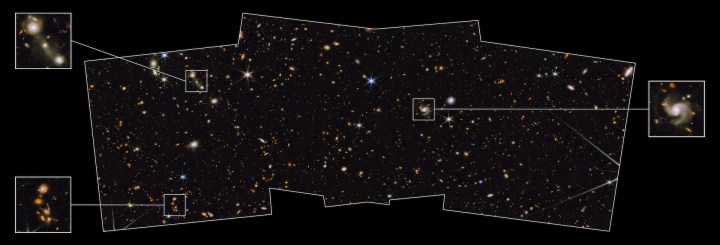
As well as providing new information about objects like exoplanets and giving new views of some famous space scenes, the James Webb Space Telescope is also being used to observe large patches of the sky in wide-scale surveys. Researchers from one such Webb survey, called the Prime Extragalactic Areas for Reionization and Lensing Science or PEARLS, recently released their first results showing an area of the sky called the North Ecliptic Pole.
This image shows around 2% of the sky, as captured by both Webb’s Near-Infrared Camera or NIRCam and the Hubble Space Telescope’s Advanced Camera for Surveys. This is just a part of the PEARLS survey, but shows thousands of galaxies including some extremely distant ones. You can see a zoomable version of the image on the Webb website.
“For over two decades, I’ve worked with a large international team of scientists to prepare our Webb science program,” said lead author of the research, Rogier Windhorst of Arizona State University, in a statement. “Webb’s images are truly phenomenal, really beyond my wildest dreams. They allow us to measure the number density of galaxies shining to very faint infrared limits and the total amount of light they produce. This light is much dimmer than the very dark infrared sky measured between those galaxies.”
Some of the interesting features being studied by the PEARLS survey include the accretion disks which form around supermassive black holes in the center of galaxies, a pair of overlapping galaxies called the VV 191 galaxy system, and some extremely old galaxies with very high redshift, the light of which has been traveling for almost 13.5 billion years.
“I was blown away by the first PEARLS images,” said coauthor Rolf Jansen. “Little did I know, when I selected this field near the North Ecliptic Pole, that it would yield such a treasure trove of distant galaxies, and that we would get direct clues about the processes by which galaxies assemble and grow. I can see streams, tails, shells, and halos of stars in their outskirts, the leftovers of their building blocks.”
The research is published in The Astronomical Journal.



