In a twist of irony, it was revealed last month that anti-virus software maker Avast is harvesting its users’ browsing history and selling the data through its Jumpsuit subsidiary.
Though Jumpsuit isn’t a household name, it’s been reported that the Avast subsidiary counts brands like Google, Intuit, Home Depot, Microsoft, and Expedia as clients, potentially amassing millions of dollars for packaging your private browsing data, ranging from Google Maps location searches to browsing history, for marketing purposes. If you’re a fan of the company’s premium or free anti-virus product, we’ll show you how to limit data sharing to maintain your privacy.
How to stop data sharing in Avast

If checked the wrong box during the installation guide or later change your mind, you can make changes within the software’s settings menu. Here’s how to do it on a PC:
Step 1: Open the Avast anti-virus software from the Windows Start menu.
Step 2: Click on the Menu button on the upper right-hand side.
Step 3: Select Settings. Under the General tab, choose “Personal Privacy.”
Step 4: If you don’t want Avast to share your browsing data with Jumpshot or marketing companies, be sure to uncheck the box that reads “Allow usage data to be shared with 3rd parties for analysis of trends, business, and marketing.” For the privacy-conscious user, you may want to uncheck the other two options as well.
“We understand you may not want your data to be used for trend analytics, and if that is your preference, we respect your choice,” Avast stated in its consent policy. “If you would like to withdraw your consent, you may choose to opt-out in your product settings at any time.”
While this should put the data sharing to a stop, it’s unclear at this time if it’s possible to delete data that has already been collected under the terms of use prior to opting out. Avast’s website offers the opportunity for users to delete their own account, though it’s unclear if account deletion will also retroactively delete all collected data, including browsing history and any location searches.
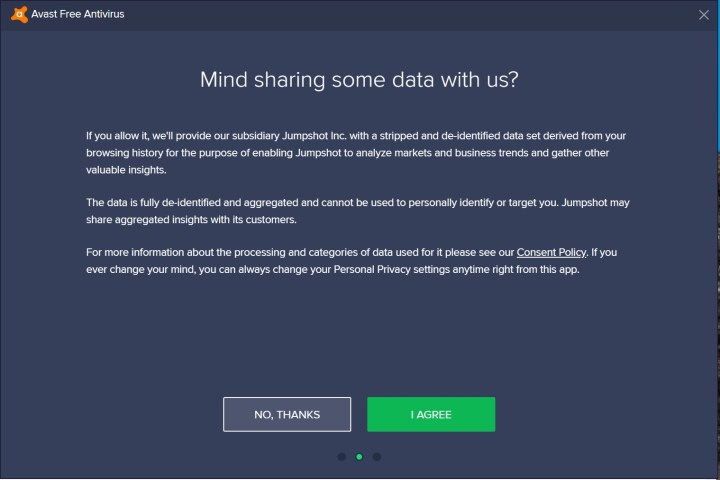
It’s also important to note that Avast’s free anti-virus product does not require you to create an account, so data can still be collected in the background.
If you’re new to Avast’s anti-virus software, you’ll want to limit data sharing from the get-go. The installation guide will offer you options to opt into or out of data sharing in order for Jumpshot “to analyze market and business trends and gather other valuable insights.” During this section of the installation wizard, be sure to click on the “No, thanks” to sharing.
The cost of free
Since Motherboard and PCMag had unveiled the results of their investigation into Avast’s data collection practice, the company justified its actions stating that all the data that was collected has been “fully de-identified and aggregated” so that it “cannot be used to personally identify or target you.” However, security experts remain skeptical. The investigation revealed that Avast had collected information such as timestamp , persistent device IDs, and collected URLs.
“For both paid and free versions, we continuously monitor for, minimize, disconnect and remove all direct identifiers during the normal performance of the products and services,” the company states in its privacy policy.
Avast claims that the data harvesting is a necessary part of its business in order to be able to offer its products to users for free. While the anonymous data may not reveal much data about any individual, marketers can combine that data with other information they have on users to gain more insight.
We’ve reached out to Avast for comment, but did not receive a response in time for publication.
Editors' Recommendations
- It’s time to stop trusting your antivirus software
- Here’s how you could protect your RTX 4090 from melting
- Is your Mac acting strange? Here’s how to reset the PRAM and SMC
- Here’s how to manage your kids’ Mac usage with Screen Time
- Norton vs. McAfee: Which Antivirus software is best for your small business?


