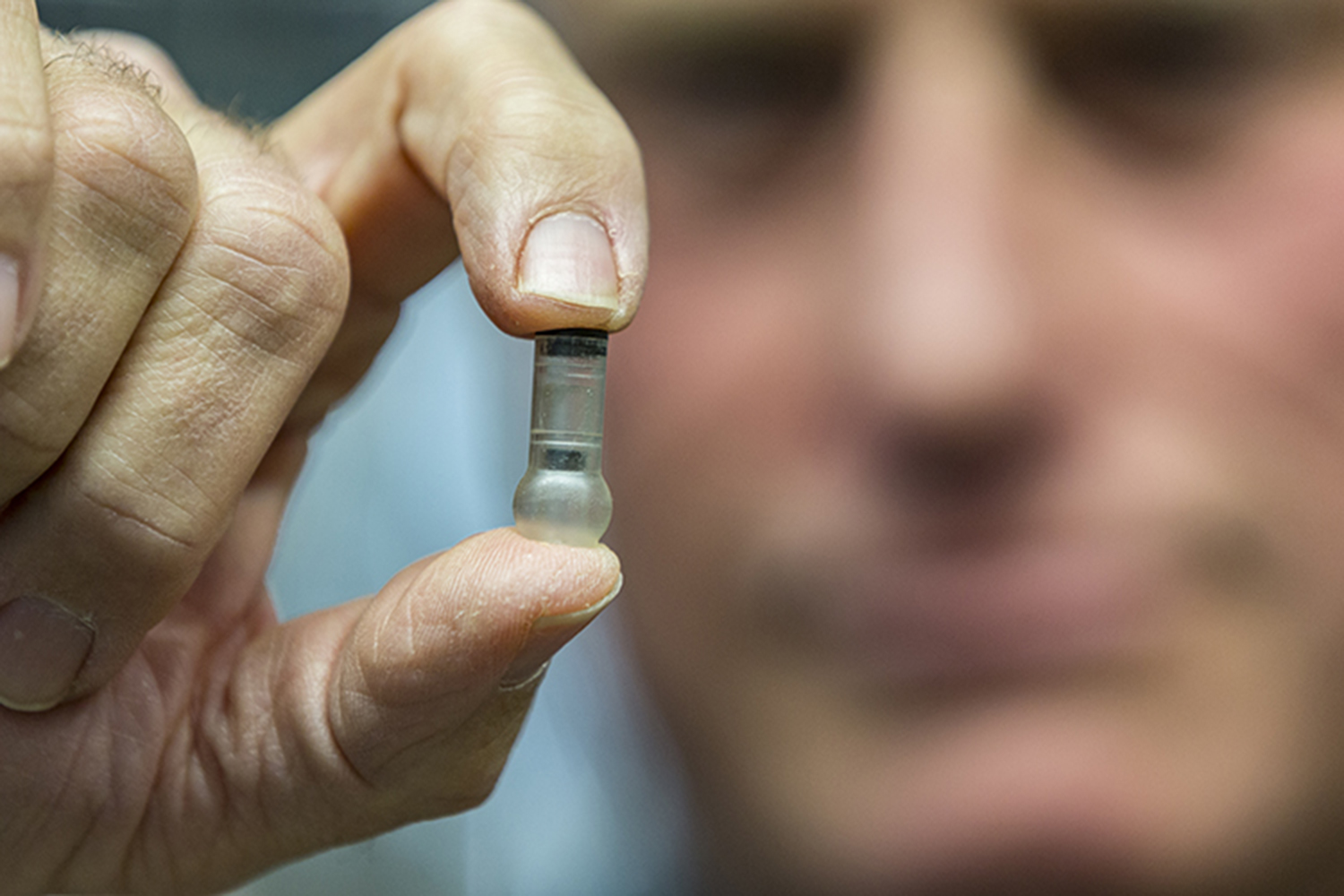
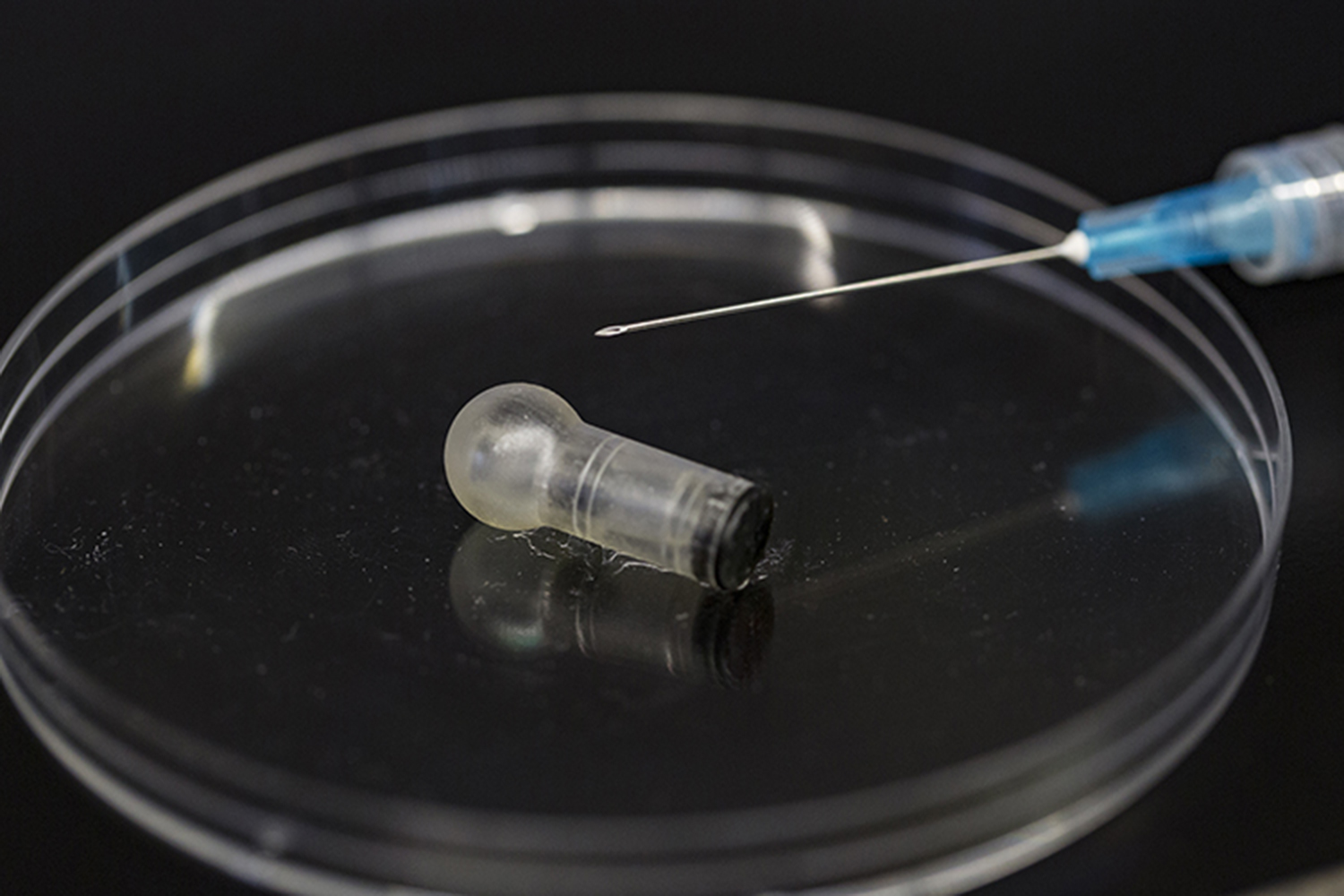
Injections, however, are pretty damn painful, especially for tiny tots who are most at risk of disease. That might change within a decade though thanks to a needle-free device called the MucoJet that make vaccinations practically painless. Developed by researchers in Dorian Liepmann’s lab at the University of California, Berkeley, the pill-sized, 3D-printed device shoots a stream of vaccine into the tissue of the cheek.
To activate the MucoJet, a patient first need to squeeze the device together, creating a reaction and increasing pressure inside. The patient then holds the device on the inside of her cheek for about ten seconds, at which point the pressure breaks a membrane and shoots a concentrated stream of vaccine through a small nozzle.
The MucoJet is needle-free (and thus virtually painless) and may also be able to address viruses more effectively than conventional techniques, according to Kiana Aran, a professor of mechanical and bioengineering who developed the MucoJet while working in Liepmann’s lab.
“The majority of modern vaccines are injected intramuscularly or subcutaneously, although the majority of pathogens actually access the body via the mucosal surfaces,” she told Digital Trends. A few vaccines are administered through the mucosal surfaces — including oral polio and rotavirus vaccine but, Aran said, these have limited safety and utility since they contain live viral components. With MucoJet, the researchers think they may be able to design safer and more effective mucosal vaccines.
So far, the researchers have demonstrated a proof of concept, successfully delivering vaccine-size molecules to cells in the mouths of animals. A paper describing the device was published last week in the journal Science Translational Medicine. Future research will entail testing the MucoJet on larger animals, such as monkeys and pigs. The researchers think the product may come to market in the next five to ten years.