In the ever-evolving landscape of artificial intelligence, ChatGPT stands out as a groundbreaking development that has captured global attention. From its impressive capabilities and recent advancements to the heated debates surrounding its ethical implications, ChatGPT continues to make headlines.
- What is ChatGPT?
- When was ChatGPT released?
- How to use ChatGPT
- How to use the ChatGPT iPhone, Android, and Mac apps
- Is ChatGPT free to use?
- What is Project Strawberry?
- Who created ChatGPT?
- ChatGPT’s numerous controversies
- Can ChatGPT’s outputs be detected by anti-plagiarism systems?
- What are ChatGPT plugins?
- Is there a ChatGPT API?
- What’s the future of ChatGPT?
- ChatGPT alternatives worth trying
- Are ChatGPT chats private?
- Will ChatGPT replace Google Search?
- Is Copilot the same as ChatGPT?
- Can you write essays with ChatGPT?
- Can ChatGPT write and debug code?
- What is the ChatGPT character limit?
- What is Auto-GPT?
- Who owns the copyright to content created by ChatGPT?
Whether you’re a tech enthusiast or just curious about the future of AI, dive into this comprehensive guide to uncover everything you need to know about this revolutionary AI tool.
What is ChatGPT?
ChatGPT (which stands for Chat Generative Pre-trained Transformer) is an AI chatbot, meaning you can ask it a question using natural language prompts and it will generate a reply. Unlike less-sophisticated voice assistant like Siri or Google Assistant, ChatGPT is driven by a large language model (LLM). These neural networks are trained on huge quantities of information from the internet for deep learning — meaning they generate altogether new responses, rather than just regurgitating canned answers. They’re not built for a specific purpose like chatbots of the past — and they’re a whole lot smarter. The current version of ChatGPT is based on the GPT-4 model, which was trained on all sorts of written content including websites, books, social media, news articles, and more — all fine-tuned in the language model by both supervised learning and RLHF (Reinforcement Learning From Human Feedback).
When was ChatGPT released?
OpenAI released ChatGPT in November 2022. When it launched, the initial version of ChatGPT ran atop the GPT-3.5 model. In the years since, the system has undergone a number of iterative advancements with the current version of ChatGPT using the GPT-4 model family. GPT-5 is reportedly just around the corner. GPT-3 was first launched in 2020, GPT-2 released the year prior to that, though neither were used in the public-facing ChatGPT system.
How to use ChatGPT
First, go to chatgpt.com. If you’d like to maintain a history of your previous chats, sign up for a free account. You can use the system anonymously without a login if you prefer. Users can opt to connect their ChatGPT login with that of their Google-, Microsoft- or Apple-backed accounts as well. At the sign up screen, you’ll see some basic rules about ChatGPT, including potential errors in data, how OpenAI collects data, and how users can submit feedback. If you want to get started, we have a roundup of the best ChatGPT tips.

Using ChatGPT itself is simple and straightforward, just type in your text prompt and wait for the system to respond. You can be as creative as you like, and see how your ChatGPT responds to different prompts. If you don’t get the intended result, try tweaking your prompt or giving ChatGPT further instructions The system understands context based on previous responses from the current chat session, so you can refine your requests rather than starting over fresh every time.
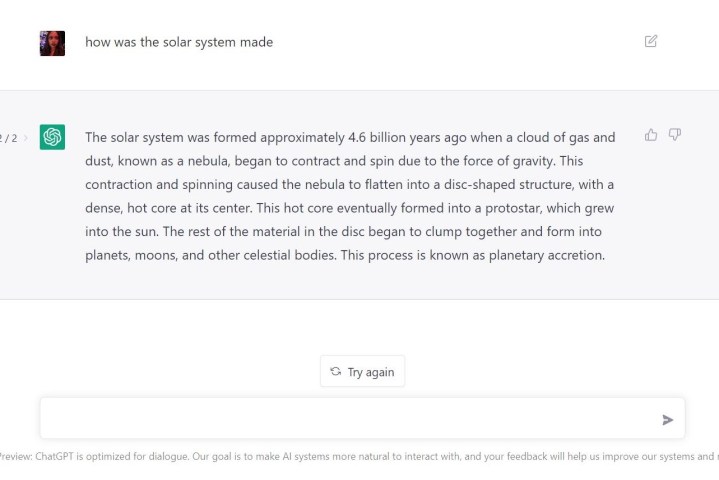
For example, starting with “Explain how the solar system was made” will give a more detailed result with more paragraphs than “How was the solar system made,” even though both inquiries will give fairly detailed results. Take it a step further by giving ChatGPT more guidance about style or tone, saying “Explain how the solar system was made as a middle school teacher.”
