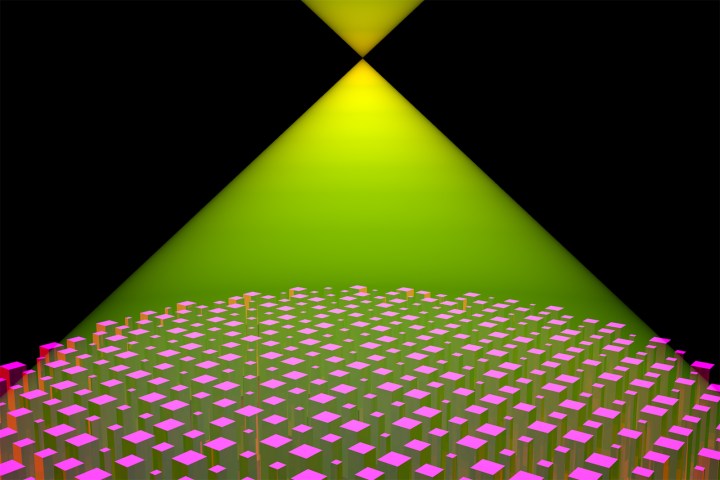
The group from the Harvard John A. Paulson School of Engineering and Applied Sciences created the first planar, or flat, lens last year using a 600-nanometer thick metasurface pattern made from titanium dioxide. The flat lens was revolutionary enough to be named among Science Magazine’s top discoveries of 2016.
The problem? The lens could only focus one wavelength (i.e. one color) at a time. Traditional lenses use multiple glass pieces not just to focus the light, but to make sure each different wavelength or color focuses on the same point. The first flat lens, while exciting in its ability to focus light with a single layer, couldn’t make those wavelengths meet using that single layer. When the wavelengths don’t meet, the image has visible color fringing around objects, known as chromatic aberration.
The same research group, however, has now enhanced the lens to capture several different wavelengths by optimizing the way the tiny pillars that make up the metasurface lens are placed. Adjusting the pattern of the nanopillars allows the new lens to focus wavelengths from 490 to 550 nm without that color distortion.
The lens’ range means it can only capture blues, greens, and everything in between, but the tweaked design is at least the first to capture a continuous range of different wavelengths, instead of a single wavelength at a time.
Like the initial lens, the concept could eventually have a variety of uses. Since the lens uses only a single layer of readily available material, the lens could theoretically be mass produced more affordably than traditional glass optics, not to mention the advantages of its much smaller profile.
“This method for dispersion engineering can be used to design various ultrathin components with a desired performance,” said Zhujun Shi, a co-first author of the paper and a PhD student in the Capasso Lab. “This platform is based on single-step lithography and is compatible with high throughput manufacturing technique[s] such as nano-imprinting.”
The research group is aiming to advance and commercialize the technology with a startup company, working closely with the Harvard Office of Technology Development, and has already filed a portfolio of related patents.
Editors' Recommendations
- Nikon’s new 800mm lens for Z-mount cameras lightens the load
- Nikon apparently can’t make enough of its $8,000 58mm f/0.95 lens



