A stunning new image from the James Webb Space Telescope shows a famous supernova remnant called Cassiopeia A, or Cas A. When a massive star comes to the end of its life and explodes in a huge outpouring of light and energy called a supernova, it leaves behind a dense core that can become a black hole or a neutron star. But that’s not all that remains after a supernova: the explosion can leave its mark on nearby clouds of dust and gas that are formed into intricate structures.
The image of Cas A was taken using Webb’s MIRI instrument, which looks in the mid-infrared range. Located 11,000 light-years away, Cassiopeia A is one of the brightest objects in the sky in the radio wavelength, and is also visible in the optical, infrared, and X-ray wavelengths. To see the different features picked up in different wavelengths, you can look at the slider comparison of the Webb infrared image alongside a Hubble visible light image of the same object.
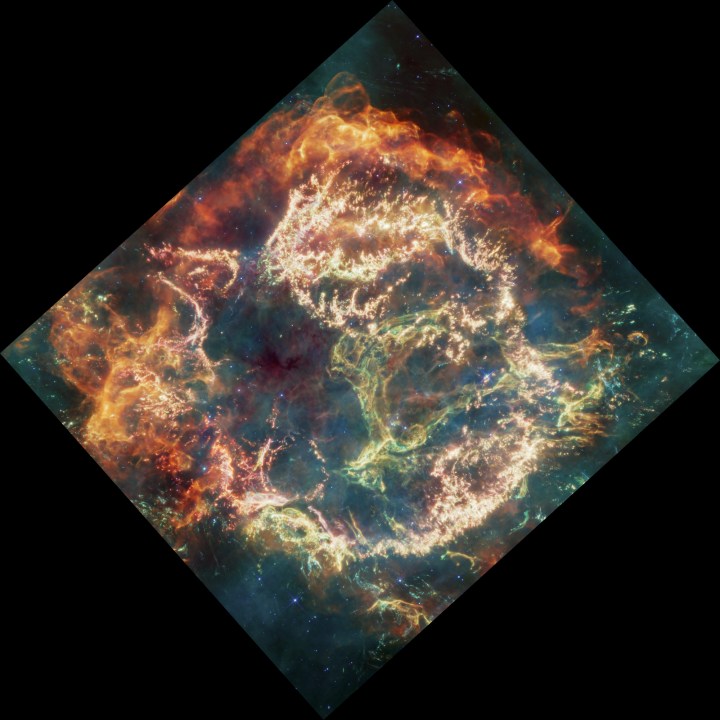
With Webb’s high sensitivity, new details are visible in this remnant. “Compared to previous infrared images, we see incredible detail that we haven’t been able to access before,” said Tea Temim of Princeton University, a co-investigator of the Webb observation program, which took the image, in a statement.
By studying these details, astronomers can learn about the aftereffects of supernovae — which is particularly important because these explosions create many of the heavier elements in our universe such as silicon, sulfur, and iron. “Cas A represents our best opportunity to look at the debris field of an exploded star and run a kind of stellar autopsy to understand what type of star was there beforehand and how that star exploded,” said principal investigator Danny Milisavljevic of Purdue University.
“By understanding the process of exploding stars, we’re reading our own origin story,” said Milisavljevic. “I’m going to spend the rest of my career trying to understand what’s in this data set.”
Editors' Recommendations
- James Webb observes extremely hot exoplanet with 5,000 mph winds
- James Webb images capture the galactic winds of newborn stars
- See the stunning Vela supernova remnant in exquisite detail in expansive image
- See planets being born in new images from the Very Large Telescope
- See what James Webb and Hubble are observing right now with this tool