You also have the option for more specific input requests, for example, an essay with a set number of paragraphs or a link to a specific Wikipedia page. We got an extremely detailed result with the request “write a four-paragraph essay explaining Mary Shelley’s Frankenstein.”
ChatGPT is capable of automating any number of daily work or personal tasks from writing emails and crafting business proposals, to offering suggestions for fun date night ideas or even drafting a best man’s speech for your buddy’s wedding. So long as the request doesn’t violate the site’s rules on explicit or illegal content, the model will do its best to fulfill the commands.
Since its launch, people have been experimenting to discover everything the chatbot can and can’t do — and the results have been impressive, to say the least. Learning the kinds of prompts and follow-up prompts that ChatGPT responds well to requires some experimentation though. Much like we’ve learned to get the information we want from traditional search engines, it can take some time to get the best results from ChatGPT. It really all depends on what you want out of it. To start out, try using it to write a template blog post, for example, or even blocks of code if you’re a programmer.

Our writers experimented with ChatGPT too, attempting to see if it could handle holiday shopping or even properly interpret astrological makeup. In both cases, we found limitations to what it could do while still being thoroughly impressed by the results.
Following an update on August 10, you can now use custom instructions with ChatGPT. This allows you to customize how the AI chatbot responds to your inputs so you can tailor it for your needs. You can’t ask anything, though. OpenAI has safeguards in place in order to “build a safe and beneficial artificial general intelligence.” That means any questions that are hateful, sexist, racist, or discriminatory in any way are generally off-limits.
You shouldn’t take everything that ChatGPT (or any chatbot, for that matter) tells you at face value. When ChatGPT first launched it was highly prone to “hallucinations.” The system would repeat erroneous data as fact. The issue has become less prevalent as the model is continually fine tuned, though mistakes do still happen. Trust but verify!
What’s more, due to the way that OpenAI trains its underlying large language models — whether that’s GPT-3.5, GPT-4, GPT-4o, GPT-4o mini, or the upcoming GPT-5 — ChatGPT may not be able to answer your question without help from an internet search if the subject is something that occurred recently. For example, GPT-3.5 and 3.5 Turbo cannot answer questions about events after September 2021 without conducting an internet search to find the information because the data that the model was initially trained on was produced before that “knowledge cutoff date.” Similarly, GPT-4 or GPT-4 Turbo have cutoff dates of December 2023, though GPT-40 and GPT-4o mini (despite being released more recently) have a cutoff of October 2023.
While ChatGPT might not remember all of recorded history, it will remember what you were discussing with it in previous chat sessions. Logged-in users can access their chat history from the navigation sidebar on the left of the screen, and manage these chats, renaming, hiding or deleting them as needed. You can also ask ChatGPT follow-up questions based on those previous conversations directly through the chat window. Users also have the option to use ChatGPT in dark mode or light mode.
ChatGPT isn’t just a wordsmith. Those users paying $20/month subscription for ChatGPT Plus or $30/month/user for ChatGPT Teams, gain access to the Dall-E image generator, which converts text prompts into lifelike generated images. Unfortunately, image generation is not currently available to users at the free tier. Regardless of subscription status, all users can use image or voice inputs for their prompt.
How to use the ChatGPT iPhone, Android, and Mac apps

ChatGPT is available through the OpenAI web, as well as a mobile app for both iOS and Android devices. The iOS version was an immediate hit when it arrived at the App Store, topping half a million downloads in less than a week.
If you can use ChatGPT on the web, you can use it on your phone. Logging on or signing up through the app is nearly identical to the web version and nearly all of the features found on the desktop have been ported to the mobile versions. The app lets you toggle between GPT-4o mini, GPT-4, and GPT-4o as well. The clean interface shows your conversation with GPT in a straightforward manner, hiding the chat history and settings behind the menu in the top right.
