The moon was long thought to be geologically dead, with no processes occurring inside its core. But increasing evidence over the last decades suggests that the moon isn’t static and could, in fact, still be tectonically active. Now, new research from NASA suggests that the shrinking of the moon over time is causing moonquakes and the formation of faults near its south pole.
The research is part of NASA’s interest in the lunar south pole, given the agency’s intention to send astronauts there. Researchers have modeled lunar activity to look for the source of moonquakes seen during the Apollo missions.
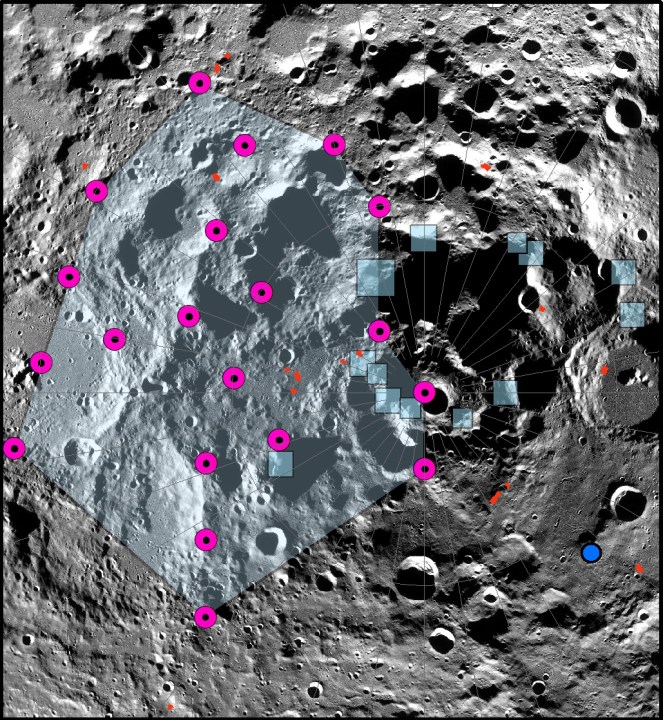
“Our modeling suggests that shallow moonquakes capable of producing strong ground shaking in the south polar region are possible from slip events on existing faults or the formation of new thrust faults,” said lead researcher Tom Watters of the Smithsonian Institution in a statement. “The global distribution of young thrust faults, their potential to be active, and the potential to form new thrust faults from ongoing global contraction should be considered when planning the location and stability of permanent outposts on the Moon.”
Evidence of this movement also comes from the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO), an orbiting spacecraft that takes images of the moon’s surface using its camera. These images show small, young faults that form cliff-like structures.
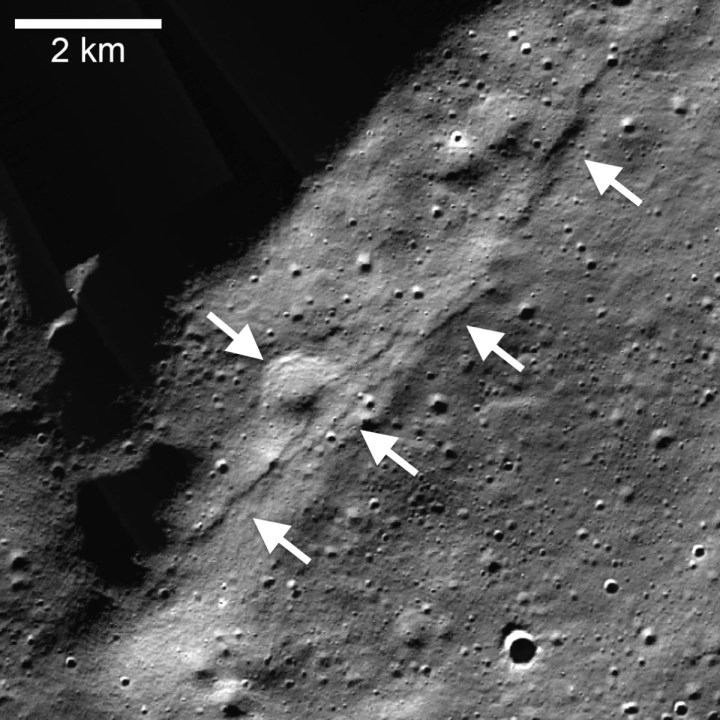

The faults are forming due to activity beneath the surface as the moon’s interior cools, causing it to shrink overall. The gravity of Earth also contributes by creating tidal forces that affect the moon’s interior.
This could create activity like landslides on the lunar surface, which could cause problems for future astronauts. Experts say that they need to perform more research into this activity on the moon to choose the best location for landing any future crewed missions there.
“To better understand the seismic hazard posed to future human activities on the Moon, we need new seismic data, not just at the South Pole, but globally,” said another researcher, Renee Weber of NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center. “Missions like the upcoming Farside Seismic Suite will expand upon measurements made during Apollo and add to our knowledge of global seismicity.”
The research is published in The Planetary Science Journal.



