“We simply want the chance, with a search warrant, to try to guess the terrorist’s passcode without the phone essentially self-destructing and without it taking a decade to guess correctly,” Comey wrote in a post on Lawfare. “That’s it. We don’t want to break anyone’s encryption or set a master key loose on the land.”
But that is a statement that has continually been disproved, and even Comey has said “of course” the FBI would use a legal precedent to its advantage, under oath to the House Judiciary Committee.
“That’s just the way the law works, which I happen to think is a good thing,” he said.
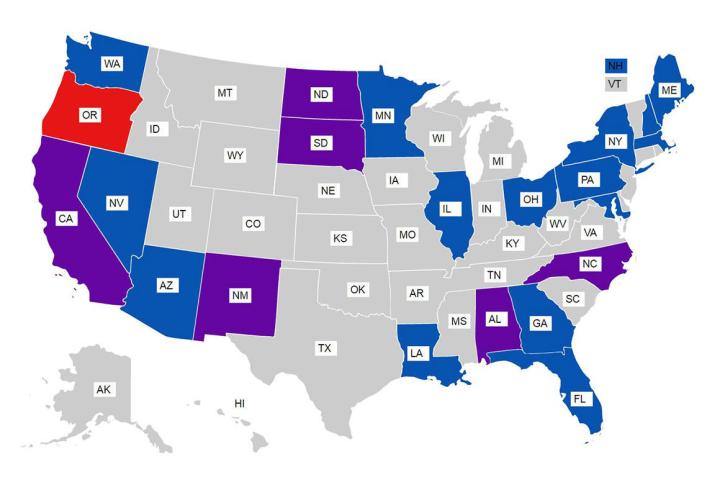
The American Civil Liberties Union just disclosed that the federal government has used the All Writs Act to order tech companies to unlock customer’s devices more than 63 times since 2008.
“We uncovered 63 confirmed cases in which the government applied for an order under the All Writs Act to compel Apple or Google to provide assistance in accessing data stored on a mobile device,” according to the ACLU’s post. “To the extent we know about the underlying facts, these cases predominantly arise out of investigations into drug crimes.”
The All Writs Act of 1789 allows the courts to issue orders that force third parties to comply with the government’s requests.
“We carefully scrutinize subpoenas and court orders to make sure they meet both the letter and spirit of the law.”
Most of the orders were directed to Apple, but nine of them had the government asking Google to reset passwords on specific devices.
“We carefully scrutinize subpoenas and court orders to make sure they meet both the letter and spirit of the law,” a Google spokesperson told Digital Trends. “However, we’ve never received an All Writs Act order like the one Apple recently fought that demands we build new tools that actively compromise our products’ security. … We would strongly object to such an order.”
It’s hard to tell in which cases the companies complied, but it looks as though Google, like Apple, has resisted in certain cases.
The ACLU has created an interactive map of the United States, showing each state where the government has used the All Writs Act, and it’s chock full of related court documents and case references, should you want to take a look.