Some devices go beyond just the app, too. For instance, the Infinix Folax is an Android phone that integrated ChatGPT throughout the device. Instead of just an app, the phone replaces the typical smart assistant (Google Assistant) with ChatGPT.
There’s even an official ChatGPT app released for the Mac that can be used for free. The app is capable of all sorts of new things that bring Mac AI capabilities to new levels — and you don’t even have to wait for macOS Sequoia later this year.
Is ChatGPT free to use?
Yes, ChatGPT is completely free to use, though with some restrictions. Even with a free tier account, users will have access to the GPT-4o and GPT-40 mini models, though the number of queries that users can make of the larger model are limited. Upgrading to a paid subscription drastically increases that query limit, grants access to other generative AI tools like Dall-E image generation, and the ability to create custom GPTs. The company came under fire in September 2024 when news broke that OpenAI could raise subscription prices to more than $2000/month for access to future cutting-edge models.
It’s not free for OpenAI to continue running it, of course. Initial estimates are currently that OpenAI spends around $3 million per month to continue running ChatGPT, which is around $100,000 per day. A report from April 2023 indicated that the price of operation is closer to $700,000 per day.
Beyond the cost of the servers themselves, some troubling information and accusations have come to light regarding what else has been done to safeguard the model from producing offensive content.
What is Project Strawberry?
Project Strawberry was the code name for OpenAI’s latest family of “reasoning” models, which reportedly can use logic similarly to humans. The company released Strawberry to the public in September 2024, renaming the two versions “o1” and “o1-mini” for the smaller and more responsive iteration.
The o1 model “has been trained using a completely new optimization algorithm and a new training dataset specifically tailored for it,” OpenAI’s research lead Jerry Tworek, told The Verge. It relies on a combination of reinforcement learning and “chain of thought” reasoning to return more accurate responses than its predecessor models.
o1 and o1-mini are currently only available to pay-tier subscribers (Plus, Teams, Enterprise, and Edu). The company reportedly has plans to eventually release o1-mini to free-tier users but has not disclosed a timeline for that to take place.
Who created ChatGPT?
OpenAI, a San Francisco-based AI research lab, created ChatGPT and released the very first version of the LLM in 2018. The organization started as a non-profit meant for collaboration with other institutions and researchers, funded by high-profile figures like Peter Thiel and Elon Musk, the latter of whom left the company after an internal power struggle to found rival firm, xAI.
OpenAI later transitioned to a for-profit structure in 2019 and is now led by CEO, Sam Altman. It runs on Microsoft’s Azure system infrastructure and is powered by Nvidia’s GPUs, including the new supercomputers just announced this year. Microsoft has invested heavily in OpenAI since 2019 as well, expanding its partnership with the AI startup in 2021 and again in 2023, when Microsoft announced a multi-billion dollar round of investments that included naming its Azure cloud as OpenAI’s exclusive cloud provider.
ChatGPT’s numerous controversies
Although ChatGPT is an extremely capable digital tool, it isn’t foolproof. The AI is known for making mistakes or “hallucinations,” where it makes up an answer to something it doesn’t know. Early on, a simple example of how unreliable it can sometimes be involved misidentifying the prime minister of Japan.
Beyond just making mistakes, many people are concerned about what this human-like generative AI could mean for the future of the internet, so much so that thousands of tech leaders and prominent public figures have signed a petition to slow down the development. It was even banned in Italy due to privacy concerns, alongside complaints from the FTC — although that’s now been reversed. Since then, the FTC has reopened investigations against OpenAI on questions of personal consumer data is being handled.
In addition, JPMorgan Chase has threatened to restrict the use of the AI chatbot for workers, especially for generating emails, which companies like Apple have also prohibited internally. Following Apple’s announcement at WWDC 2024 that it would be integrating OpenAI’s technology into its mobile and desktop products, Tesla CEO and sore loser Elon Musk similarly threatened to ban any device running the software from his businesses — everything from iPhones to Mac Studios. Other high-profile companies have been disallowing the use of ChatGPT internally, including Samsung, Amazon, Verizon, and even the United States Congress.
