AMD finally shared more details on its FidelityFX Super Resolution 3 (FSR 3) this week, and it’s exactly what everyone was asking for. It supports frame generation, and it works across GPUs from AMD and Nvidia. The company is even releasing a driver-based version of its Fluid Motion Frames tech, potentially enabling game support for thousands of titles. It’s all good stuff.
But a big question remains: How is AMD going to deal with latency?
I wrote about the latency concern with Nvidia’s Deep Learning Super Sampling 3 (DLSS 3) in my last column entry — and why I choose to leave the feature off in most games. It’s one of the most pressing issues with the recent push of frame interpolation features, and AMD’s solution, at least in its current state, leaves a lot to be desired.
Defining latency
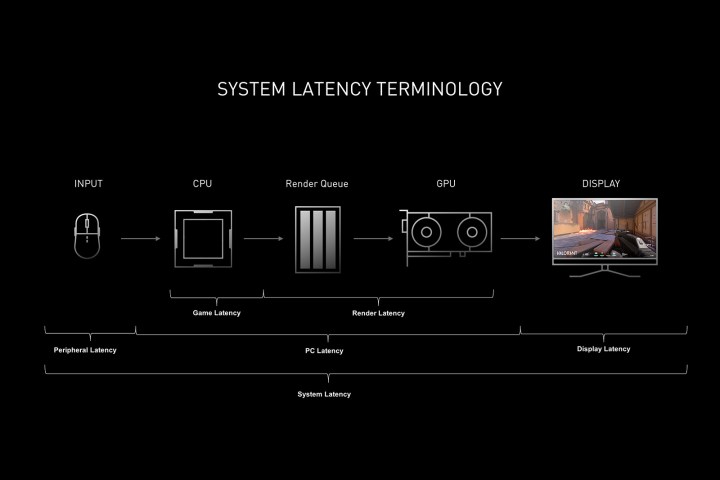
Let’s back up and define what we’re talking about with latency first. Your total system latency is the time it takes from the moment you click your mouse to the effect happening on your screen. It includes all the time it takes for that input to travel down your mouse cable, be processed by your PC, shot out your display cable, and finally show up on your screen.
With features like FSR 3 and DLSS 3, we’re focused on PC latency — that is, how much time does it take between when your PC receives the input and when it sends the final product out to your display. For this, Nvidia has Reflex and AMD has its Anti-Lag feature. In theory, both attempt to reduce latency by minimizing the render queue. Instead of frames being stored in a queue for your GPU to render, they’re passed directly from your CPU to your GPU so you get the latest frame as fast as possible.

AMD and Nvidia go about this in different ways, though. Reflex is a per-game feature, while Anti-Lag comes through AMD’s driver. That means you can use Anti-Lag in far more games, but it also starts processing much later in the game-to-render pipeline. You can see this at work in Cyberpunk 2077. Reflex delivers a 49% reduction in average PC latency, while Anti-Lag delivers a 38% reduction. On top of that, the RX 6700 XT I tested showed higher average latency overall compared to the RTX 3060 Ti.
This is just one game, but I’d recommend reading the Igor’s Lab analysis of Anti-Lag and Reflex, in which it found that “Nvidia’s approach — from within the game, so to speak — to clearing the congestion in the render pipeline is not only more efficient, but much more effective” (translated from German).
Why latency matters (and how you can reduce it)

Latency is a critical component of frame interpolation because only half of the frames you see are actually responding to your actions. Add on top of that some processing time, and your latency will theoretically go up with DLSS 3 or FSR 3 compared to running the game with the feature turned off. Especially if you’re coming from a low frame rate, where latency is already high, the overhead from generating frames can make your games feel sluggish. At least, that’s what we’ve seen with DLSS 3 up to this point.
For its part, AMD says that “FSR 3 already has latency-reducing technology that works across all GPUs.” We’ll have to wait until FSR 3 is out to see how much that actually does. On top of that, AMD is also introducing its new Anti-Lag+ feature.
This wasn’t covered at all in the FSR 3 announcement, but according to slides shared with press, AMD imagines FSR 3 working as an ecosystem of Anti-Lag+, Super Resolution, and Fluid Motion Frames. We’ve extensively tested Super Resolution, we have a good grip on what Fluid Motion Frames does, but Anti-Lag+ remains a bit of a mystery.
Here’s how AMD described it when I asked: “AMD Radeon Anti-Lag helps synchronize CPU and GPU processing during gameplay to reduce input latency. Anti-Lag’s synchronization point, however, is placed at a fixed location in the rendering pipeline. AMD Radeon Anti-Lag+ further reduces latency through intelligent synchronization placement that considers the holistic rendering pipeline. As a result, Anti-Lag+ can further reduce latency where it matters most.”

Like Anti-Lag, Anti-Lag+ also comes through AMD Software, which is the software suite that you get along with new GPU drivers. AMD says Anti-Lag+ isn’t required for FSR 3 to work, either. That’s a different approach than Nvidia has taken with DLSS 3, which forces Reflex on whenever you enable DLSS Frame Generation.
Despite being through the driver, AMD tells me that Anti-Lag+ won’t automatically work with any game. The company says “it still requires to be profiled on a per-game basis in our driver to provide the optimal experience, so it supports a select number of titles.”
On top of that, Anti-Lag+ only works with AMD’s latest graphics cards like the RX 7900 XTX and RX 7900 XT. If you have anything older, you’ll have to stick with the regular Anti-Lag if you want to further reduce your latency in games.
From AMD’s view, Anti-Lag and Anti-Lag+ are ways to further reduce latency, not a replacement for the latency-saving benefits it says FSR 3 has — the company used “bonus latency reduction” to describe the features when I asked them. There are some obvious concerns here, though. Either FSR 3 needs to seriously reduce latency on its own, or Anti-Lag+ needs to deliver far and above what Anti-Lag current does.
An uphill battle

AMD is fighting an uphill battle with FSR 3. Since the original version of FSR, the company has always traded some level of image quality in order to support as many GPUs as possible, and FSR 3 continues that trend. This time around, though, AMD is also dealing with the latency issues that come up with frame interpolation.
It would be great if FSR 3’s built-in latency reduction can overcome the inherent issues, or if features like Anti-Lag and Anti-Lag+ can help push it into an acceptable latency point. But it’s not a stretch to say that the success of the feature hinges on this issue. We’ll have plenty of discussions about image quality and performance once FSR 3 is here, but if the latency isn’t in check, it doesn’t matter what the feature can deliver otherwise.
Thankfully, we don’t have to wait much longer. AMD has confirmed the feature will arrive in September in both Forspoken and Immortals of Aveum, and I’ll be sure to test it as soon as the updates drop.
Editors' Recommendations
- It’s time to stop ignoring the CPU in your gaming PC
- The RTX 4090 is more popular on Steam than any AMD GPU
- Razer’s most boring product is also one of its best
- Gigabyte just confirmed AMD’s Ryzen 9000 CPUs
- 4 CPUs you should buy instead of the Ryzen 7 7800X3D





