If you’re one of many people who use Chrome as your default web browser, then you might want to take some steps to ensure that it’s extra secure. This can help you in a world where hackers are always after passwords and can easily spoof websites to look like the real thing.
Well, Google has a lot of tools built right into Chrome that can help with that protection. From Safe Browsing to encrypting passwords and more, we got you covered with five easy ways to dramatically increase security in Google Chrome.
Change your Safe Browsing settings
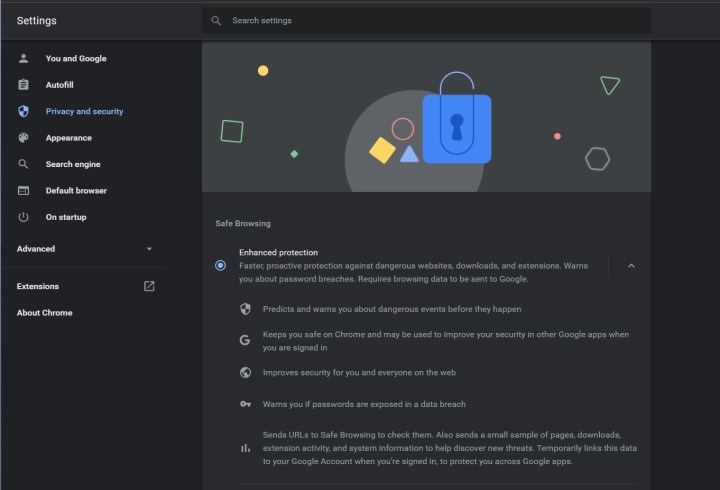
Our first tip is one that’s enabled by default but can be tweaked for enhanced security. Click the Three Dots at the top right of your screen, choose Settings, and then head to Privacy and Security followed by Security. There will be a section for Safe Browsing.
Under this section, you’ll want to choose the Enhanced Protection option. You probably have Standard Protection on as default, but switching it over to enhanced can give you better protection against dangerous websites, downloads, and extensions. Chrome will even warn you about password breaches. Just keep in mind that Chrome might send your URLs to Safe Browsing to check it across threats. The data will be temporarily linked to your Google Account.
Encrypt your passwords stored in your Google Account

Next up is another simple tip in regard to encryption. Once you visit Chrome’s Settings menu, click the You and Google option at the top of the screen. You’ll need to be logged into a Google Account for this.
Under Sync, choose Encryption Options. Look for the option that says Encrypt Synced Passwords With Your Google Account. This option will save your passwords in Google’s servers, behind their own encryption methods. That makes it harder for a hacker to access your passwords as they will be encrypted in transit, but there is a small chance that Google might also be able to read them.
However, you can also choose the second option to improve the security a bit more. With the sync passphrase, you can use the encryption without having Google read the passwords, as only you have the unlock key to view the passwords. This means it’s encrypted at two ends, both at your end and at the other end.
This second route, though, complicates sync a bit. You’ll need your passphrase whenever you turn on sync somewhere new, and you’ll have to enter it on your devices where you have sync turned on. Your feed also won’t show suggestions based on sites you visit in Chrome, and you can’t view your password online or use Smart Lock for Passwords. History won’t sync, either.
Turn off FLoC

You probably heard about FLoC. This controversial Chrome feature essentially goes through your browsing history to see which large group of people, or “cohort,” your recent browsing activity is most similar to. It’s meant for advertisers to select ads for the group as an alternative to Cookies, but some worry that it can be used to gather more data about you or turn Google into more of a monopoly with control over how advertisers can target users.
Facing pushback around FLoC, Google enabled a new Privacy Sandbox that you can visit to disable the feature. Simply visit Chrome’s Settings, go to Privacy and Security, and click the link to Privacy Sandbox. From there, you can flip a switch to disable Sandbox trials, as well as FLoC.
Always use HTTPS

Fourth on our list is a simple trick to ensure you’re only going to safe websites. Many websites used to depend on the Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP.) This sounds cool, but HTTP can leave your browser’s open request to view a website in plain text. As a result, any hacker who can monitor the connection can read the request. This is risky in cases where you enter a password or a credit card number. Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS) fixes that by encrypting HTTP requests and responses as random characters, making it harder to monitor.
In Google Chrome, you should make sure that the browser is set to always use HTTPS. If you visit an HTTP website, you’ll get warned that it’s not secure. To do this, click the Privacy and Security section in Settings, and look for the Always Use Secure Connection option.
Watch your extensions

Extensions are a great addition to Chrome, as they can help correct your spelling and grammar, block ads, and more. Not all extensions are good, though. If you’re not careful, extensions can end up hijacking your browser or your private information and even spy on you. It’s always a good practice to ensure any extensions you add are coming from trusted sources only.
To manage extensions in Chrome visit chrome://extensions/ in the address bar. From here, you can click the Details button to see the details and permissions of each extension and go back to the listing in the Chrome Web Store. You can even remove untrusted extensions.
Editors' Recommendations
- The best web browsers for 2024
- Google may build Gemini AI directly into Chrome
- Google just settled a $5B privacy suit involving Chrome browser
- Google has a great idea to fix your tab chaos in Chrome
- I found a Chrome extension that makes web browsing bearable again