There’s also the concern that generative AI like ChatGPT could result in the loss of many jobs — as many as 300 million worldwide, according to Goldman Sachs. In particular, it’s taken the spotlight in Hollywood’s writer’s strike, which wants to ensure that AI-written scripts don’t take the jobs of working screenwriters. Fat lot of good that did.
In 2023, many people attempting to use ChatGPT received an “at capacity” notice when trying to access the site. It’s likely behind the move to try and use unofficial paid apps, which had already flooded app stores and scammed thousands into paying for a free service.
Because of how much ChatGPT costs to run, it seems as if OpenAI has been limiting access when its servers are “at capacity.” It can take as long as a few hours to wait out, but if you’re patient, you’ll get through eventually. Of the numerous growing pains ChatGPT has faced, “at capacity” errors had been the biggest hurdle keeping people from using the service more. In some cases, demand had been so high that the entire ChatGPT website has gone down for several hours for maintenance multiple times over the course of months.
Multiple controversies have also emerged from people using ChatGPT to handle tasks that should probably be handled by an actual person — like being the mayor of Cheyenne, Wyoming. One of the worst cases of this is generating malware, which the FBI recently warned ChatGPT is being used for. More startling, Vanderbilt University’s Peabody School came under fire for generating an email about a mass shooting and the importance of community.
There are also privacy concerns. A recent GDPR complaint says that ChatGPT violates user’s privacy by stealing data from users without their knowledge, and using that data to train the AI model. ChatGPT was even made able to generate Windows 11 keys for free, according to one user. Of course, this is not how ChatGPT was meant to be used, but it’s significant that it was even able to be “tricked” into generating the keys in the first place.
Can ChatGPT’s outputs be detected by anti-plagiarism systems?
Teachers, school administrators, and developers are already finding different ways around this and banning the use of ChatGPT in schools. Others are more optimistic about how ChatGPT might be used for teaching, but plagiarism is undoubtedly going to continue being an issue in terms of education in the future. There are some ideas about how ChatGPT could “watermark” its text and fix this plagiarism problem, but as of now, detecting ChatGPT is still incredibly difficult to do.
ChatGPT launched an updated version of its own plagiarism detection tool in January 2023, with hopes that it would squelch some of the criticism around how people are using the text generation system. It uses a feature called “AI text classifier,” which operates in a way familiar to other plagiarism software. According to OpenAI, however, the tool is a work in progress and remains “imperfect.” Since the advent of GPTs in April 2024, third party developers have also stepped in with their own offerings, such as Plagiarism Checker.
What are ChatGPT plugins?
They’re a feature that doesn’t exist anymore. The announcement of ChatGPT plugins caused a great stir in the developer community, with some calling it “the most powerful developer platform ever created.” AI enthusiasts have compared it to the surge of interest in the iOS App Store when it first launched, greatly expanding the capabilities of the iPhone.
Essentially, developers would be able to build plugins directly for ChatGPT, to open it up to have access to the whole of the internet and connect directly to the APIs of specific applications. Some of the examples provided by OpenAI include applications being able to perform actions on behalf of the user, retrieve real-time information, and access knowledge-based information.
However, in 2024, OpenAI reversed course on its plugin plans, sunsetting the feature and replacing them with GPT applets. OpenAI’s GPT applets were released in conjunction with the unveiling of GPT-4o, They’re small, interactive JavaScript applications generated by GPT-4 and available on the ChatGPT website. These applets are various tools designed to perform specific, often singular, tasks such as acting as calculators, planners, widgets, image apps, and text transformation utilities.
Is there a ChatGPT API?
Yes. APIs are a way for developers to access ChatGPT and plug its natural language capabilities directly into apps and websites. We’ve seen it used in all sorts of different cases, ranging from suggesting parts in Newegg’s PC builder to building out a travel itinerary with just a few words. Many apps had been announced as partners with OpenAI using the ChatGPT API. Of the initial batch, the most prominent example is Snapchat’s MyAI.
Recently, OpenAI made the ChatGPT API available to everyone, and we’ve seen a surge in tools leveraging the technology, such as Discord’s Clyde chatbot or Wix’s website builder. Most recently, GPT-4 has been made available as an API “for developers to build applications and services.” Some of the companies that have already integrated GPT-4 include Duolingo, Be My Eyes, Stripe, and Khan Academy.
What’s the future of ChatGPT?
