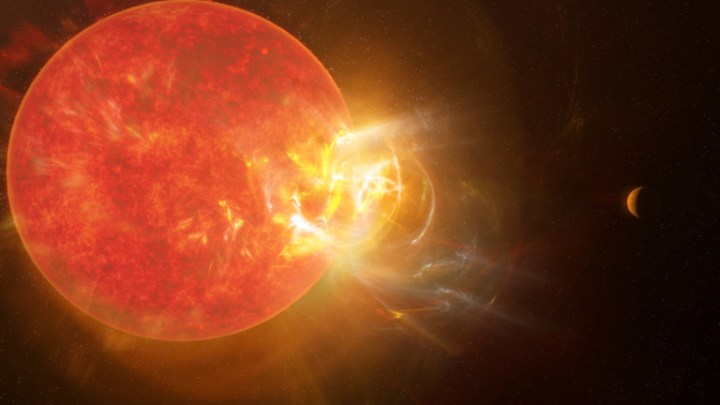
A team of astronomers has observed the largest ever stellar flare emitted by our neighboring star, Proxima Centauri. The flare is 100 times more powerful than any solar flare coming from our sun and could be relevant to the search for habitable worlds.
Proxima Centauri is a type of star called a red dwarf, with a lower mass than our sun and giving off less light. But despite its seemingly calm exterior, the star undergoes dramatic stellar flares.
“Stars like Proxima Centauri look different from our sun, and they behave differently too,” explained co-author of the research, Parke Loyd of the Arizona State University, in a statement. “In particular, they flare a lot more than the sun, but we are only beginning to understand the magnitude and character of their flares.”
The researchers wanted to know whether these stellar flares are similar to the solar flares given out by our sun and whether both are caused by the same mechanisms. So they observed Proxima Centauri using telescopes including Hubble over a period in 2019 and looked in the ultraviolet wavelength to identify bursts of radiation.
“When the data from the Hubble Space Telescope came in and we made our first plot of how much ultraviolet light Proxima Centauri was emitting at each instant of the observations, it immediately became clear that we had caught a remarkable event,” said Loyd. “It was extremely bright and extremely brief. In only a few seconds the star’s ultraviolet radiation grew about 14,000 times brighter. ”
As well as learning about stars, this research could be important in the search for habitable exoplanets. “A lot of the exoplanets that we’ve found so far are around these types of stars,” lead author Meredith MacGregor of the University of Colorado-Boulder said. “But the catch is that they’re way more active than our sun. They flare much more frequently and intensely.”
Proxima Centauri hosts at least two planets, one of which, Proxima b, is in the habitable zone. But flares from the star may make these planets less hospitable for life.
“Humans cannot see ultraviolet light, but some animals, like some species of jumping spiders, can,” Loyd explained. “Imagining we could see ultraviolet light and we were standing on the planet Proxima Centauri b when this flare happened, we would have experienced a blinding flash, just about at the limit of our visual range.
“If organisms do exist on a planet like this, I suspect they would have to react very quickly to protect themselves at the earliest indication of a flare, and they would need to do this several times per day.”
Editors' Recommendations
- Biggest stellar black hole to date discovered in our galaxy
- SpaceX is gearing up for a record-breaking rocket flight
- Scientists investigate star formation in the famous Whirlpool Galaxy
- Watch this footage of a shooting star captured from the space station
- Record-breaking supermassive black hole is oldest even seen in X-rays




