Did an application decide to freeze on you? Getting the spinning beachball of death on MacOS? Or are things just running a bit too slow for your liking? Then you'll need to know how to force quit on a Mac, allowing you to close out of unresponsive programs.
Apple gives you a few different options when it comes to force quitting on a Mac, and most of them take just a few seconds to execute. Keep in mind that force quitting an application can be risky, as the software won't ask you to save any files or progress. That means you'll want to be absolutely sure you can safely close the software without losing any unsaved work.
Once you've verified you won't be deleting anything important, here's everything you need to know about using the force quit feature on Mac. Note that these steps will work on MacOS Sonoma, MacOS Big Sur, and most other versions of MacOS.
Use the Finder
First up is Apple’s recommended course of action for when an app starts to wear out its welcome.
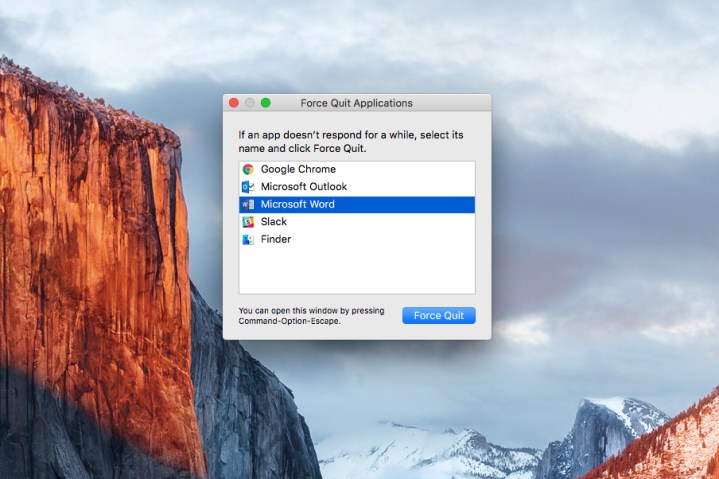
Step 1: Click on the Apple icon in the top-left corner of your screen and select Force Quit from the list.
Step 2: This should bring up the Force Quit Applications window that displays your open applications.
Step 3: Just select the one that’s giving you trouble and click Force Quit at the bottom.
Keyboard shortcuts
If that doesn’t work, it’s time for keyboard shortcuts.
Step 1: Similar to Ctrl+Alt+Del on Windows 11, hit Opt + Cmd + Esc on your keyboard (on some Mac keyboards, Opt is labeled as Alt).
Step 2: Like other methods, this will bring up the Force Quit Applications window.
Step 3: Just select the application that’s giving you trouble and click Force Quit. Also, if you’re looking for even more keyboard shortcuts to speed up your computing on MacOS, check out our handy guide.
Try the Option key
This program can be tricky and fickle, causing issues that might be hard to solve. You’re probably better off handling issues yourself by going in and choosing the specific apps you want to shut down.
Step 1: Just Right-Click or Ctrl-Click on the misbehaving app in your Dock.
Step 2: Then, press and hold the Option key, which turns the Quit selection to Force Quit in the list of options.
Step 3: There’s no need to panic if this doesn’t close down the app because there are other avenues to find a solution. It’s just time to get creative.
Launch Activity Monitor
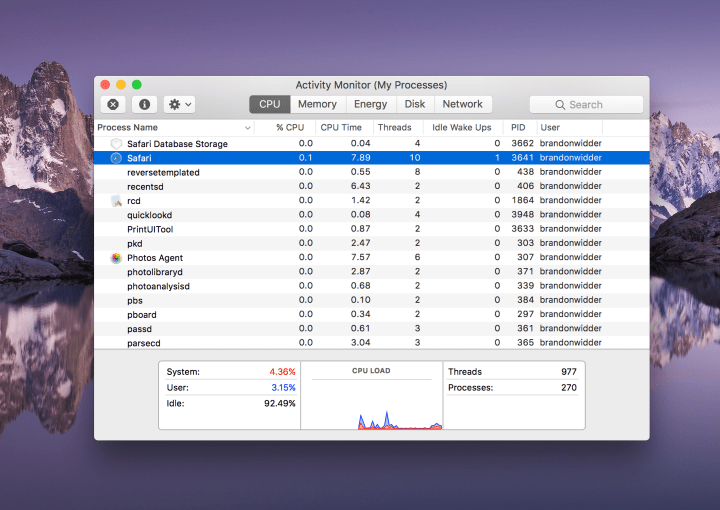
Step 1: Open the Activity Monitor by clicking on the Spotlight icon — i.e., the magnifying glass in the top-right corner of your screen — and typing Activity Monitor in the text box. Then select the app from the list.
Step 2: From the task manager that displays everything running on your computer, find the misbehaving app, select it, and click the button that resembles a Stop Sign in the top-left corner.
Step 3: If that still doesn’t do the trick, it might be a good idea to save all your open work and restart your iMac or MacBook, which will likely solve the problem. There is one last method you can try if restarting your device is out of the question.
Use Terminal
For technically savvy users, this method is complicated, but it’s the last trick we have up our sleeve if nothing else has worked.
Step 1: Open your Applications folder, scroll down to Utilities, and launch Terminal.
Step 2: After a few moments, Terminal will display your username, followed by a dollar sign. Using your keyboard, type the word Top and press the Return key.
Step 3: Terminal displays your CPU and RAM usage diagnostics, along with a table that shows all of your open applications. This includes background applications, which often use a lot of RAM without us realizing it. The Command column displays the name of each active application. The column on the very left displays the process identifier (PID) for each application. The PID is how your computer keeps track of open applications.
Step 4: Choose the application you need to quit from the Command column and copy the application’s PID. You can do this by highlighting it and typing the keyboard shortcut Cmd + C to copy. Close this Terminal window.
Step 5: Open a new Terminal window and type the command Kill. Hit the spacebar once, and type Cmd + V to paste the PID you previously copied. You will get a message similar to “Kill 93142.” Hit the Return key to tell Terminal to close the problematic application.
Editors' Recommendations
- How to change the login picture on a Mac
- How to change your MAC address on Windows and Mac
- How to create a Memoji on a Mac
- Best Apple deals: Save on AirPods, Apple Watch, iPad, MacBook
- How to delete messages on your Mac