There’s no doubt that the tech world has become obsessed with ChatGPT right now, and it’s not slowing down anytime soon. But the bigger development will be how ChatGPT continues to be integrated into other applications.
GPT-5 is the rumored next significant step up in, which has been teased and talked about ad nauseam over the past year. Some say that it will finish training as early as in December of 2024, paving the way toward AGI (artificial general intelligence). OpenAI CTO Mira Murati has compared it to having Ph.D.-level intelligence, while others have said it will lead to AI with better memory and reasoning. The timing seems very uncertain though, but it seems like it could launch sometime in 2025.
Beyond GPT-5, plenty of AI enthusiasts and forecasters have predicted where this technology is headed. Last year, Shane Legg, Google DeepMind’s co-founder and chief AGI scientist, told Time Magazine that he estimates there to be a 50% chance that AGI will be developed by 2028. Dario Amodei, co-founder and CEO of Anthropic, is even more bullish, claiming last August that “human-level” AI could arrive in the next two to three years. For his part, OpenAI CEO Sam Altman argues that AGI could be achieved within the next half-decade.
All that to say, if you think AI is a big deal now, we’re clearly still in the early days.
ChatGPT alternatives worth trying

ChatGPT remains the most popular AI chatbot, but it’s not without competition. Microsoft’s Copilot is a significant rival, even though Microsoft has invested heavily with the AI startup and Copilot itself leverages the GPT-4 model for its answers.
Google’s Gemini AI (formerly Google Bard) is another such competitor. Built on Google’s own transformer architecture, this family of multimodal AI models can both understand and generate text, images, audio, videos, and code. First released in March, 2o23, Gemini is available in 46 languages and in 239 countries and territories. One of its big advantages is that Gemini can generate images for free, while you’ll have to upgrade to ChatGPT Plus in OpenAI’s ecosystem.
Anthropic’s Claude family of AI have also emerged as serious challengers to ChatGPT’s dominance. In June 2024, the AI startup announced that its recently released Claude 3.5 Sonnet model outperformed both GPT-4o and Gemini Pro 1.5 at a host of industry benchmarks and significantly outperformed the older Claude 3.0 Opus by double digits while consuming 50 percent less energy.
Meta, the parent company to Facebook, has also spent the last few years developing its own AI chatbot based on its family of Llama large language models. The company finally revealed its chatbot in April 2024, dubbed Meta AI, and revealed that it leverages the company’s latest to date model, Llama 3. The assistant is available in more than a dozen countries and operates across Meta’s app suite, including Facebook, Instagram, WhatsApp, and Messenger.
Lastly, Apple had long been rumored to be working on an artificial intelligence system of its own, and proved the world right at WWDC 2024 in June, where the company revealed Apple Intelligence. The AI is “comprised of highly capable large language and diffusion models specialized for your everyday tasks” and designed to help iPhone, iPad, and Mac users streamline many of their most common everyday tasks across apps. Apple’s AI is expected to begin rolling out to users alongside the iOS 18, iPadOS 18, and Mac Sequoia software releases in fall 2024.
Are ChatGPT chats private?
It depends on what you mean by private. All chats with ChatGPT are used by OpenAI to further tune the models, which can actually involve the use of human trainers. No, that doesn’t mean a human is looking through every question you ask ChatGPT, but there’s a reason OpenAI warns against providing any personal information to ChatGPT.
It should be noted that if you don’t delete your chats, the conversations will appear in the left sidebar. Unlike with other chatbots, individual chats within a conversation cannot be deleted, though they can be edited using the pencil icon that appears when you hover over a chat. When you delete the conversations, however, it’s not that ChatGPT forgets they ever happened — it’s just that they disappear from the sidebar chat history.
Fortunately, OpenAI has recently announced a way to make your chats hidden from the sidebar. These “hidden” chats won’t be used to train AI models either. You can also opt out of allowing OpenAI to train its models in the settings.
Will ChatGPT replace Google Search?
Rather than replace it, generative AI features are being integrated directly into search. Microsoft started things off by integrating Copilot right into its own search engine, which puts a “chat” tab right into the menu of Bing search. Google, of course, made its big move with AI Overviews, which uses AI-generated answers in place of traditional search results. It launched first through its Search Generative Experience, but rolled out widely in May 2024.
