Scientists at NASA just confirmed it.
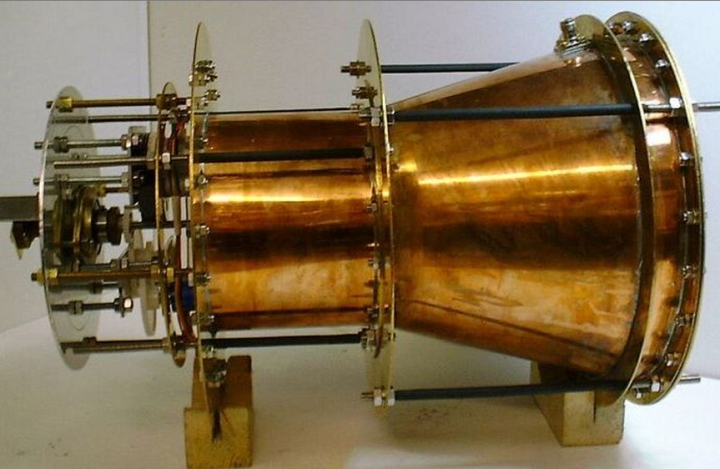
Shawyer’s engine provides thrust by “bouncing microwaves around in a closed chamber.” That’s it. There’s no need for a propellant of any kind like rocket fuel. When filled with resonating microwaves, the conical chamber of the thruster experiences a net thrust toward the wide end. These microwaves can be generated using electricity, which can be provided by solar energy. In theory, this means that the thruster can work forever, or at least until its hardware fails.
Initially, the idea was met with criticism because it flies in the face of Newtonian physics, which dictate that no closed system can have this kind of net thrust. Shawyer, however, says that net thrust occurs because the microwaves have a group velocity that’s greater in one direction when Einstein’s relativity comes into play. But can it really?
Apparently, yes. The idea was first confirmed by a group of Chinese scientists back in 2009. They built their own version of Shawyer’s thruster and were able to produce 720 milinewtons of force — but even then, nobody really believed it.
Related: NASA offering $35,000 to ‘”citizen scientist” asteroid hunters
Now, American scientists at NASA have given the EmDrive a go, and once again confirmed that it actually works. The test results were presented on July 30 at the 50th Joint Propulsion Conference in Cleveland, Ohio, and astonishingly enough, they are positive. The team behind the drive still doesn’t know why it works, just that it does.
“Test results indicate that the RF resonant cavity thruster design, which is unique as an electric propulsion device, is producing a force that is not attributable to any classical electromagnetic phenomenon and therefore is potentially demonstrating an interaction with the quantum vacuum virtual plasma,” the report reads.
Therefore, we’ve still got a long road ahead of us before we’ve got energy-harvesting, self-propelled intergalactic spacecraft, but these studies (assuming they’re not flawed) suggest we’ve made a major breakthrough in space propulsion systems. With further refinement, microwave thrusters could drastically cut the cost of satellites and space stations, and potentially even make it possible to travel to distant planets, like Mars, in weeks rather than months or years.
Editors' Recommendations
- Junk from the ISS fell on a house in the U.S., NASA confirms
- NASA astronauts will try to grow plants on the moon
- NASA’s Crew-7 astronauts splash down safely off the coast of Florida
- NASA, Boeing delay Starliner’s first crewed flight again
- How to watch SpaceX Crew-7 return to Earth this week



