As far as we know, the Earth has a unique quality among the planets of the solar system: It is the only planet with plate tectonics, where the crust is made up of plates that float on the mantle. It is thought that this tectonic activity may even be related to the development of life.
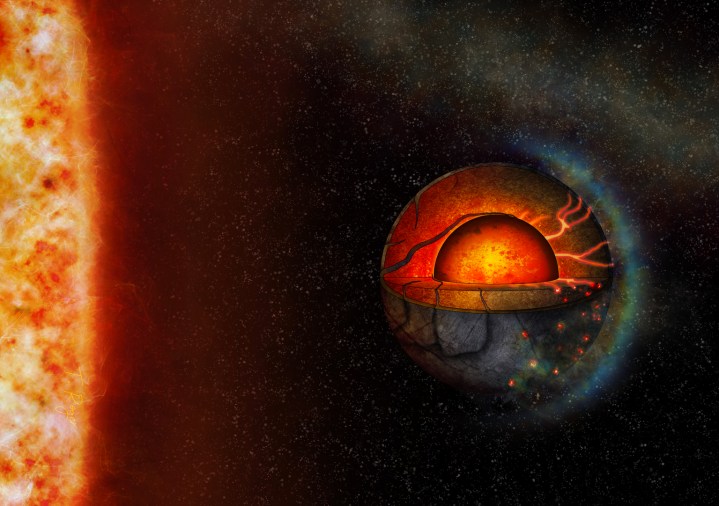
Global tectonic activity has never been observed on a planet outside our solar system, but now a new study suggests that exoplanet LHS 3844b has interior flows, carrying material from one side of the planet to the other side.
One reason tectonic activity hasn’t been observed is because it’s difficult to spot from so far away. “Observing signs of tectonic activity is very difficult, because they are usually hidden beneath an atmosphere,” the study’s lead author, Tobias Meier from the Center for Space and Habitability (CSH) at the University of Bern, explained in a statement.
However, this particular planet likely has no atmosphere and has a bunch of other unusual qualities. It orbits close to its star and is tidally locked, meaning the same side always faces the star and remains in daylight. This means the surface there gets extremely hot, reaching nearly 1,500°F on the dayside while the nightside is as cold as -400°F.
This massive difference in temperatures gave the researchers the idea that the interior of the planet might be affected. So they created computer simulations to see how this difference in heat between the two sides would affect the inside of the planet.
“Most simulations showed that there was only upwards flow on one side of the planet and downwards flow on the other. Material therefore flowed from one hemisphere to the other,” Meier said. But the researchers noticed something strange: The direction of the flow was not always the same.
You’d expect material on the hotter dayside to flow upwards, and cooler material on the nightside to sink. But sometimes, the material flowed in the opposite direction. “This initially counter-intuitive result is due to the change in viscosity with temperature: Cold material is stiffer and therefore doesn’t want to bend, break or subduct into the interior. Warm material, however, is less viscous — so even solid rock becomes more mobile when heated — and can readily flow towards the planet’s interior,” co-author Dan Bower at the University of Bern and the NCCR PlanetS explained.
This is different from the type of activity seen in the interior of Earth, but it’s another way that a planet could have materials being exchanged between the interior and the surface.
And it would have weird effects on the planet too: The researchers expect that one side of the planet would be covered in volcanoes, while the other side would have almost none. To try to confirm whether their simulations are correct, the researchers now want to perform more observations such as looking for emissions from these volcanoes.
Editors' Recommendations
- First indications of a rare, rainbow ‘glory effect’ on hellish exoplanet
- Small exoplanet could be hot and steamy according to Hubble
- See the weather patterns on a wild, super hot exoplanet
- James Webb investigates a super puffy exoplanet where it rains sand
- Hubble spots an Earth-sized exoplanet just 22 light-years away