To be clear, this kind of AI is different than just Gemini or ChatGPT. And yet, it’s also undeniable that AI will play an important role in the future of search in the near future. Despite all the problems with AI Overviews, Google seems committed to making it work.
Is Copilot the same as ChatGPT?
Although Copilot and ChatGPT are capable of similar things, they’re not exactly the same. Copilot, even though it runs the same GPT-4 model as ChatGPT, is an entirely separate product that has been fine-tuned by Microsoft.
Microsoft, as part of its multi-billion dollar investment into OpenAI, originally brought ChatGPT to Bing in the form of Bing Chat. But unlike ChatGPT, Bing Chat required downloading the latest version of Edge at the time.
Bing Chat has since been completely retooled into Copilot, which has seemingly become Microsoft’s most important product. It’s integrated into Microsoft 365 apps through Copilot Pro, while the Copilot+ expands the AI capabilities deep into Windows and laptop hardware.
Can you write essays with ChatGPT?
The use of ChatGPT has been full of controversy, with many onlookers considering how the power of AI will change everything from search engines to novel writing. It’s even demonstrated the ability to earn students surprisingly good grades in essay writing.
Essay writing for students is one of the most obvious examples of where ChatGPT could become a problem. ChatGPT might not write this article all that well, but it feels particularly easy to use for essay writing. Some generative AI tools, such as Caktus AI, are built specifically for this purpose.
Can ChatGPT write and debug code?
Absolutely. It’s one of the most powerful features of ChatGPT. As with everything with AI, you’ll want to double-check everything it produces, because it won’t always get your code right. But it’s certainly powerful at both writing code from scratch and debugging code. Developers have used it to create websites, applications, and games from scratch — all of which are made more powerful with GPT-4, of course. A recent benchmark test found that both of OpenAI’s newest models, o1-preview and o1-mini, can code with nearly the same capability and fidelity as human data engineers.
What is the ChatGPT character limit?
ChatGPT doesn’t have a hard character limit. However, the size of the context window (essentially, how long you can make your prompt), depends on the tier of ChatGPT you’re using. Free tier users receive just 8,000 characters, while Plus and Teams subscribers receive 32k-charcter context windows, and Enterprise users get a whopping 128k characters to play with.
What is Auto-GPT?
Built on GPT-4, Auto-GPT is the latest evolution of AI technology to cause a stir in the industry. It’s not directly related to ChatGPT or OpenAI — instead, it’s an open-source Python application that got into the hands of developers all over the internet when it was published on GitHub.
With ChatGPT or ChatGPT Plus, the capabilities of the AI are limited to a single chat window. Auto-GPT, at its simplest, is making AI autonomous. It can be given a set of goals, and then take the necessary steps towards accomplishing that goal across the internet, including connecting up with applications and software.
According to the official description on GitHub, Auto-GPT is an “experimental open-source application showcasing the capabilities of the GPT-4 language model. This program, driven by GPT-4, chains together LLM ‘thoughts’, to autonomously achieve whatever goal you set. As one of the first examples of GPT-4 running fully autonomously, Auto-GPT pushes the boundaries of what is possible with AI.”
The demo used on the GitHub page is simple — just create a recipe appropriate for Easter and save it to a file. What’s neat is how Auto-GPT breaks down the steps the AI is taking to accomplish the goal, including the “thoughts” and “reasoning” behind its actions. Auto-GPT is already being used in a variety of different applications, with some touting it as the beginning of AGI (Artificial General Intelligence) due to its autonomous nature.
Who owns the copyright to content created by ChatGPT?
This is a question open to debate. Much of the conversation around copyright and AI is ongoing, with some saying generative AI is “stealing” the work of the content it was trained on. This has become increasingly contentious in the world of AI art. Companies like Adobe are finding ways around this by only training models on stock image libraries that already have proper artist credit and legal boundaries.
According to OpenAI, however, you have the right to reprint, sell, and merchandise anything that was created with ChatGPT or ChatGPT Plus. So, you’re not going to get sued by OpenAI.
The larger topic of copyright law regarding generative AI is still to be determined by various lawmakers and interpreters of the law, especially since copyright law as it currently stands technically only protects content created by human beings.