Passwords are, by definition, private, but often it’s a challenge to keep them that way, and a bustling industry has emerged to protect your passwords — and thus your data — from prying eyes. There are times, however, when you do want to share a password with a friend or family member nearby who needs to log into one of your private accounts.
The one thing you should never do is to make your passwords simple and easy to remember — because that’s easy hacker bait. Using unique passwords and switching them out over time is a good way to protect your data. You should never reuse passwords under any circumstances. With that in mind, you should be ready to share complex passwords, whether it’s for your bank account or to your Netflix subscription, in the safest possible way.
Sending a password via email is risky, and many people do not feel comfortable sending sensitive information, even via the encrypted iMessage messaging service. As for leaving a phone message or sharing verbally — those methods have their own potential issues. There’s yet another easy way to share passwords: AirDrop. We’ll show you how it’s done in iOS 13, though you can also accomplish it in iOS 12 and MacOS Mojave or later. Note that iOS does not allow passwords to be saved in a screenshot, so you can’t share them that way.
Before you get started, it’s also a good idea to restrict AirDrop to Contacts Only via Settings > General > AirDrop > Contacts Only.
- On your iOS device, go to Settings > Passwords & Accounts > Website & App Passwords.
- You may be asked to type in your passcode or otherwise verify that it’s you.
- Look for the login or password that you want to share and tap it.
- Once you see the password, tap and hold the username or password and a popover will appear with options to Copy or AirDrop.
- Tap AirDrop and you’ll get the familiar interface, which will let you send it to another nearby device.
- Tap Done.
- When your recipient accepts, the password automatically gets added to their stored passwords, so that the next time they want to log in to that service, it will autofill, so you never have to share it again.
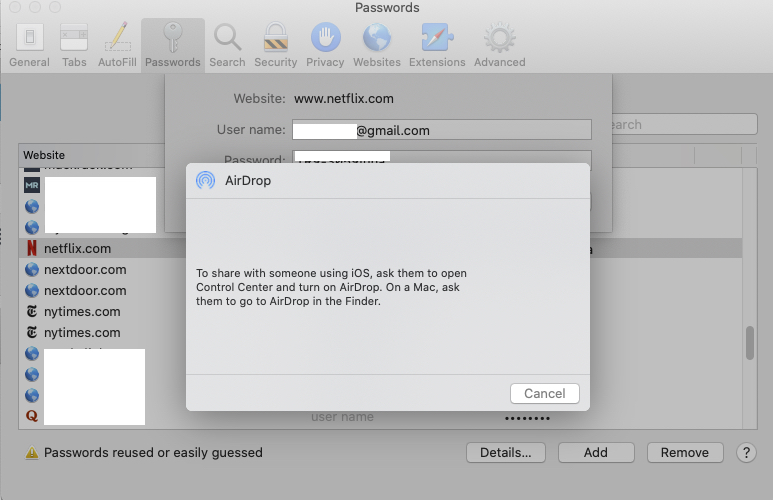
The AirDrop method works with iPhones and iPads, but also with Macs. If you AirDrop a password to a Mac, it will open in Safari and add it to your recipient’s AutoFill passwords.
Go to Safari > Preferences > Passwords and choose the login you need. You will see a Share button that lets you AirDrop the password to the device of your choice. This allows you to make your passwords as complex as they need to be in order to maintain your security, while at the same time sharing them with the other people who might need to access them.
Editors' Recommendations
- A big iPhone update is right around the corner
- Are you having iPhone alarm problems? A fix is coming soon
- An Apple insider just revealed how iOS 18’s AI features will work
- 10 iPhone productivity apps you need to download right now
- The 10 best photo editing apps for Android and iOS in 2024