Two new sets of images from NASA and the European Space Agency (ESA) have revealed more about the history of water on Mars. Scientists believe that billions of years ago, Mars had a thick, dense atmosphere that trapped heat and allowed liquid water to exist on the surface. They want to learn more about this period to see if there is any way that liquid water might still exist on the planet today.
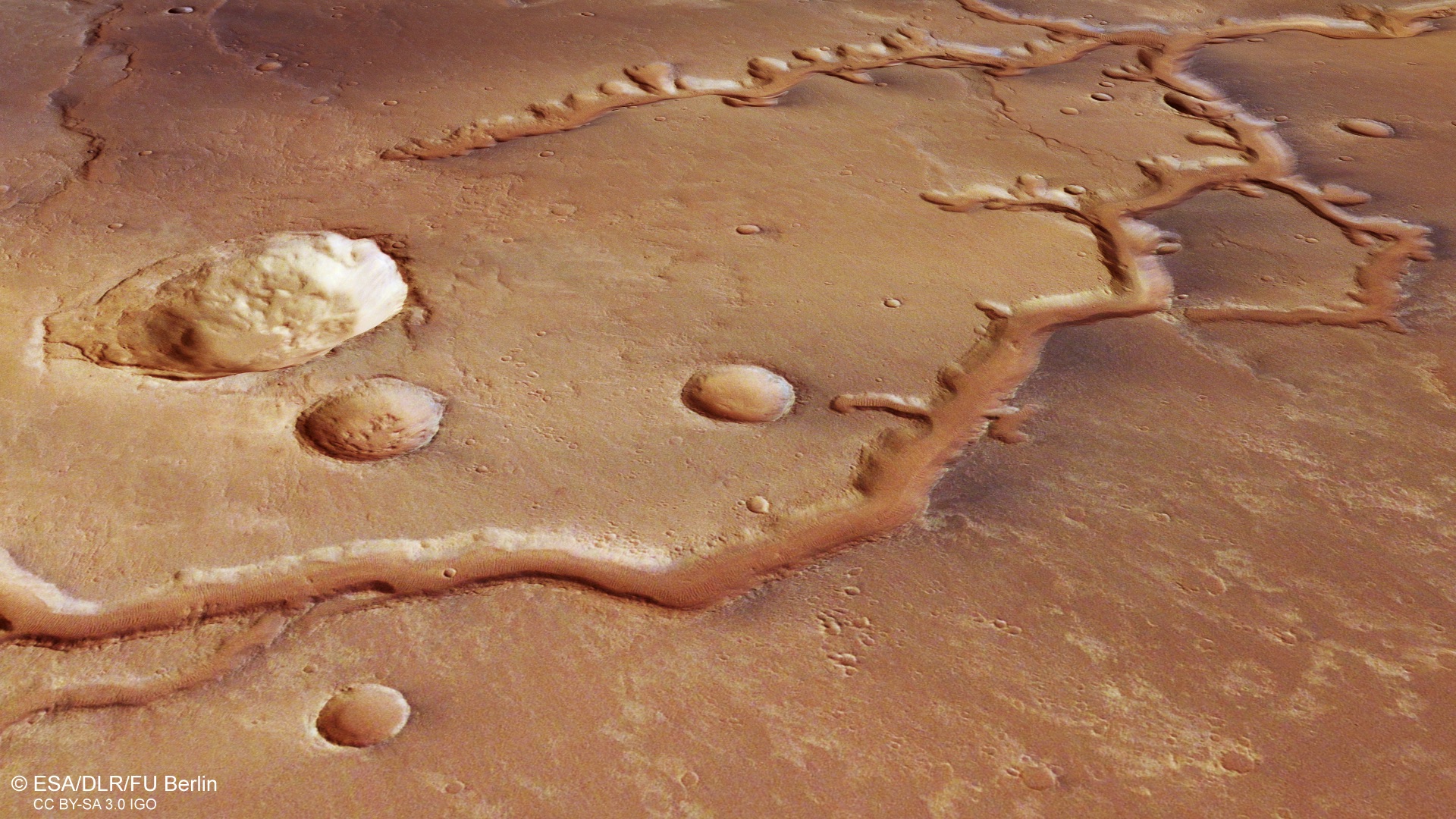
Above is an image that was taken by the ESA’s Mars Express, a spacecraft in orbit around the planet that has captured a dried-up river system called Nirgal Vallis located just south of the equator. The river system stretches for nearly 700 kilometers (435 miles) and was shaped both by the flow of water through the rock and by impacts when meteorites hit the surface. You can see the tree-like branching caused by the river’s flow as well as the round craters caused by the impacts. The system is believed to be between 3.5 and 4 billion years old.

Around the same time, 3.5 billion years ago, the surface of the Gale Crater was very different too. This crater, also located near the equator, is where the Curiosity rover is currently exploring. The rover has captured this image of a network of cracks in the ground, suggesting there was once mud in this location which cracked as it dried. This provides further evidence that there were once lakes in this area.
Located within the Gale Crater is the massive Mount Sharp, which Curiosity is slowly climbing. The steep sides of the mountain allow scientists to view different layers of bedrock, learning about the Martian environment over time. The rover is currently in an area called the “clay-bearing unit” because of the presence of clay minerals there, but it will soon be moving on to the “sulfate-bearing unit.” There appear to be different layers in this new area, which could have formed in drier conditions which came later in Mars’ history.
In the next few years, Curiosity will make its way through the sulfate-bearing unit to investigate these layers up close, with the hopes of understanding how they fit into the environmental history of Mars.



